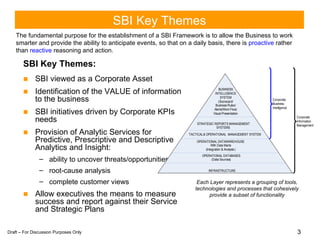
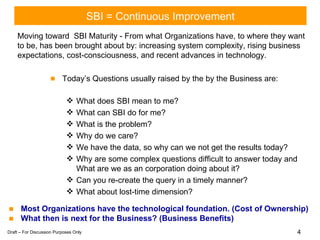
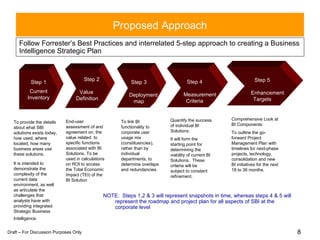
The document discusses developing a strategic intelligence framework and roadmap. It proposes a 5-step approach to create a strategic business intelligence plan, including conducting an inventory of current solutions, defining value, creating a deployment map, establishing measurement criteria, and setting enhancement targets. The goal is to develop a cohesive SBI strategy in phases, first building a solid foundation of governance, education, and communication before incrementally building business capabilities on top of that foundation.