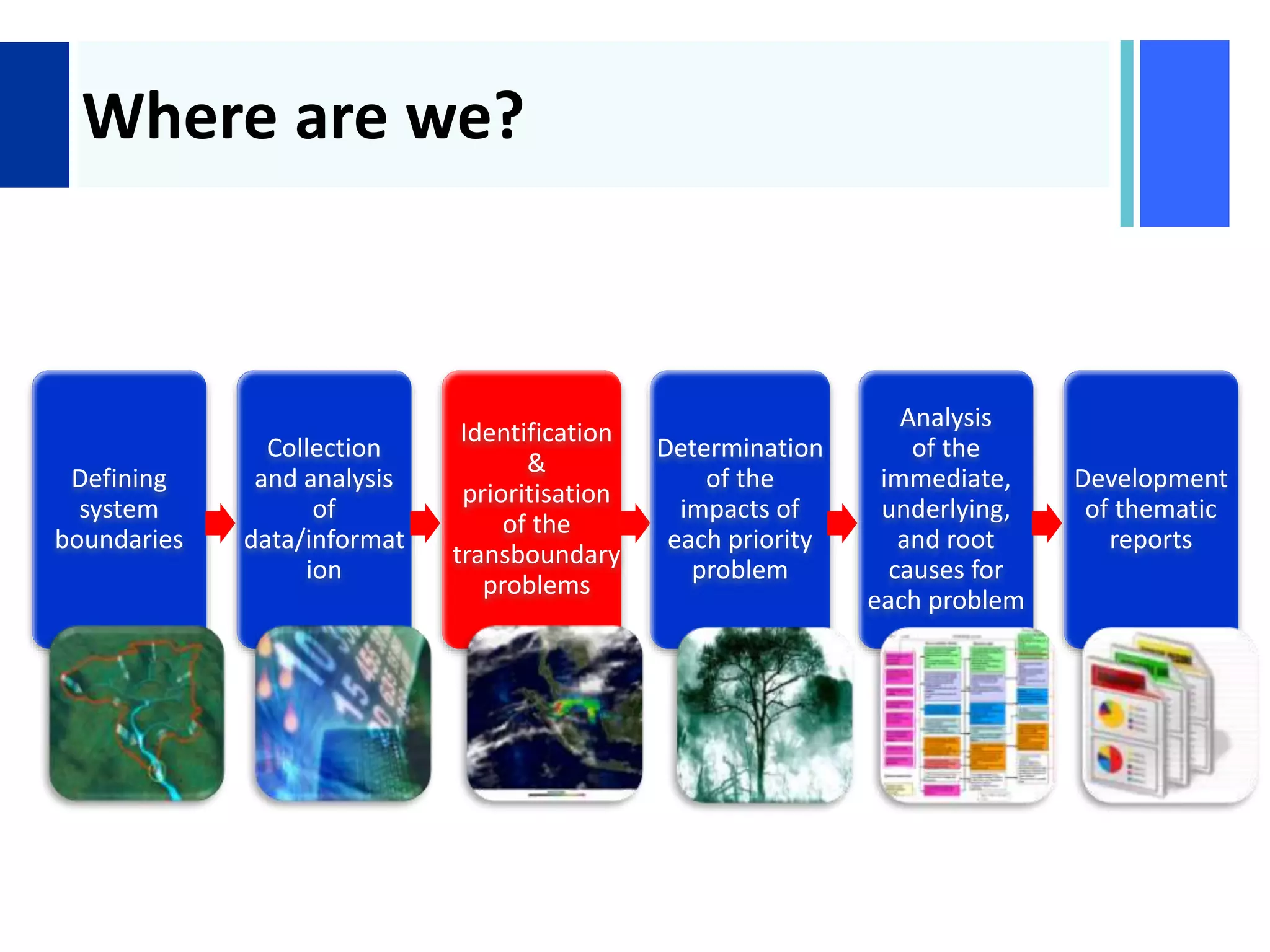
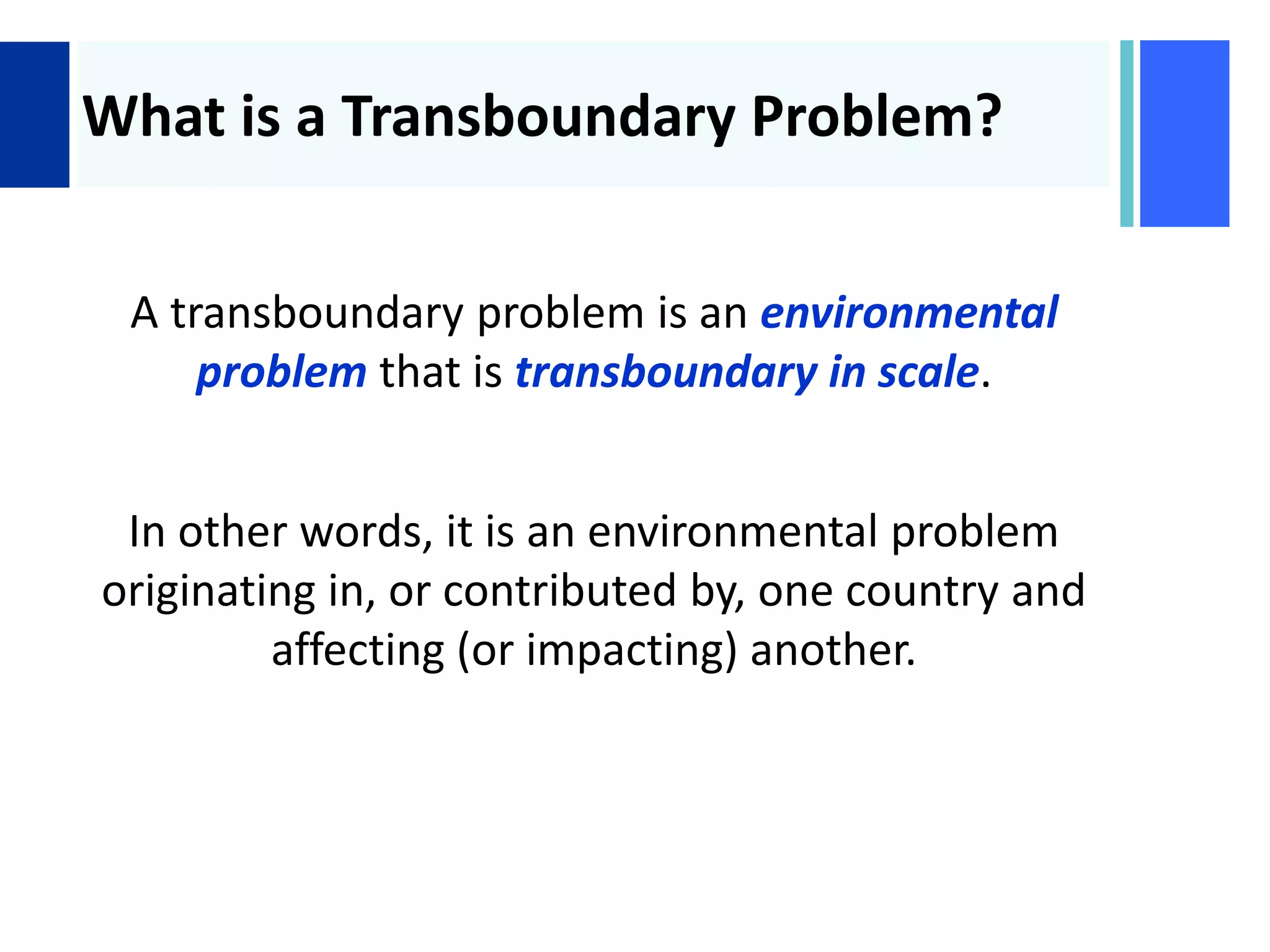
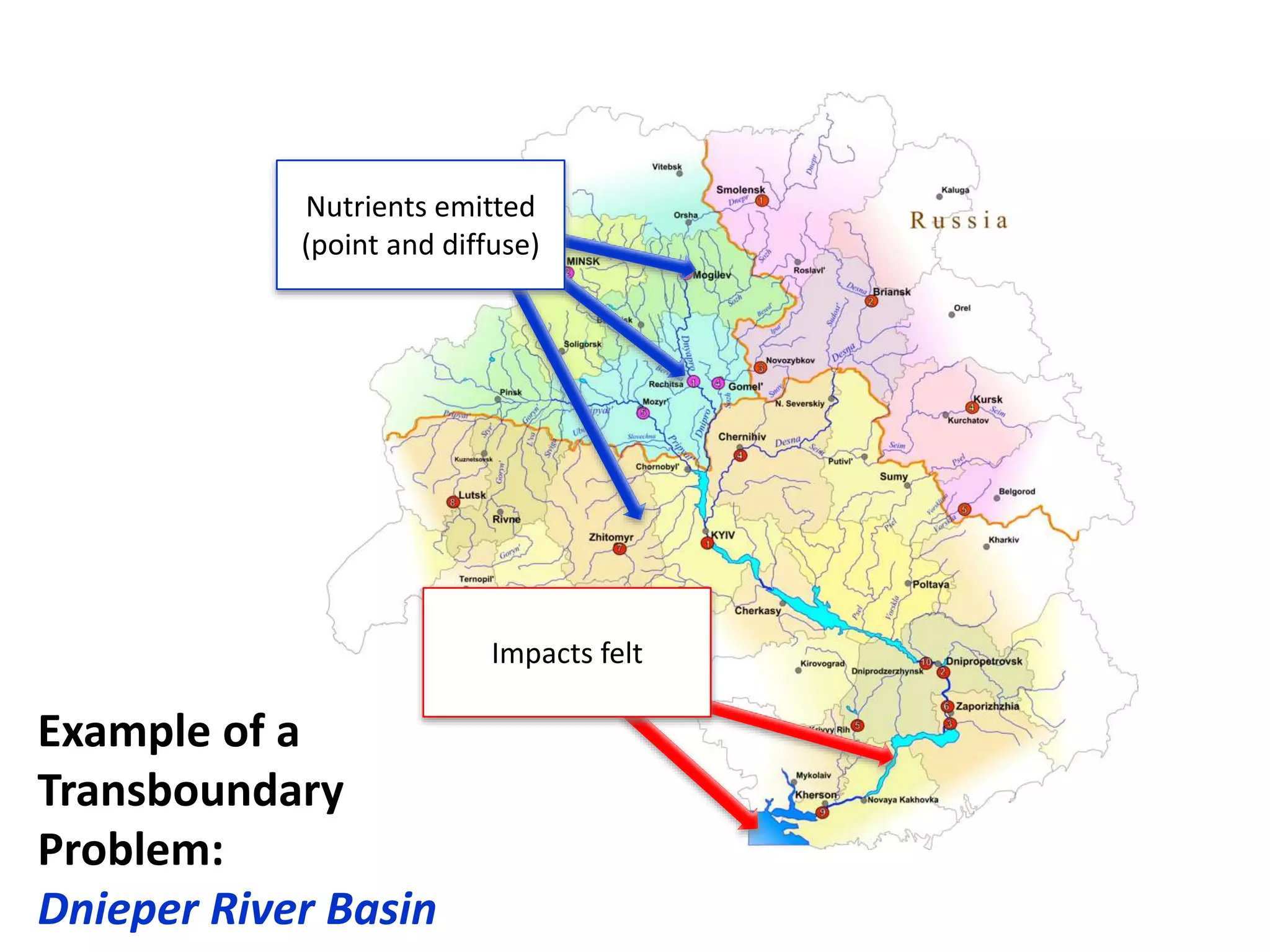
