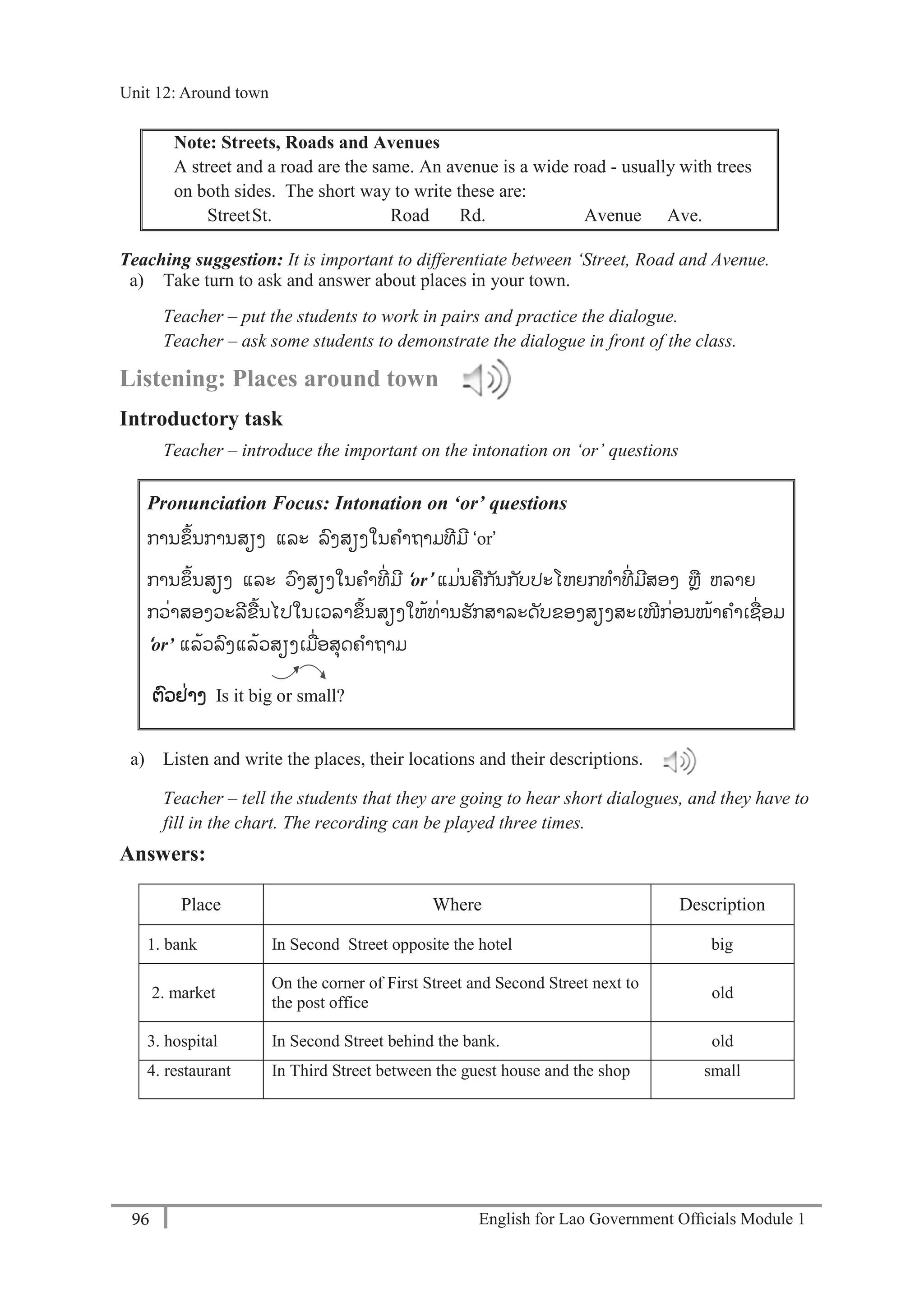
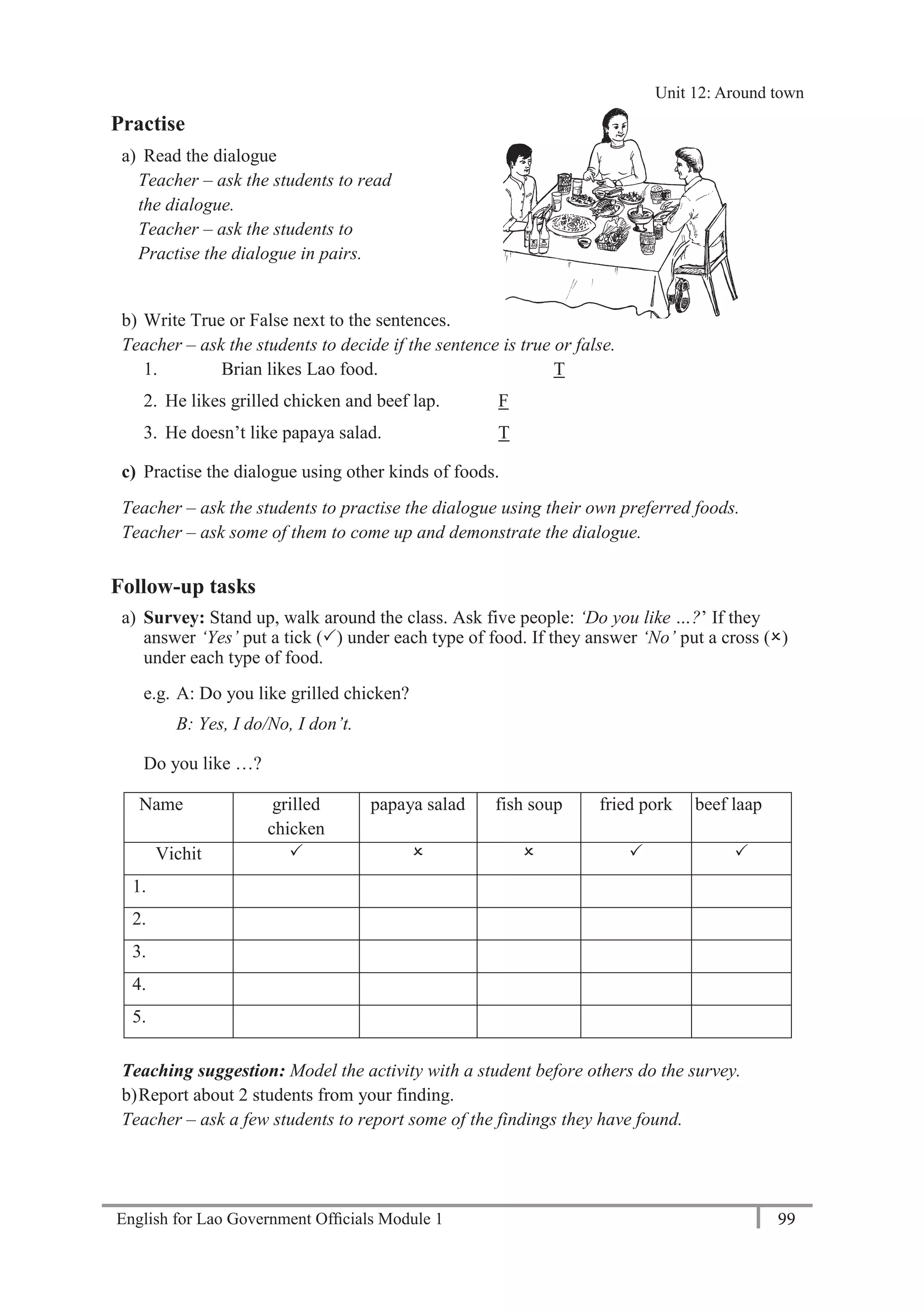
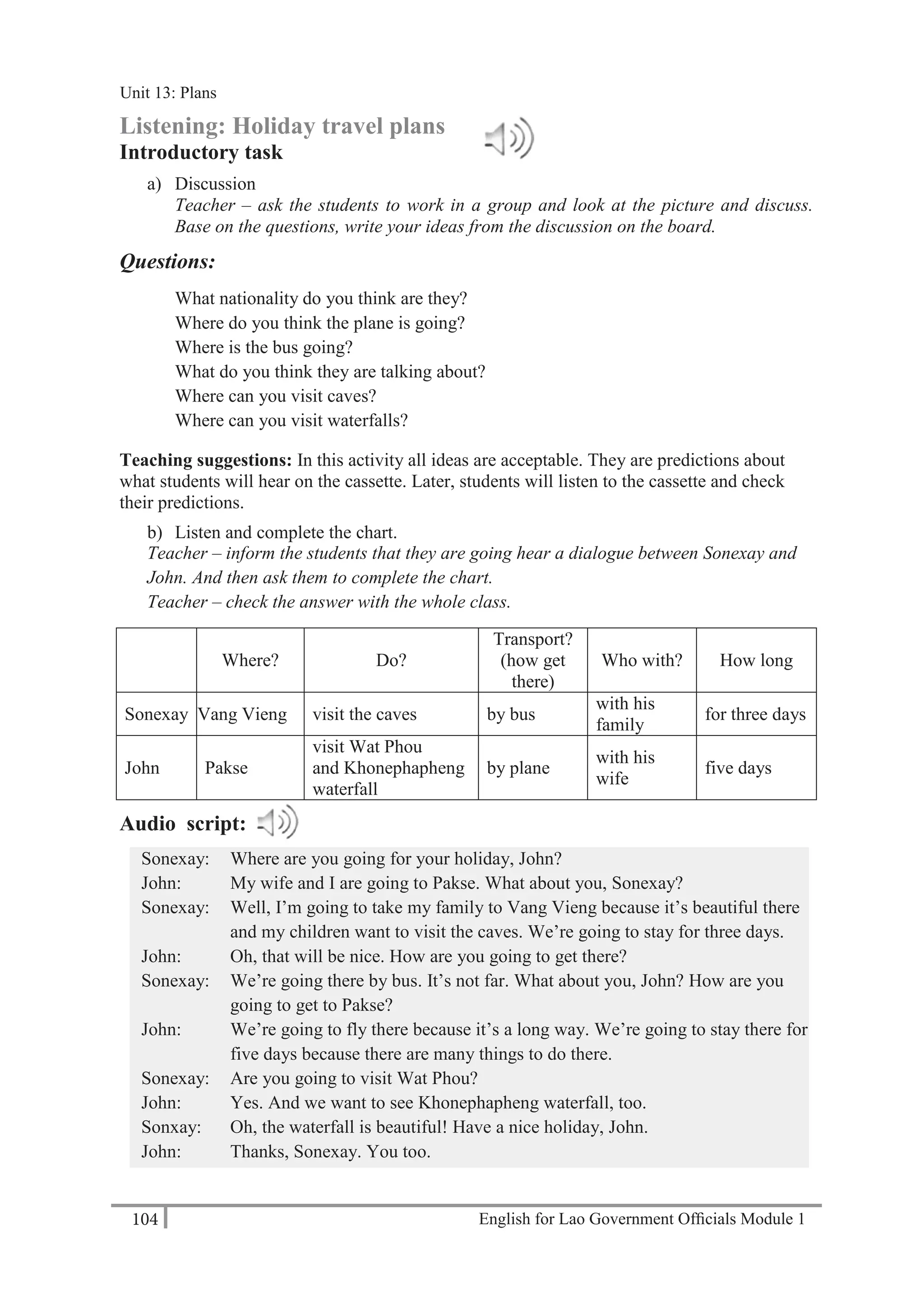
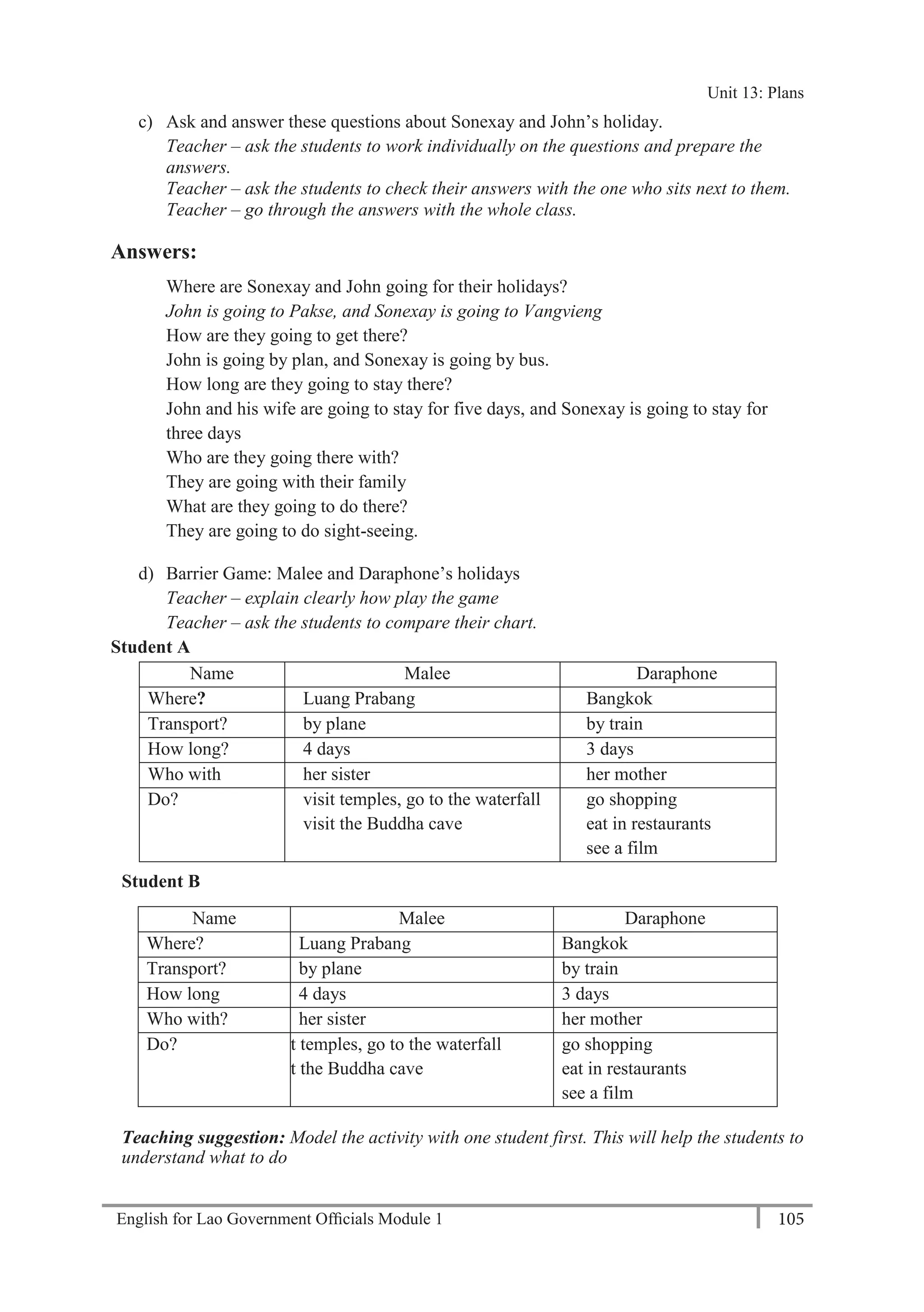
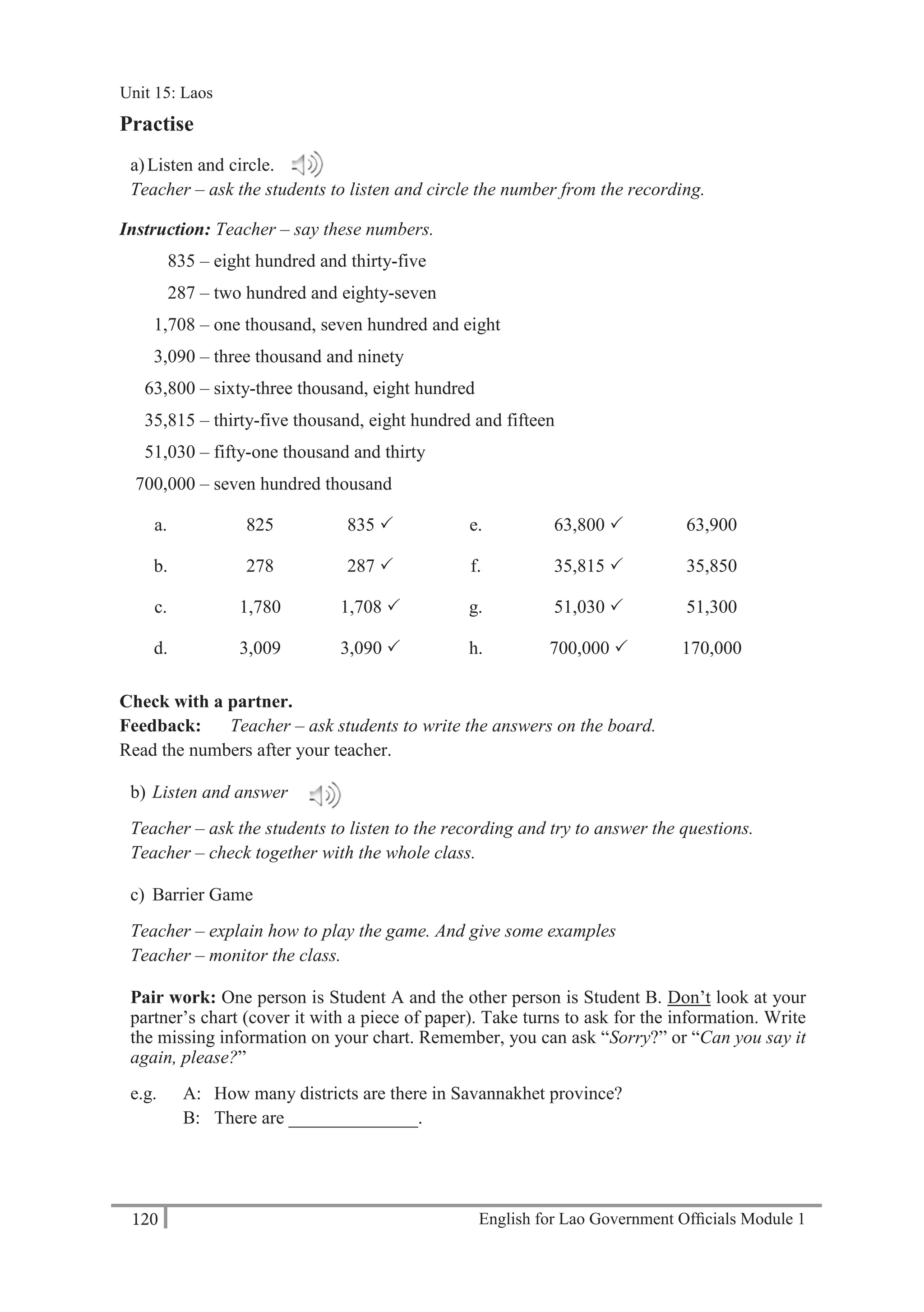
21 6450
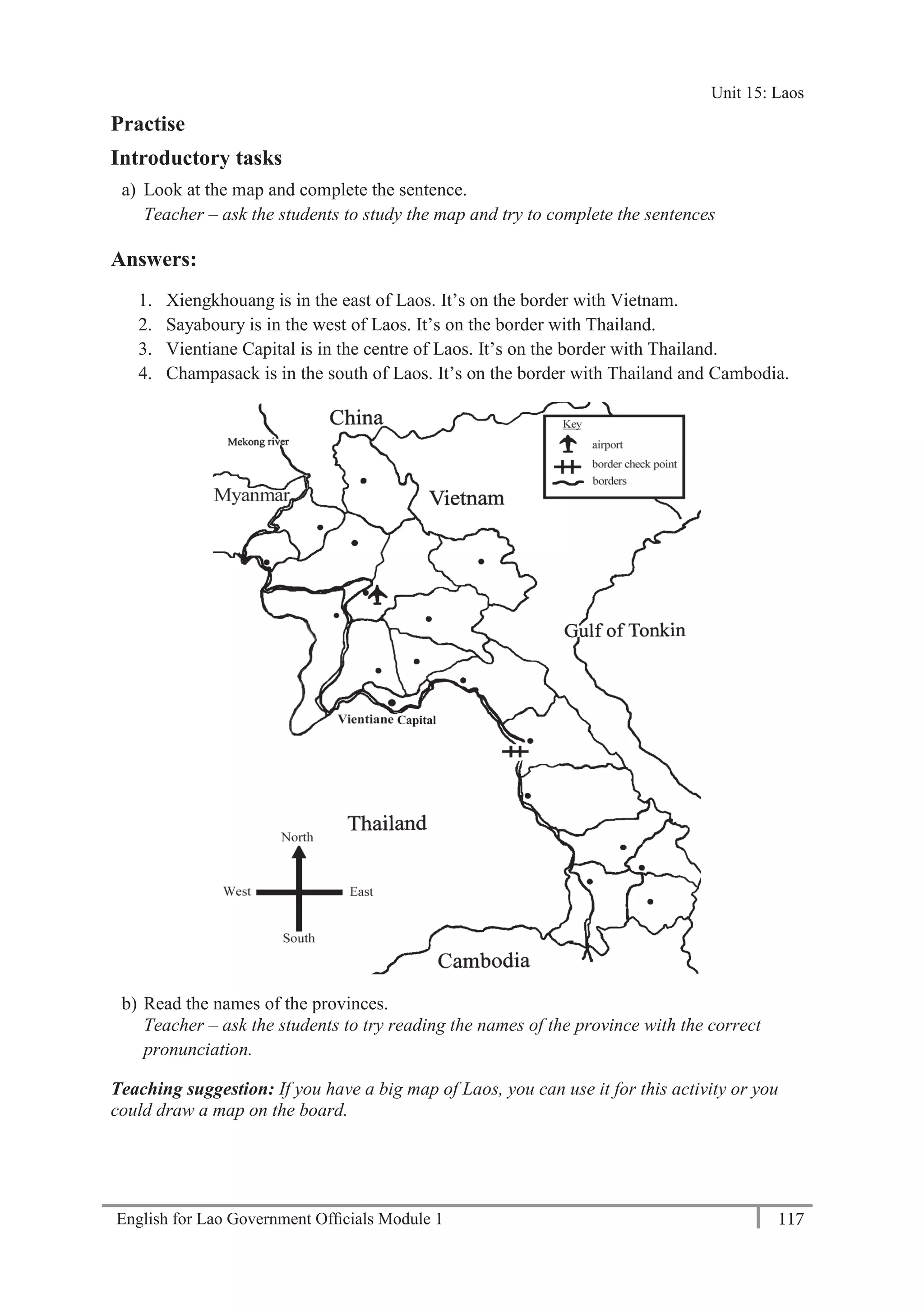
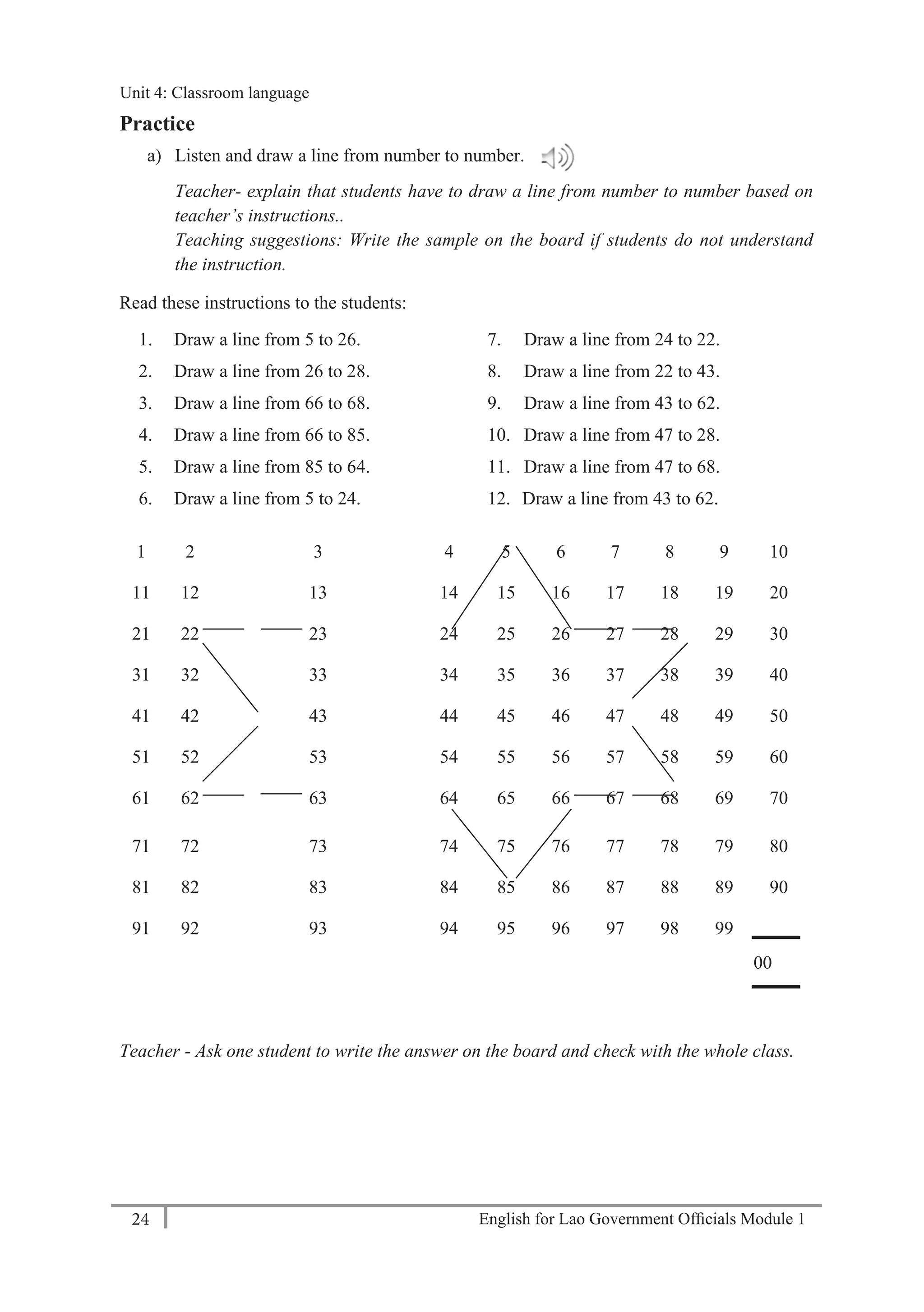
A: Thank you.
Teacher – play the tape twice. Students write the phone numbers.
b) Practise asking and telling phone