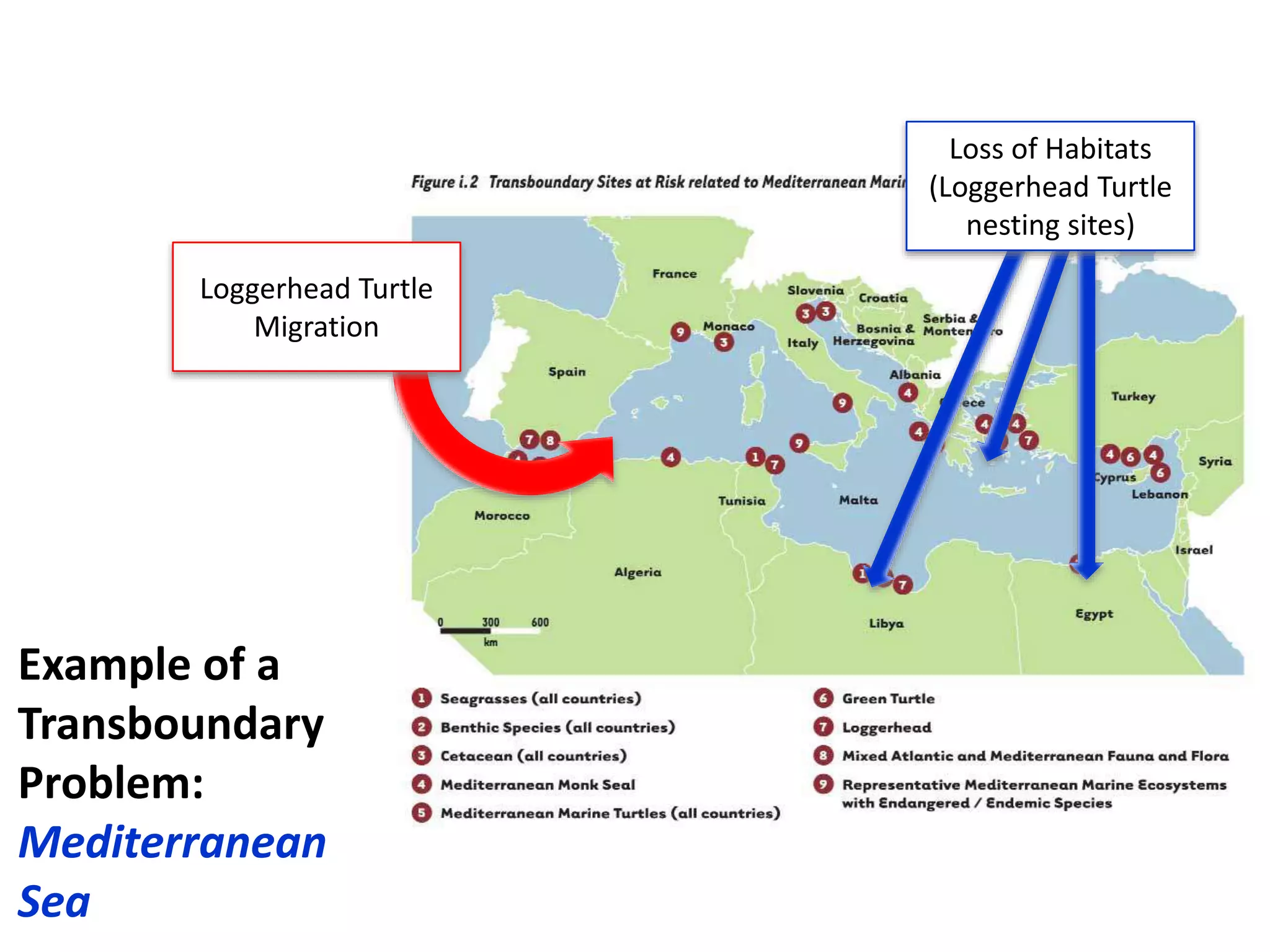
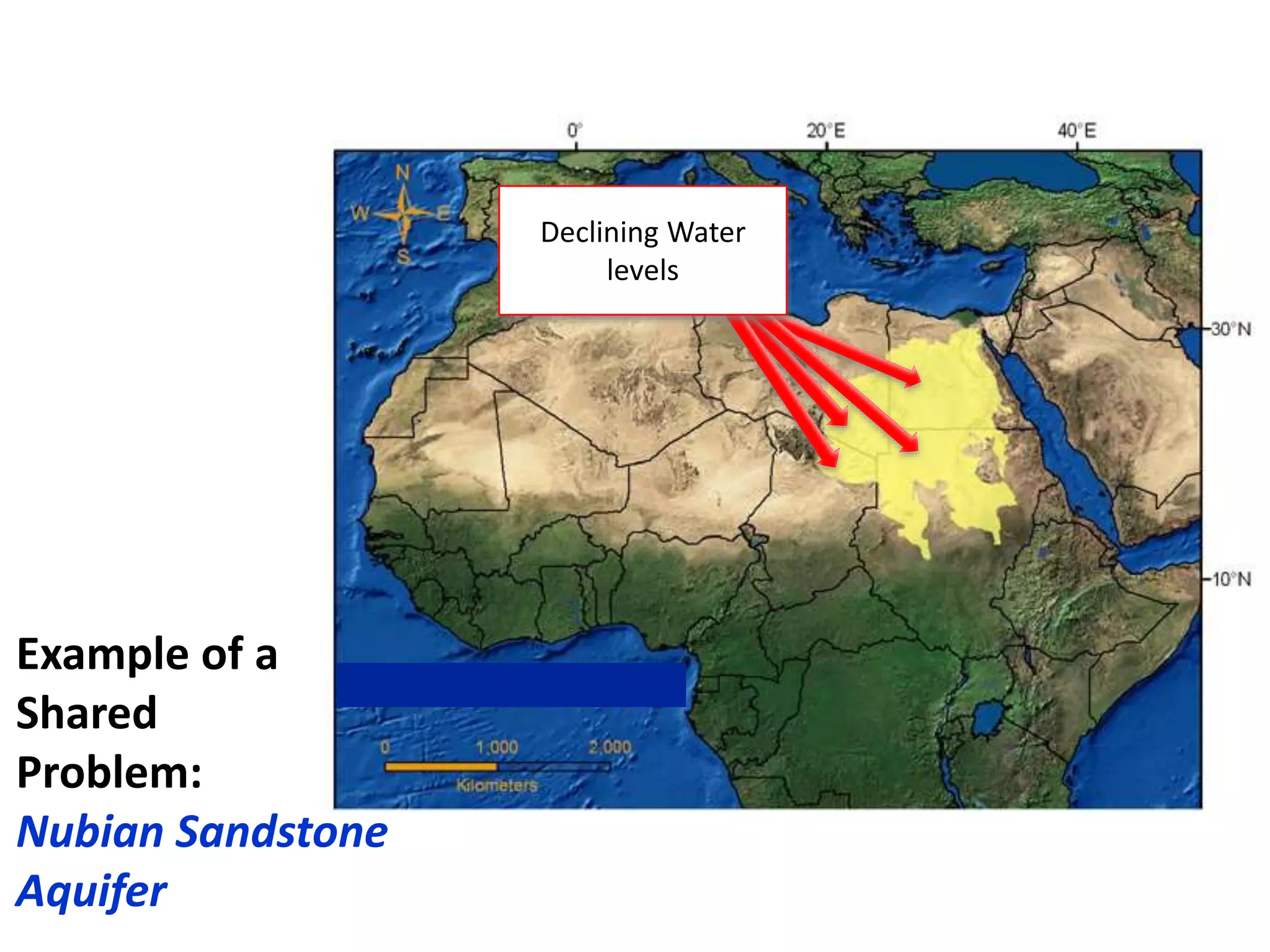