numbers in pairs. Use the numbers from exercise a).
Teacher – monitor and check pronunciation.
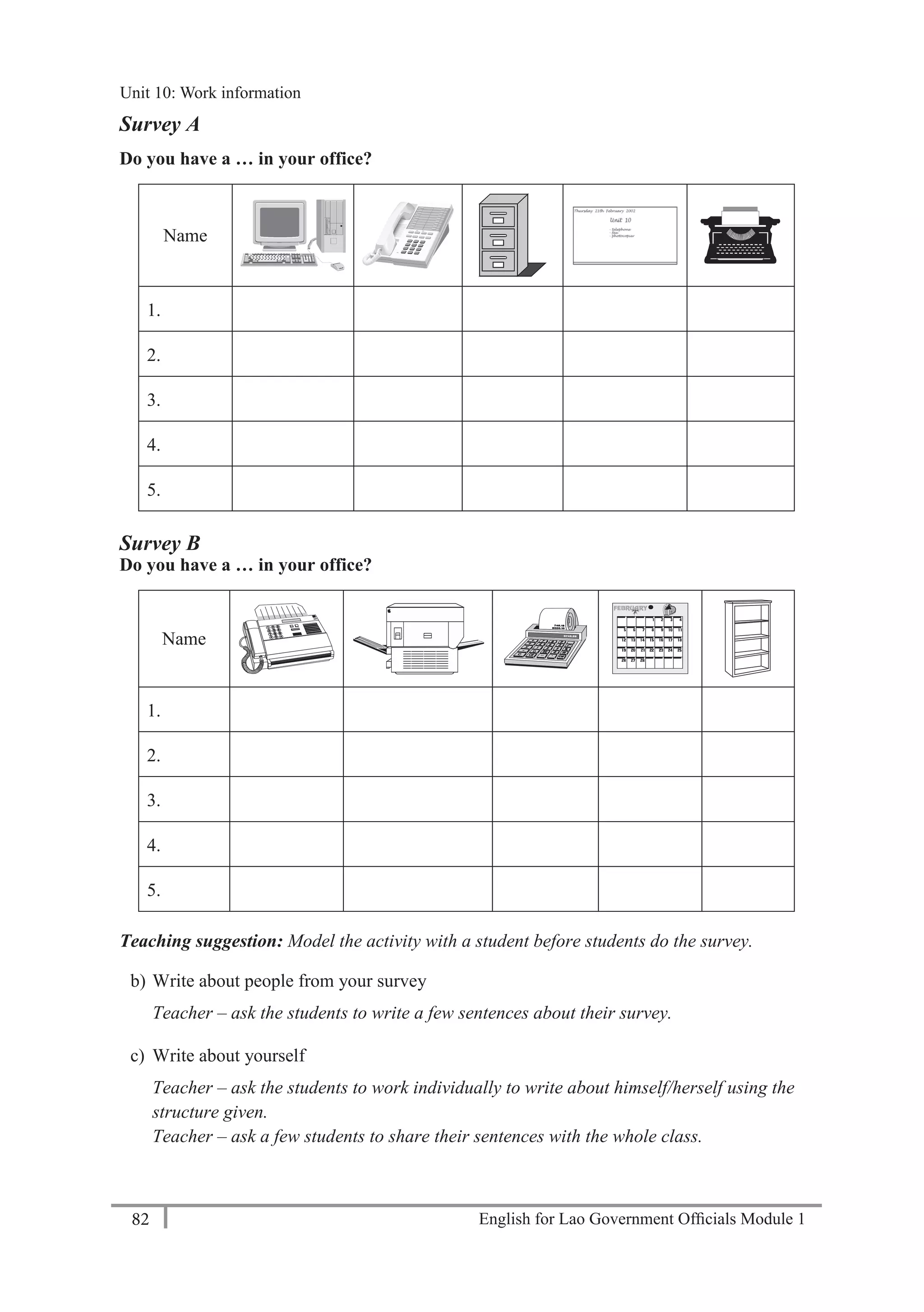
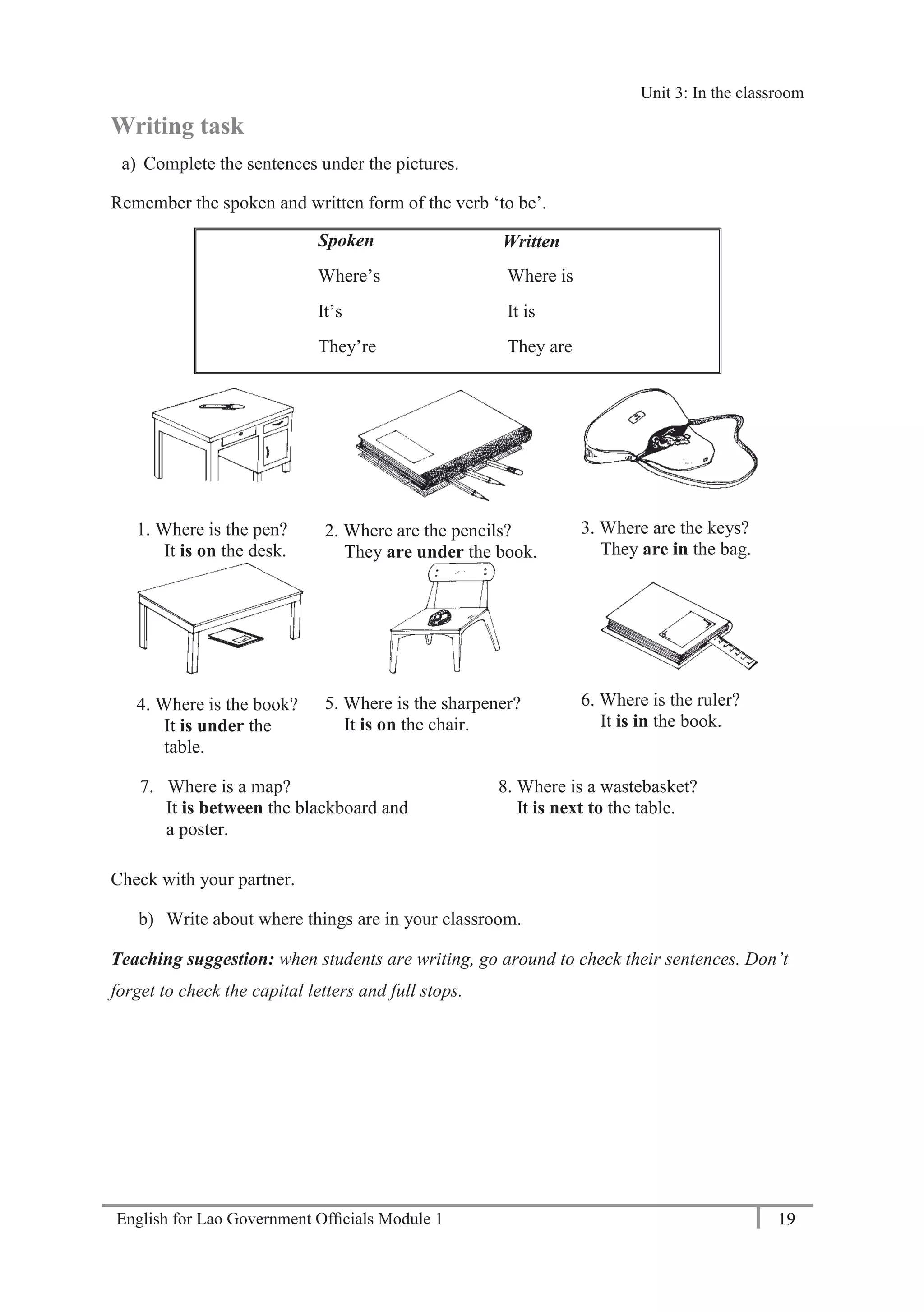
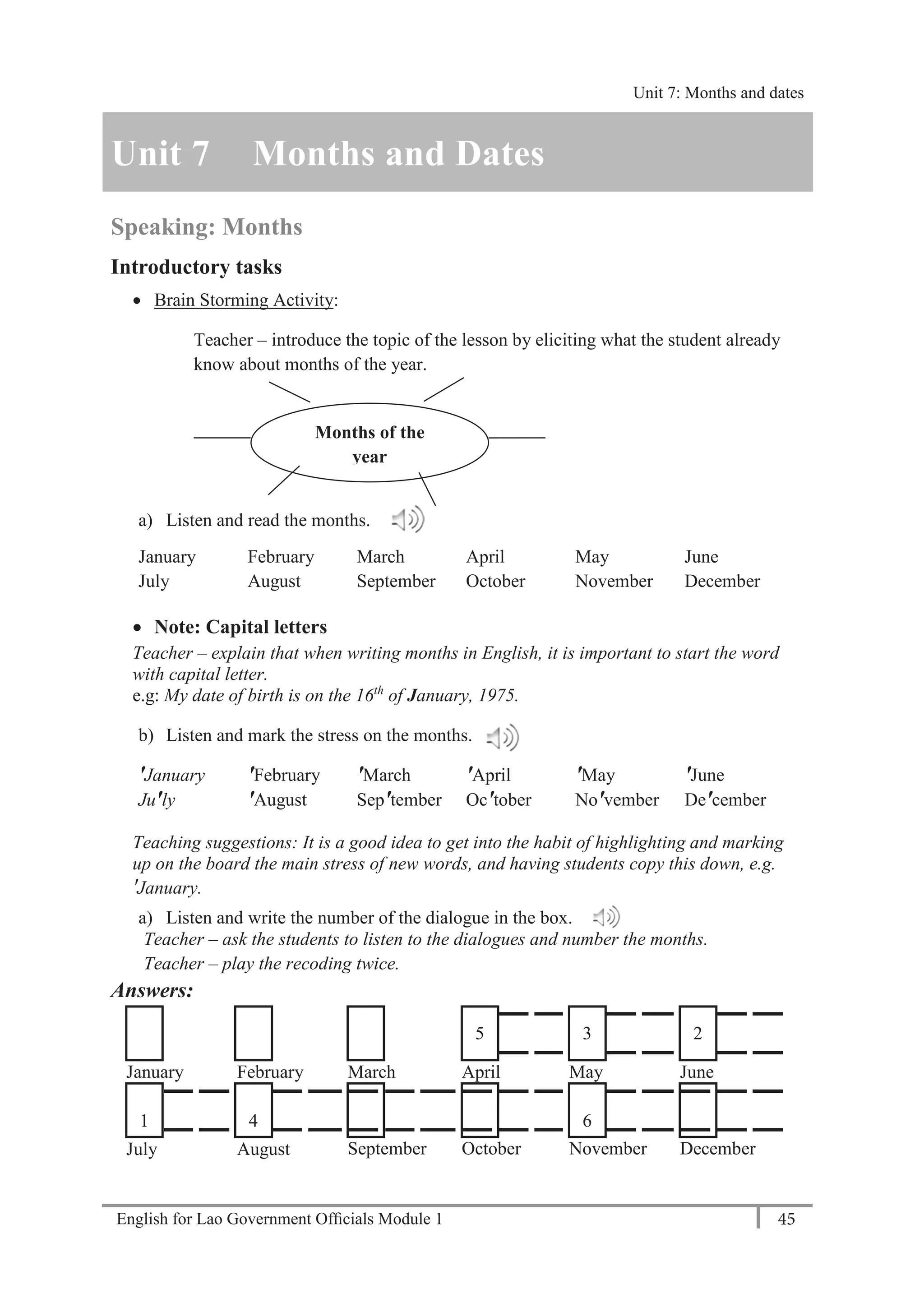
Language Focus: Numbers 11-20
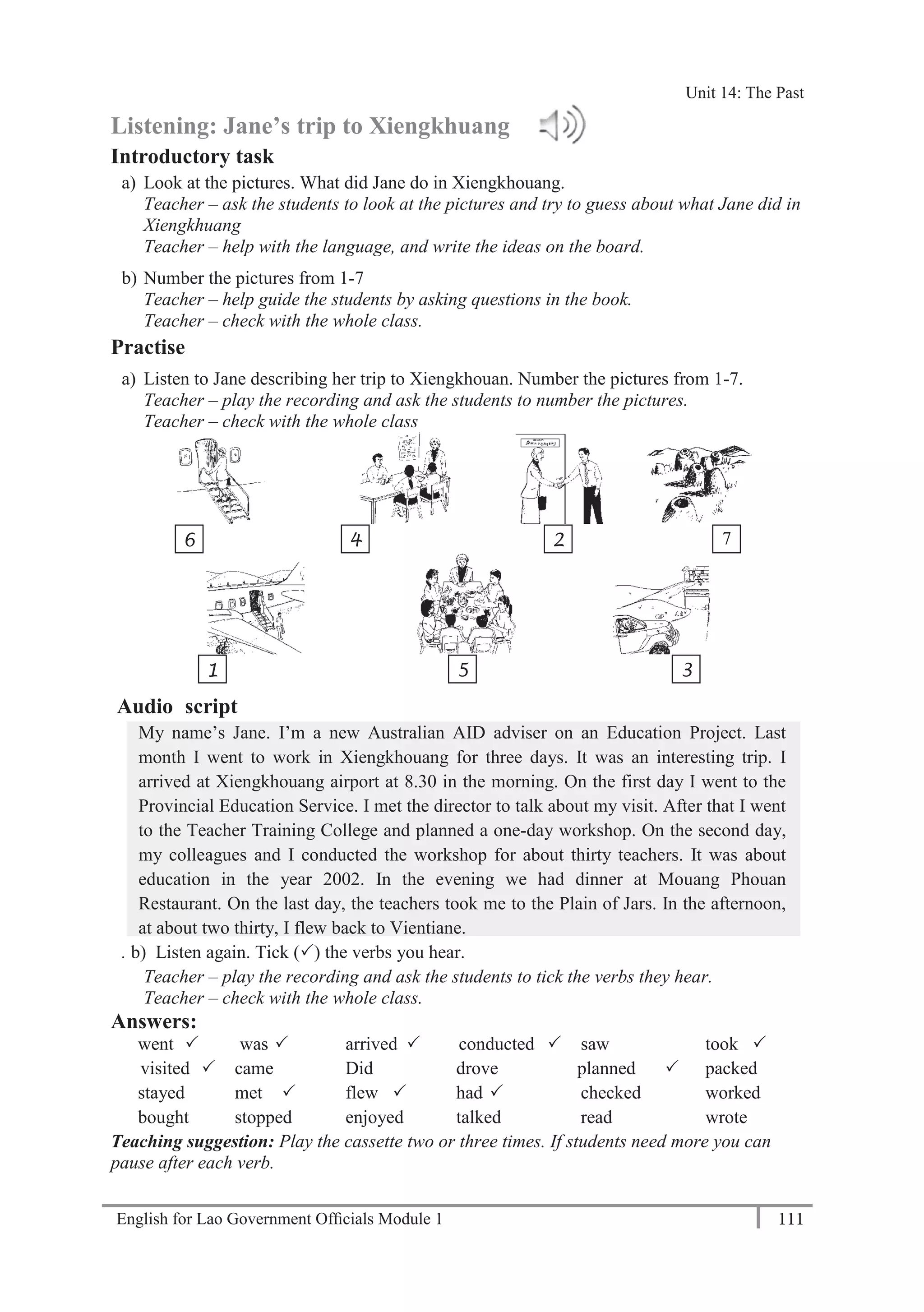
eleven, twelve, thirteen, fourteen, fifteen, sixteen, seventeen, eighteen, nineteen, twenty
Practice saying the numbers aloud.