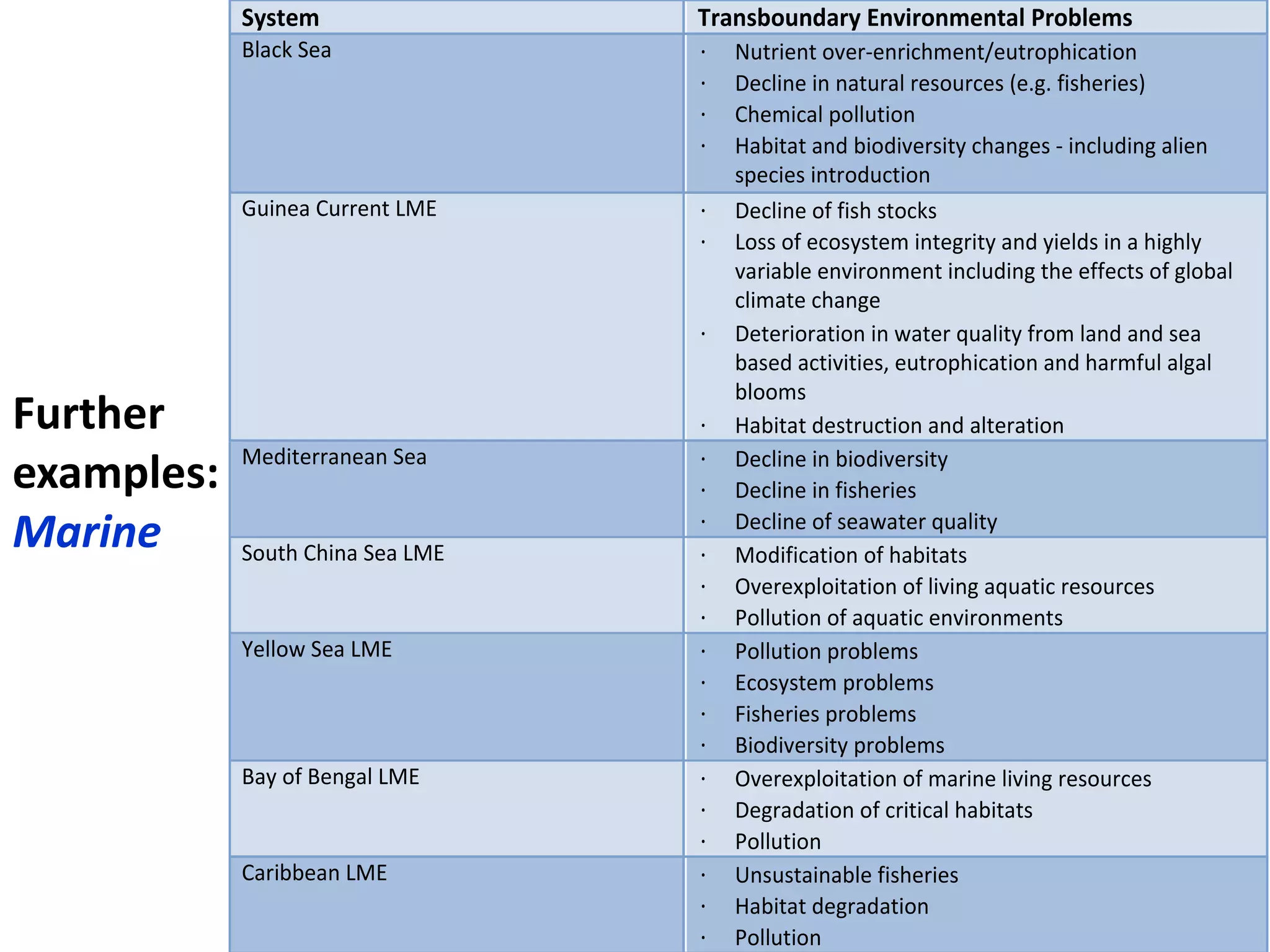
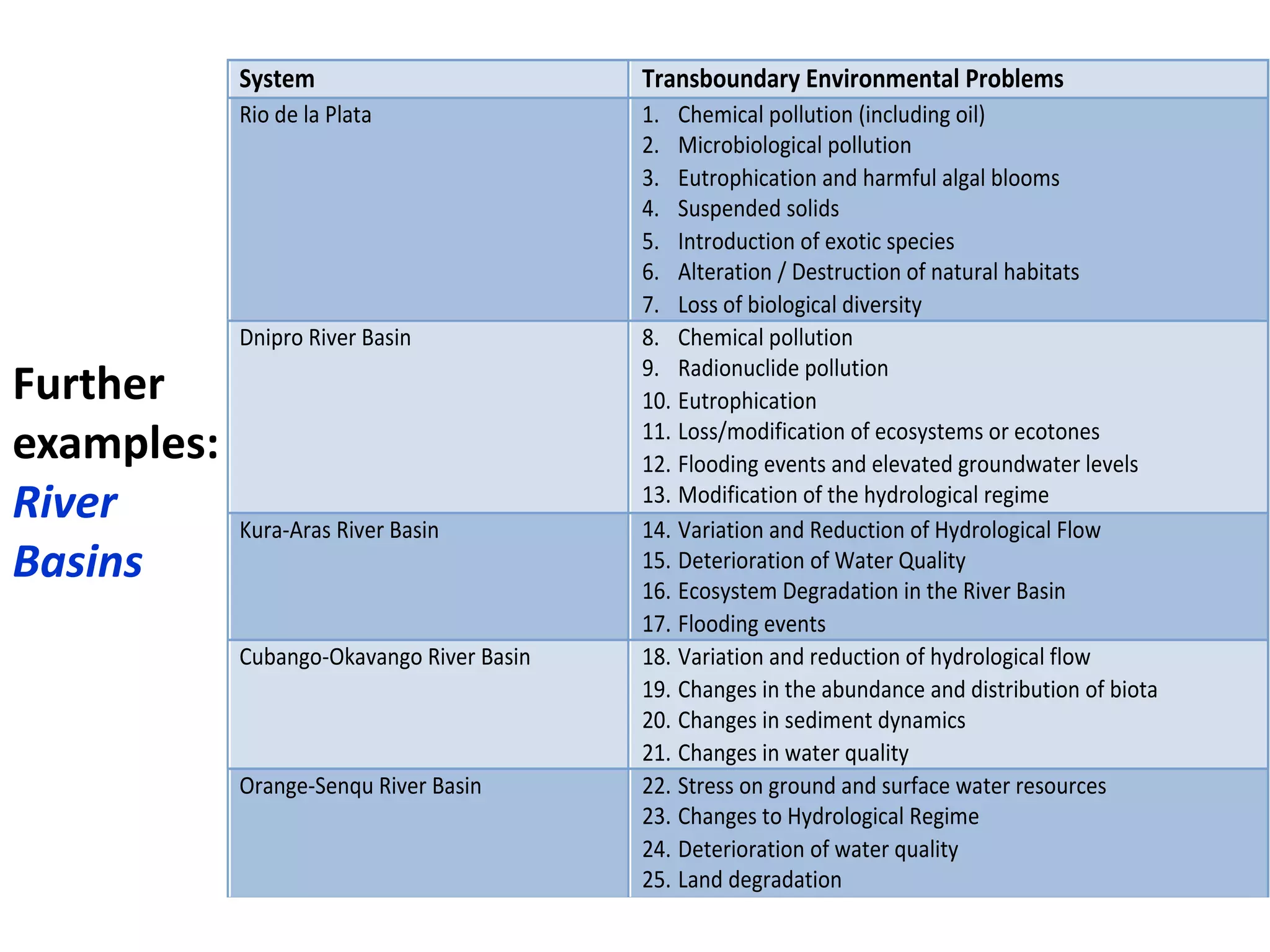
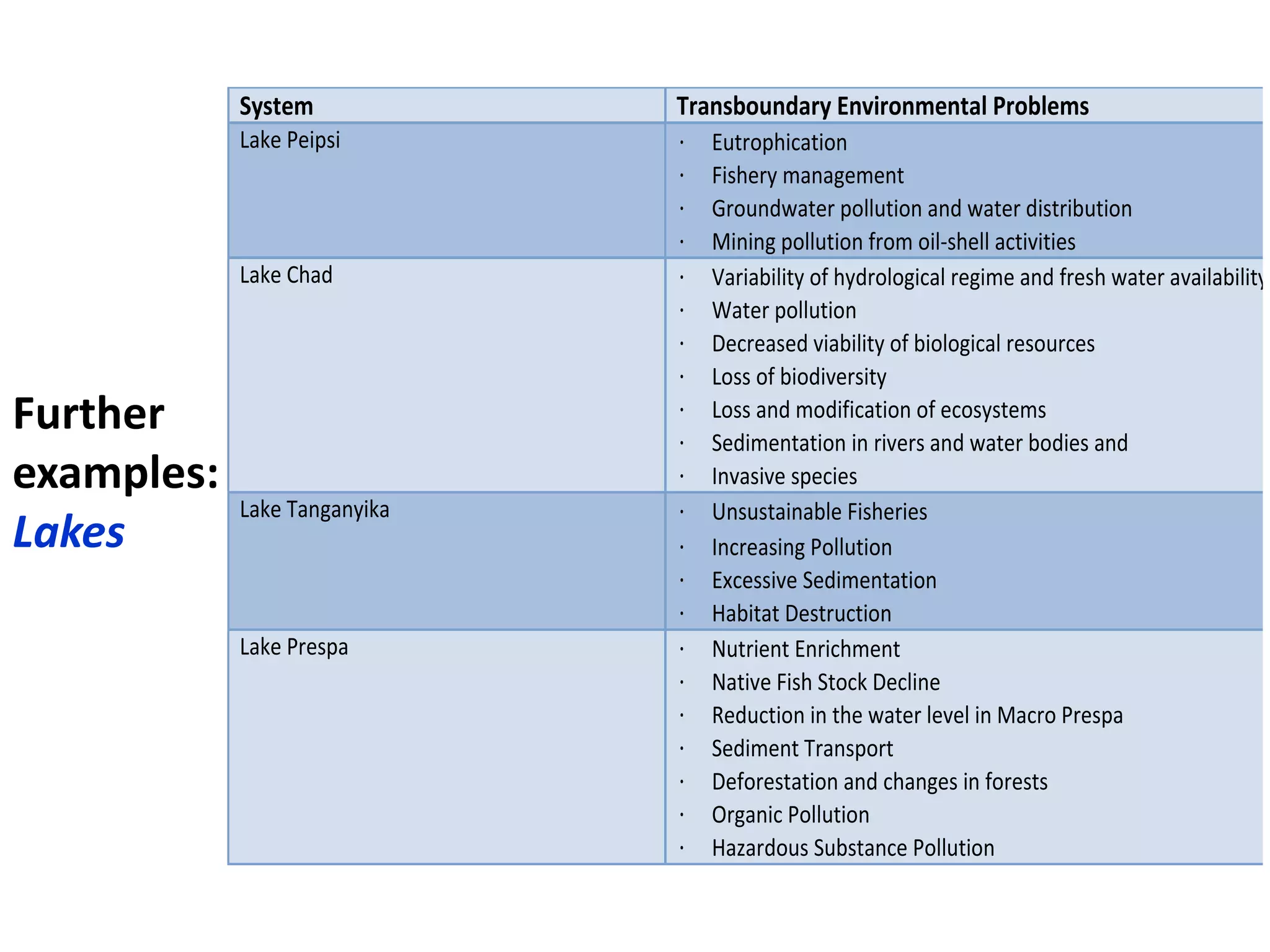