Unit 2: Personal information
�English for Lao Government Officials Module 1 11
Unit 2: Personal Information
11 English for Lao Government Officials Module 1
Reading: Personal information form
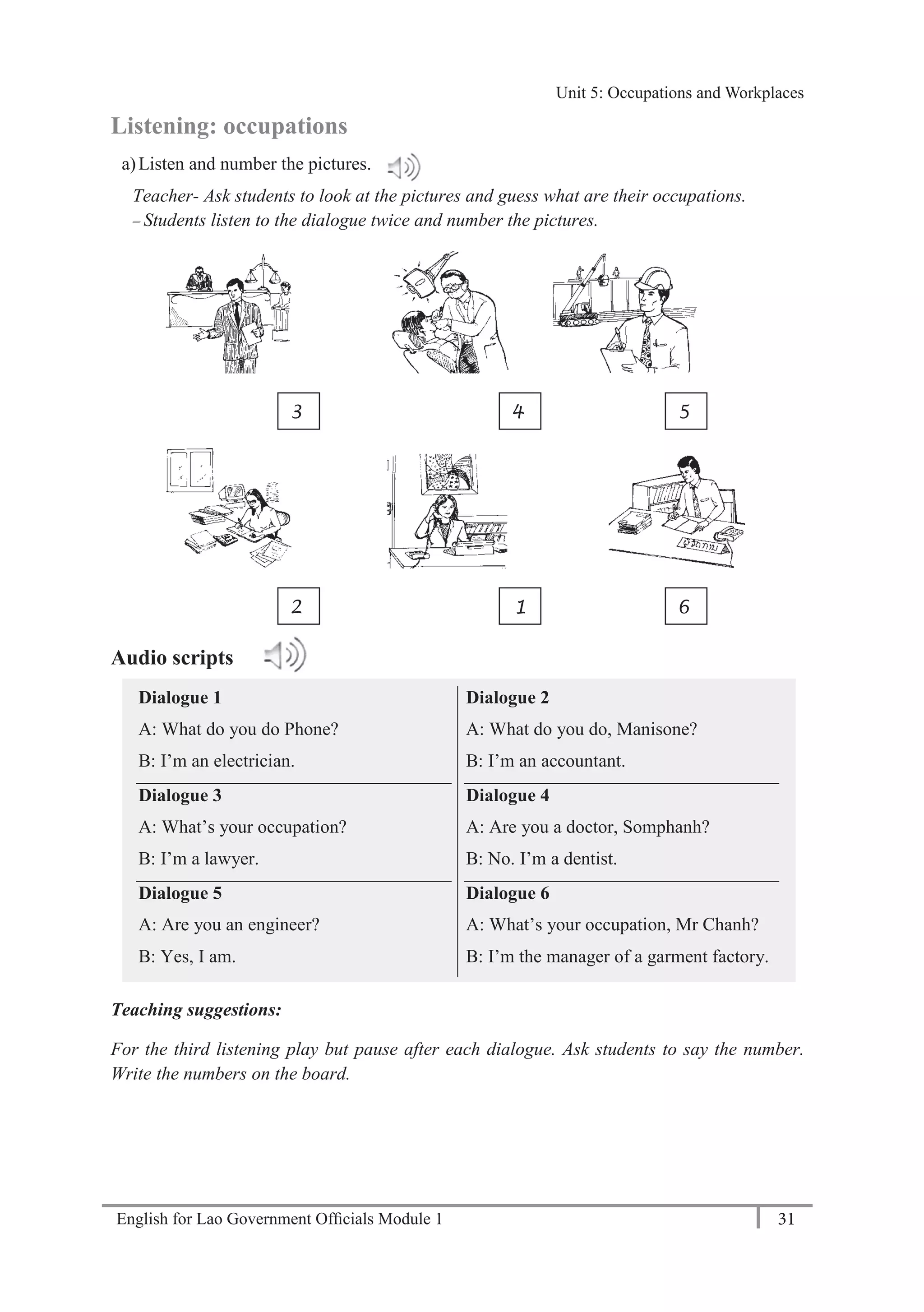
Introductory tasks
a) Read the personal information


































![English for Lao Government Officials Module 1 37
Unit 5: Occupations and Workplaces
37 English for Lao Government Officials Module 1
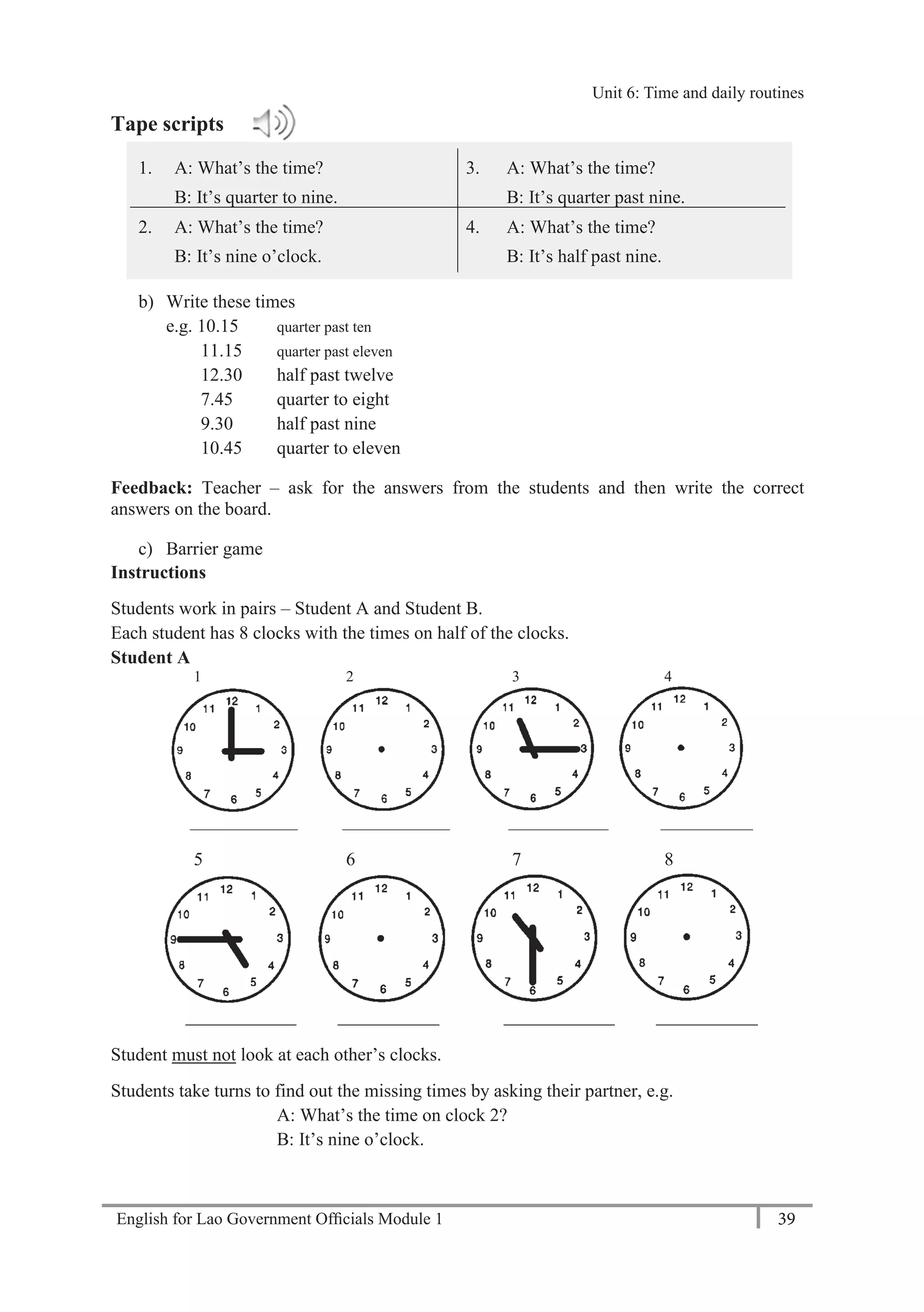
Feedback: Teacher – ask some students to talk to the class about their survey, e.g. His full
name is Mr Khampheng Sengsoulivong and he’s forty years old. He’s an accountant and he
works for the Ministry of Education and Sports..
b) Complete the form. Remember to use capital letters for names and ministries.
Mr Ms Mrs Miss [Please tick ()]
Given name: ________________ Surname: ____________________
Age: ______________________ Married Single [Please tick ()]
Occupation: ________________ Ministry: _______________________
Teaching suggestion: This is an idea for feedback after the students have completed their
forms:
1. Draw 2 forms on the board. On Form 1, write your own personal information. Talk
about it as you write, e.g. “My given name’s …(write it) and my family name’s
…(write it). I’m …years old (write it) and I’m single (tick the box) …
2. Ask a student to complete Form 2 and talk about it.
c) Write about yourself. Use the text about Khamsy as a model.
e.g. My name is _____________________. I am _________________
______________________ and _____________________. ______
d) Read and check your partner’s writing. Can you understand it?
Check:
the Present Simple
Tense
spelling
a/an
capital letters
full stops
Teaching suggestion:Walk around and monitor the students’ writing. Remind people about
capital letters etc. if necessary.
Unit 5: Occupations and Workplaces](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f6eqz0hvqjop0pbwdvuj-signature-a33602361c0adadb4b641edfb110fc80d660e2f08cc767173bcd26ac263dde62-poli-180810094725/75/Teacher-textbook-Module-1-40-2048.jpg)

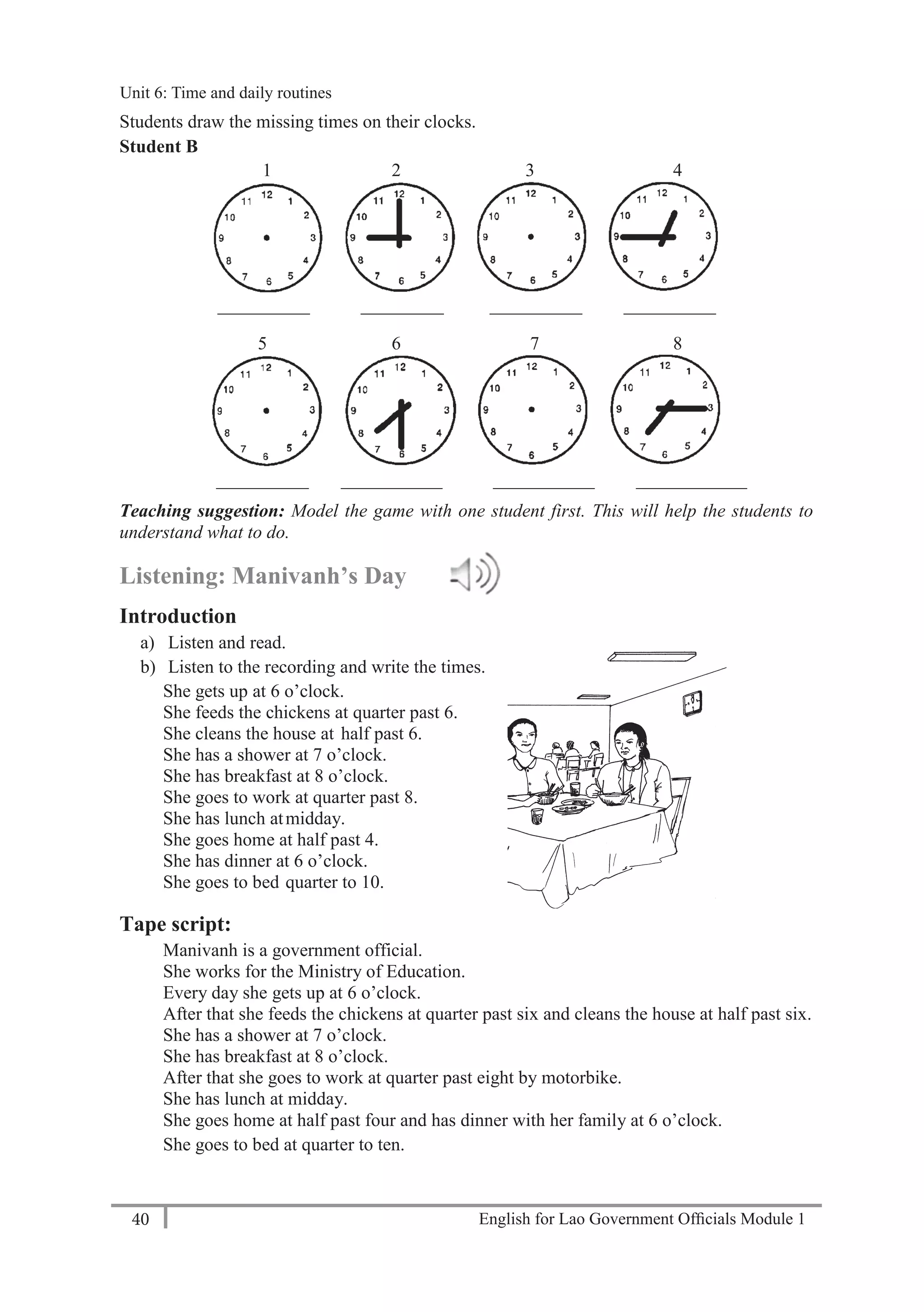










![English for Lao Government Officials Module 154
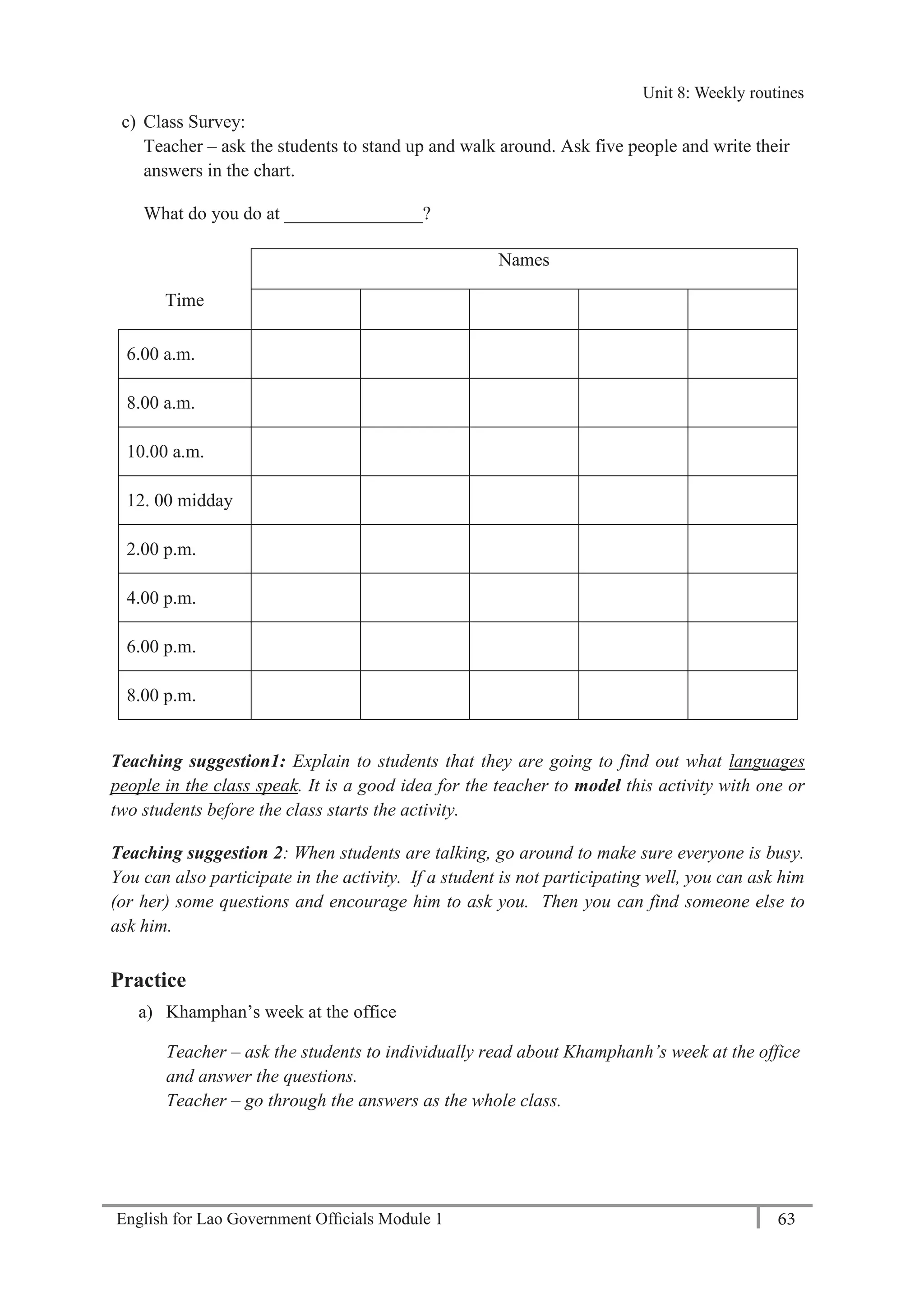
Unit 8: Weekly Routines
54 English for Lao Government Officials Module 1
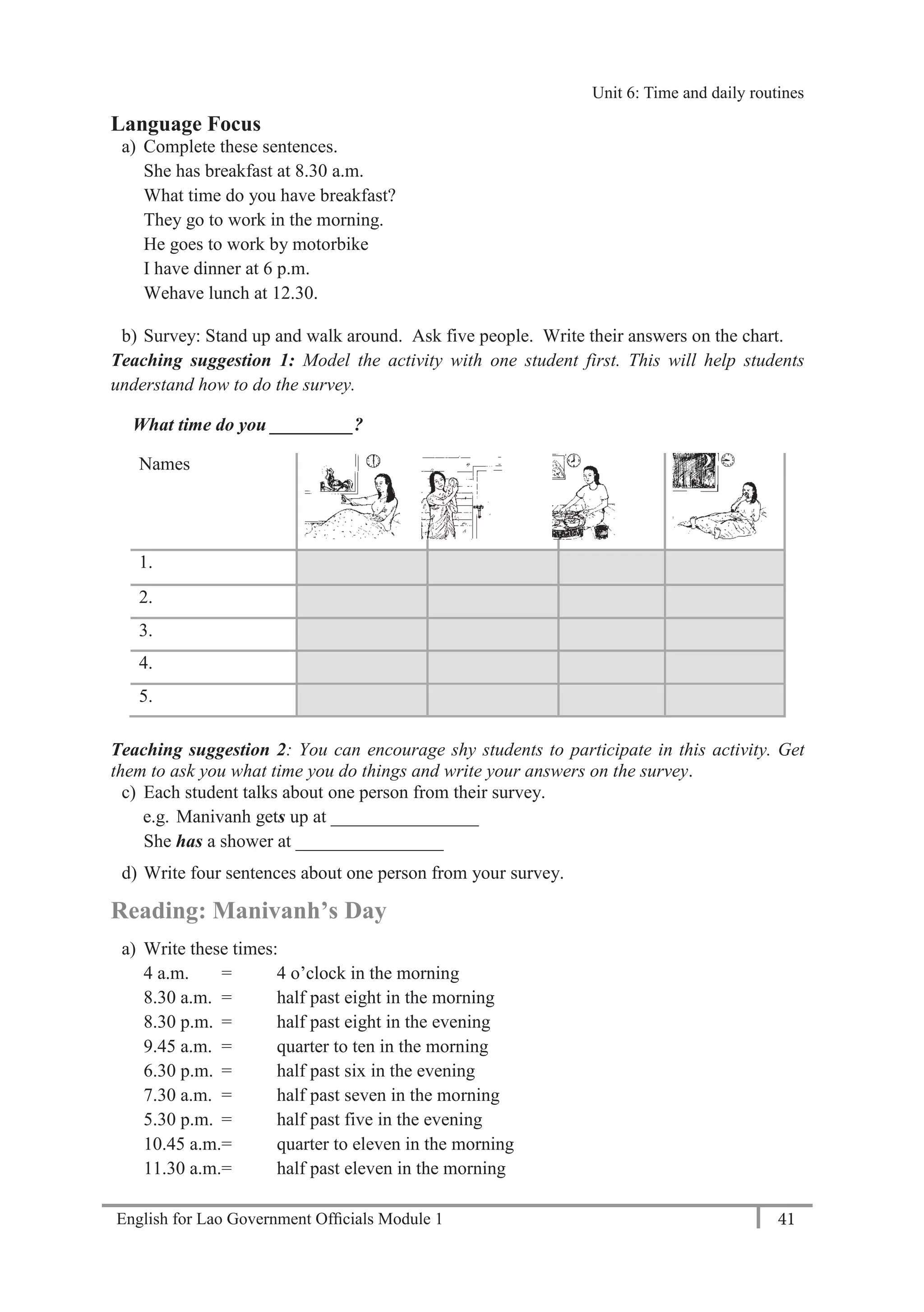
Writing: Important dates
a) List about 5 of important dates in your life
Teacher – ask the students think about of the important dates in their life, and then share
with others.
Revision
a) Ask your classmate and complete the form
Teacher – ask the students to work in pairs asking and completing the form.
Teaching suggestion 1: This is revision of previous units. Spend as much or as little time as
necessary, i.e. If students seem to be sure of these questions and answers, them only spend a
short time. If they have forgotten, spend longer. Some students will need more practice than
others.
Mr / Miss / Mrs / Ms [please circle]
Name: …………………………………………………………………………………
(Given name) (Family name)
Occupation: …………………………………………………………………………..
Workplace: …………………………………………………………………………….
Telephone: …………………………………………………………………………….
Date of birth: ………………………………………………………………………….
Married Single [please tick ()]
Number of Children: …………………………………………………………………
Teaching suggestion 1: Remind the students not to fill in the forms with full sentences.
Remind them about capital letters.
Teaching suggestion 2: When students are filling in the form, walk around and check their
writing. Help anyone who needs it.
Task 2: Report back to the class
— The teacher asks each student to report his/her partner’s information to the whole class
e.g. Her name is Ms Pansy Sanoubane. She …
Teaching suggestion 1: When students are writing, go around and (quietly) check their work
(monitor their work). If you see a mistake, point to it, but leave the student to try to decide
what is wrong by himself / herself. This is a good learning strategy.
Teaching suggestion 2: After students have finished writing, encourage them to read their
writing again. Tell them to read it carefully and correct any mistakes they find before they do
the follow-up activity.
Teaching suggestion 3: After the follow-up task, collect the students’ writing. Write
comments on the writing to give students feedback on their progress. Use the form called
‘Feedback on Progress in Writing’ which is in the Teacher’s Book on page 6.
Task 3: Give your form to someone else to read. Read another student’s form. Write about
that student.
Remember, you can say, ‘Sorry?’ or ‘Say it again, please’ if you want to hear the instruction
again.
Unit 7: Months and dates](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f6eqz0hvqjop0pbwdvuj-signature-a33602361c0adadb4b641edfb110fc80d660e2f08cc767173bcd26ac263dde62-poli-180810094725/75/Teacher-textbook-Module-1-57-2048.jpg)















![English for Lao Government Officials Module 1 77
Unit 11: Work responsibilities
77 English for Lao Government Officials Module 1
b) Write questions
Teacher – ask the students to form questions individually.
Teacher – walk around the class and help with any difficulties
Teacher – check the answers with the whole class.
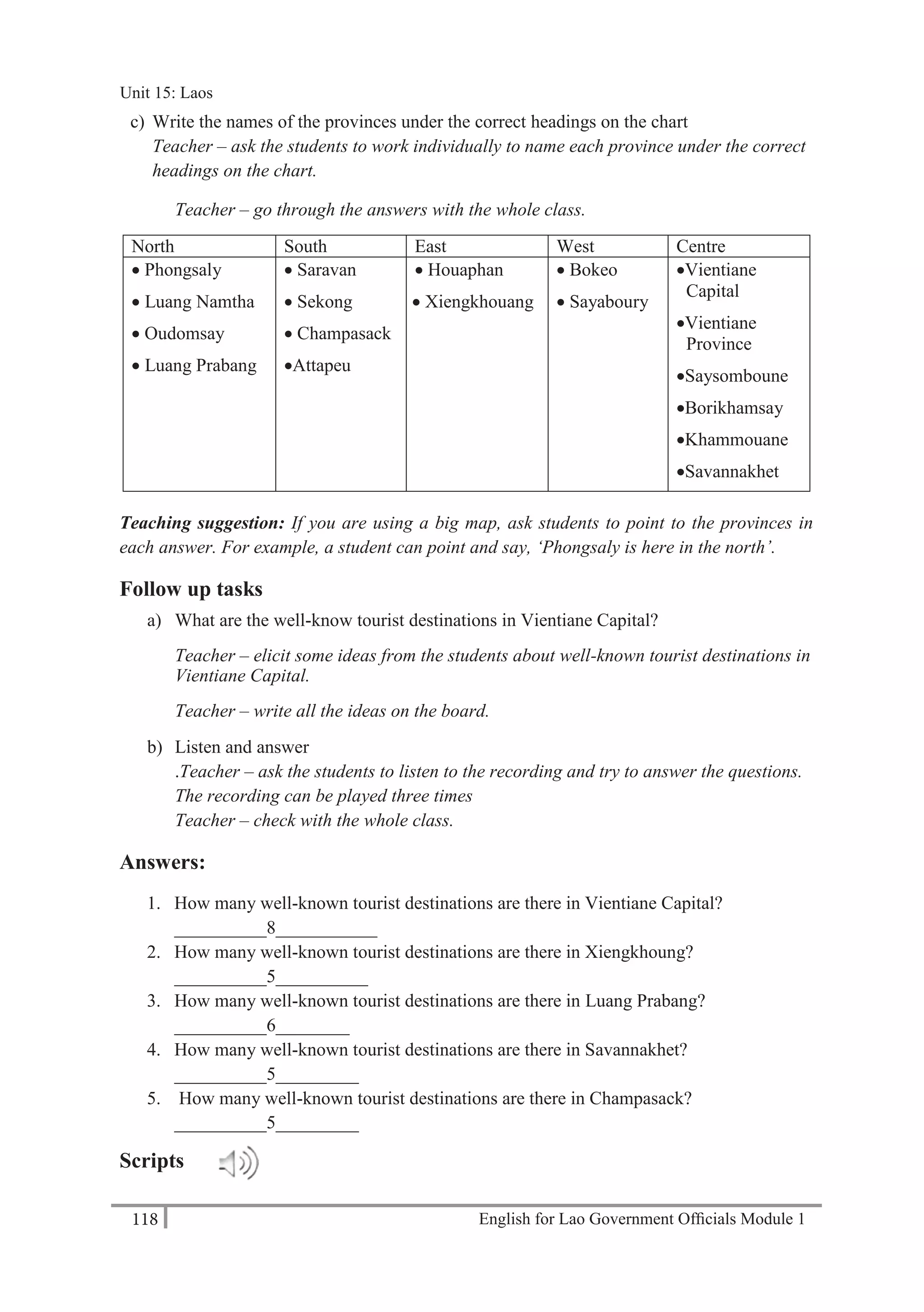
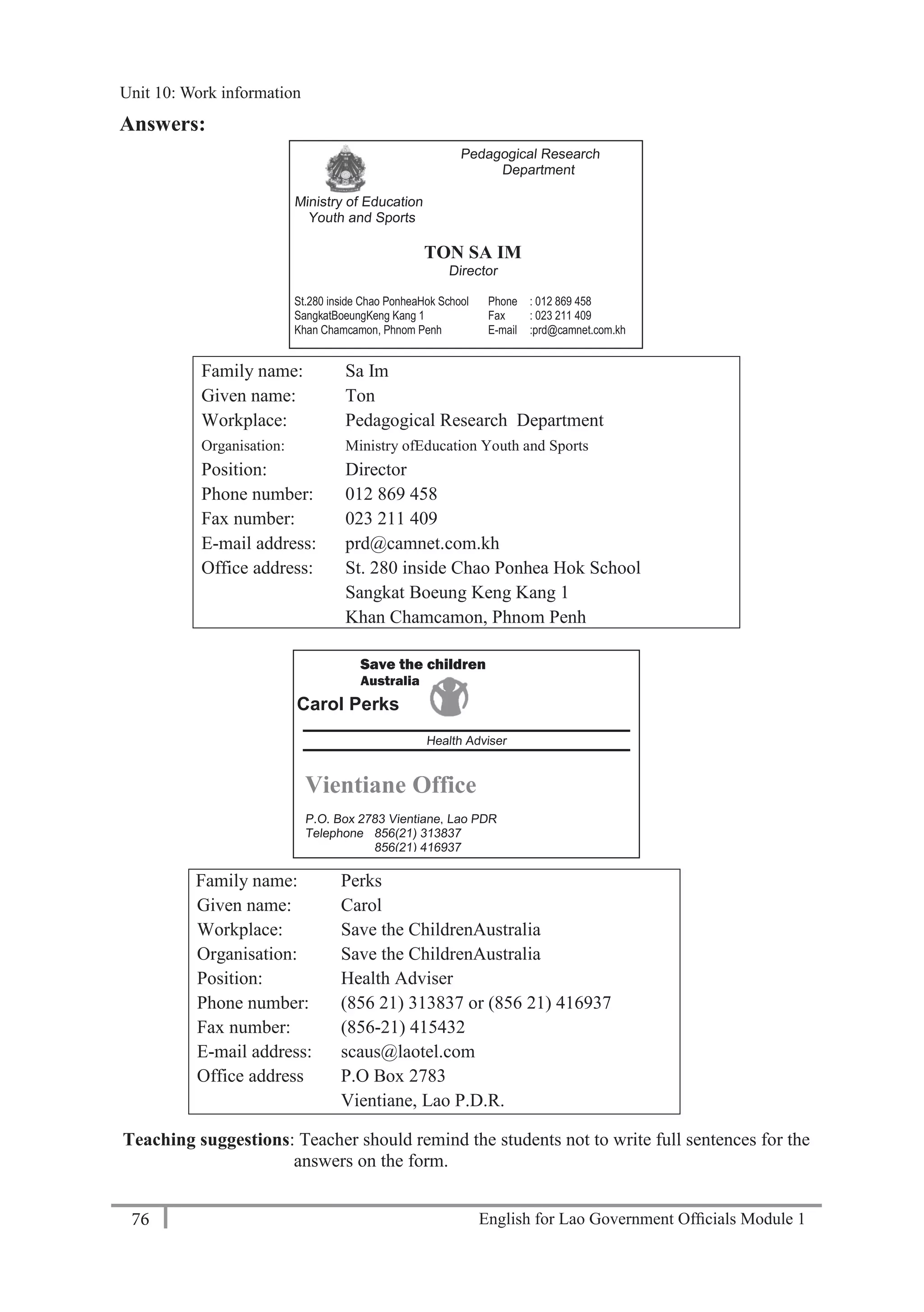
Answers:
Family name: What’s your family name?
Given name: What’s your given name?
Workplace: Where do you work?
Organisation: What organisation do you work for?
Position: What’s your position?
Phone number: What’s your phone number?
Fax number: What’s your fax number?
E-mail address: What’s your e-mail address?
Office address: What’s your office address?
c) Take turns to ask your partner questions. Complete the form about your partner.
Teacher – ask the students to work with a person who sits next to him/her, ask each other
and complete the form
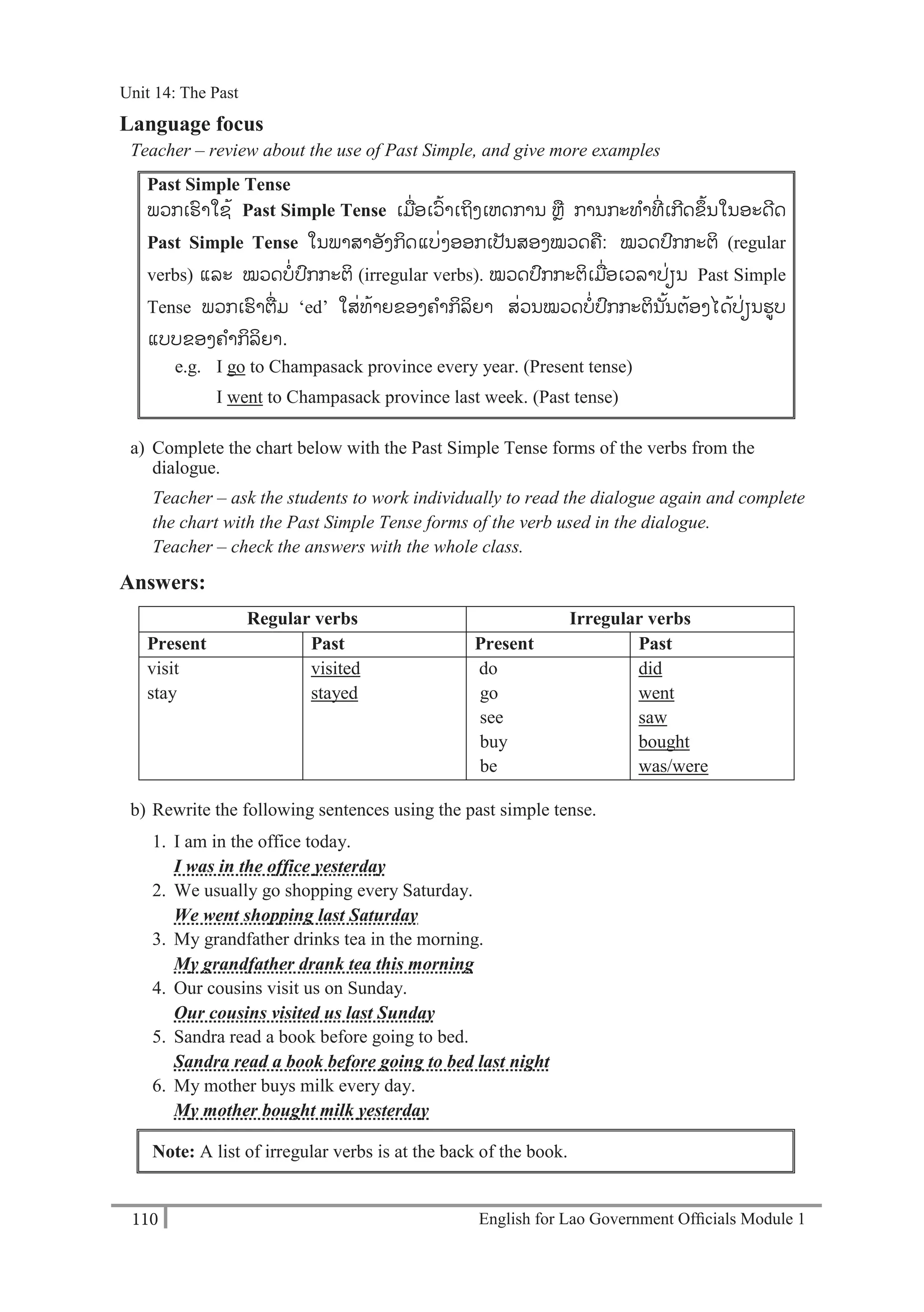
Then, teacher – ask the students to share their friends’ information to the whole class.
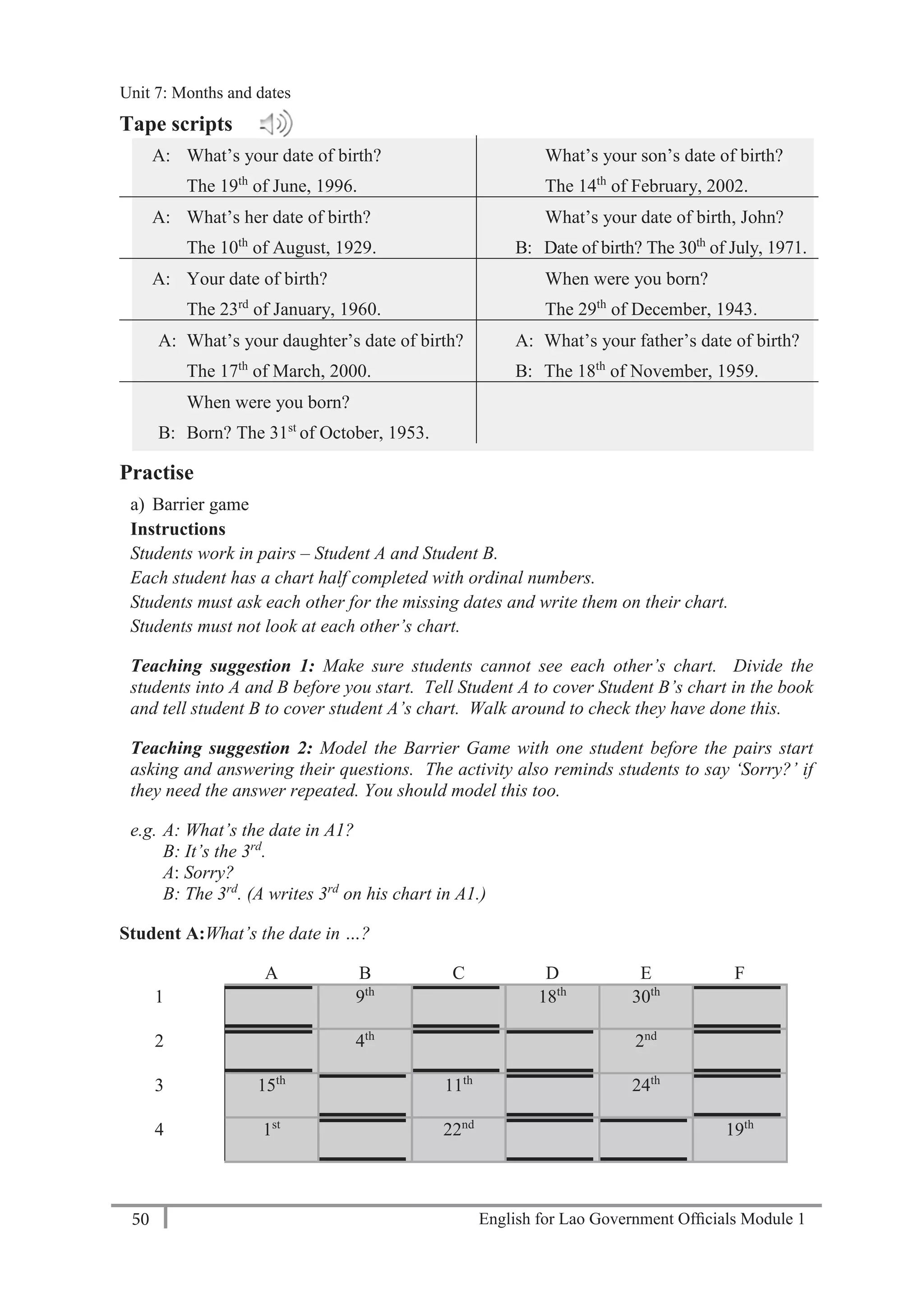
e.g. A: What’s your family name?
B: Sanoubane.
A: Can you spell it, please?
B: V-I-L-A-V-A-N-H
(Student A writes ‘Vilavanh’ on the form)
Mr / Miss / Mrs / Ms [please circle]
Name: ………………………………………………………………………………..
(Given name) (Family name)
Workplace: ……………………………………………………………………………
Organisation: …………………………………………………………………………
Position: ………………………………………………………………………………
Phone number: ……………………………………………………………………….
Fax number: ……………………………. E-mail address: ………………………...
Office address: ……………………………………………………………………….
Teaching suggestion: Walk around and monitor students’ writing. Remind them about
capital letters etc. if necessary. Teacher should also remind the students not to fill in the form
with full sentences.
a) Group work
Teacher – ask the students to work in a group of four, and take turns to report about the form
he/she has.
Teacher – walk around and correct any mistakes made by the students.
Unit 10: Work information](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f6eqz0hvqjop0pbwdvuj-signature-a33602361c0adadb4b641edfb110fc80d660e2f08cc767173bcd26ac263dde62-poli-180810094725/75/Teacher-textbook-Module-1-80-2048.jpg)