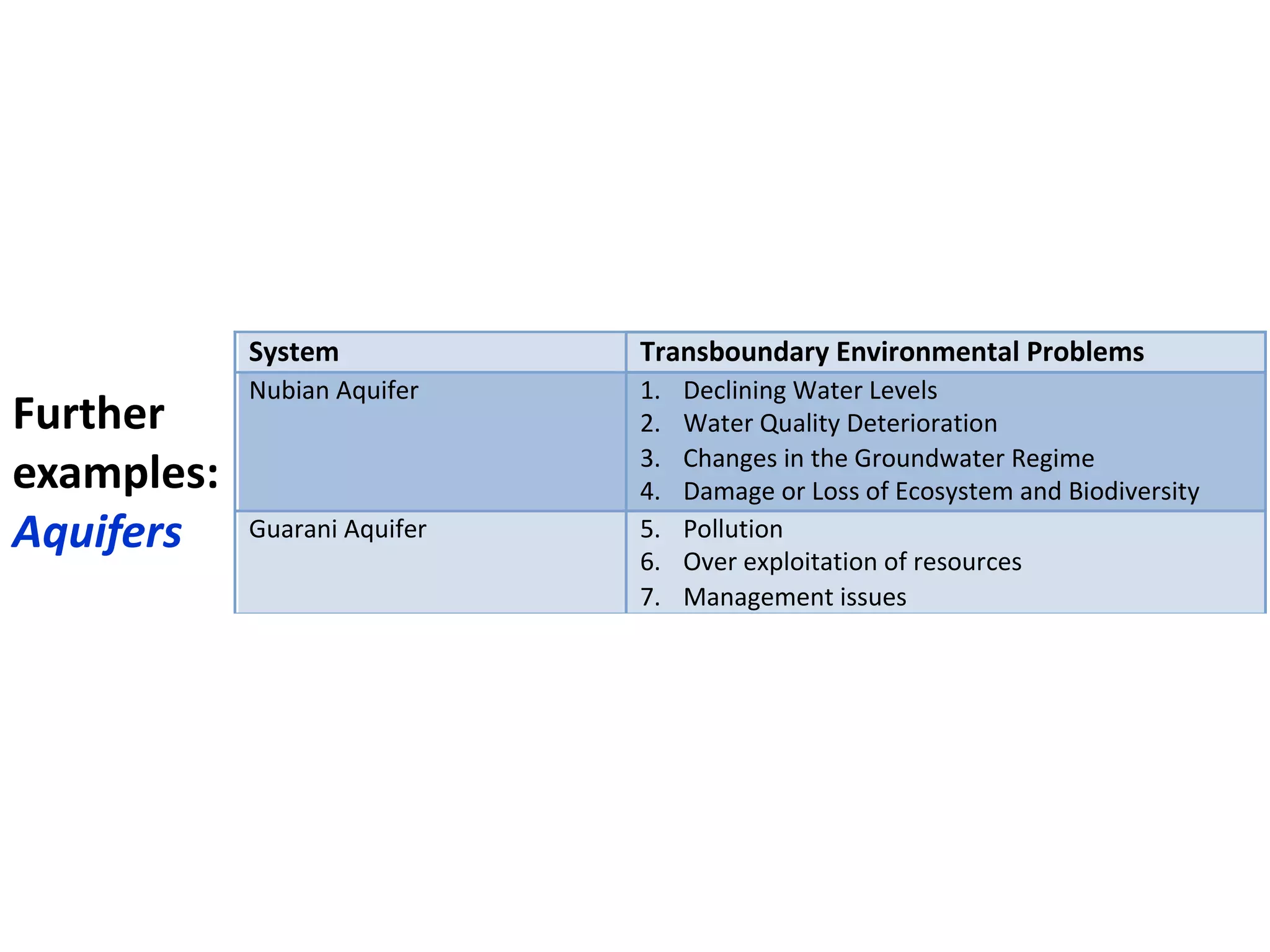
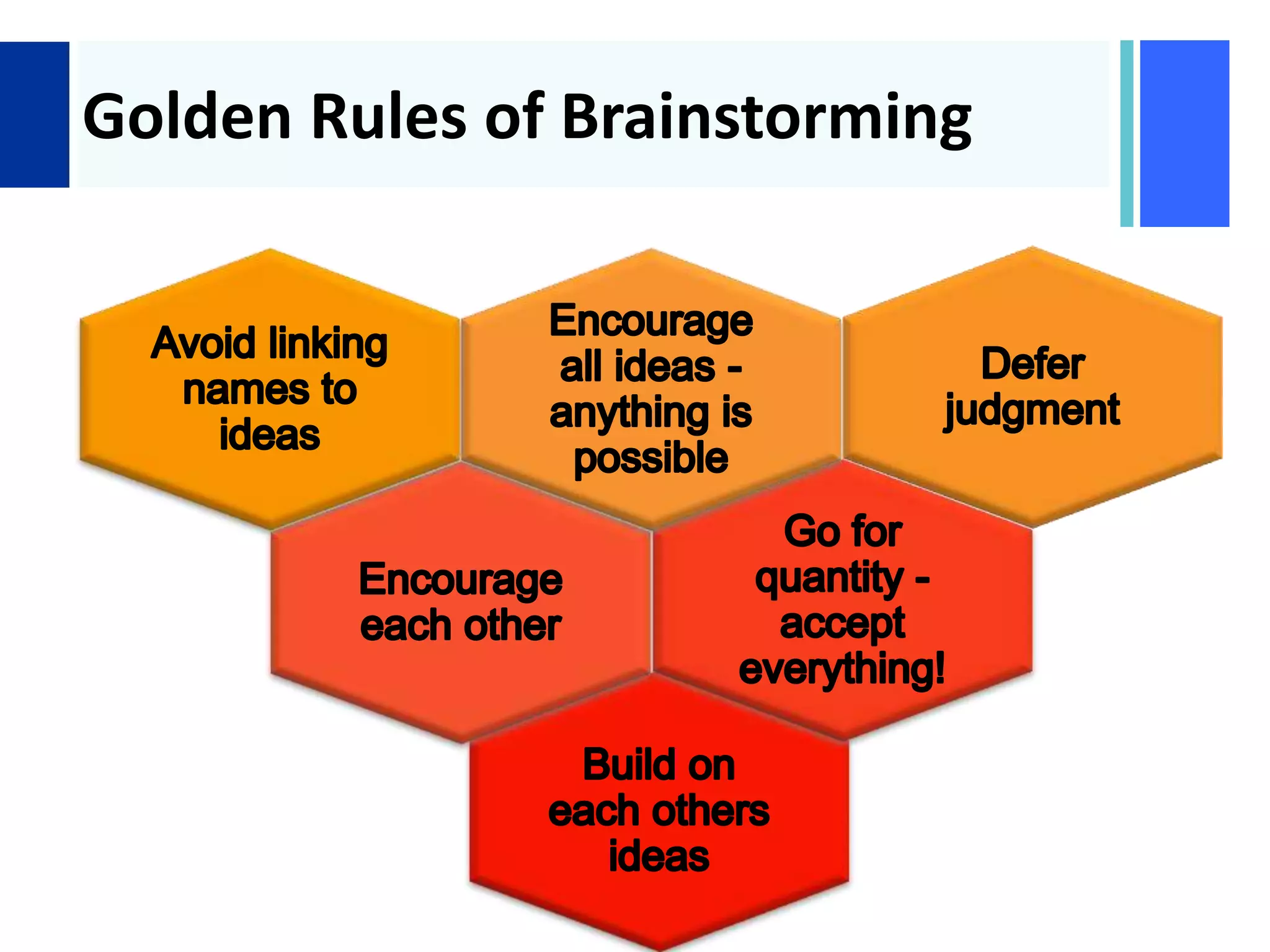
Here are the key steps in the process:
1. Brainstorm a complete list of potential transboundary problems in the water system.
2. Review the list and only keep problems that are truly transboundary in nature (originate in one country and impact another).
3. Characterize each problem in terms of its geographical scale and how strongly transboundary it is.
4. Have individual team members privately prioritize the problems based on agreed upon criteria.
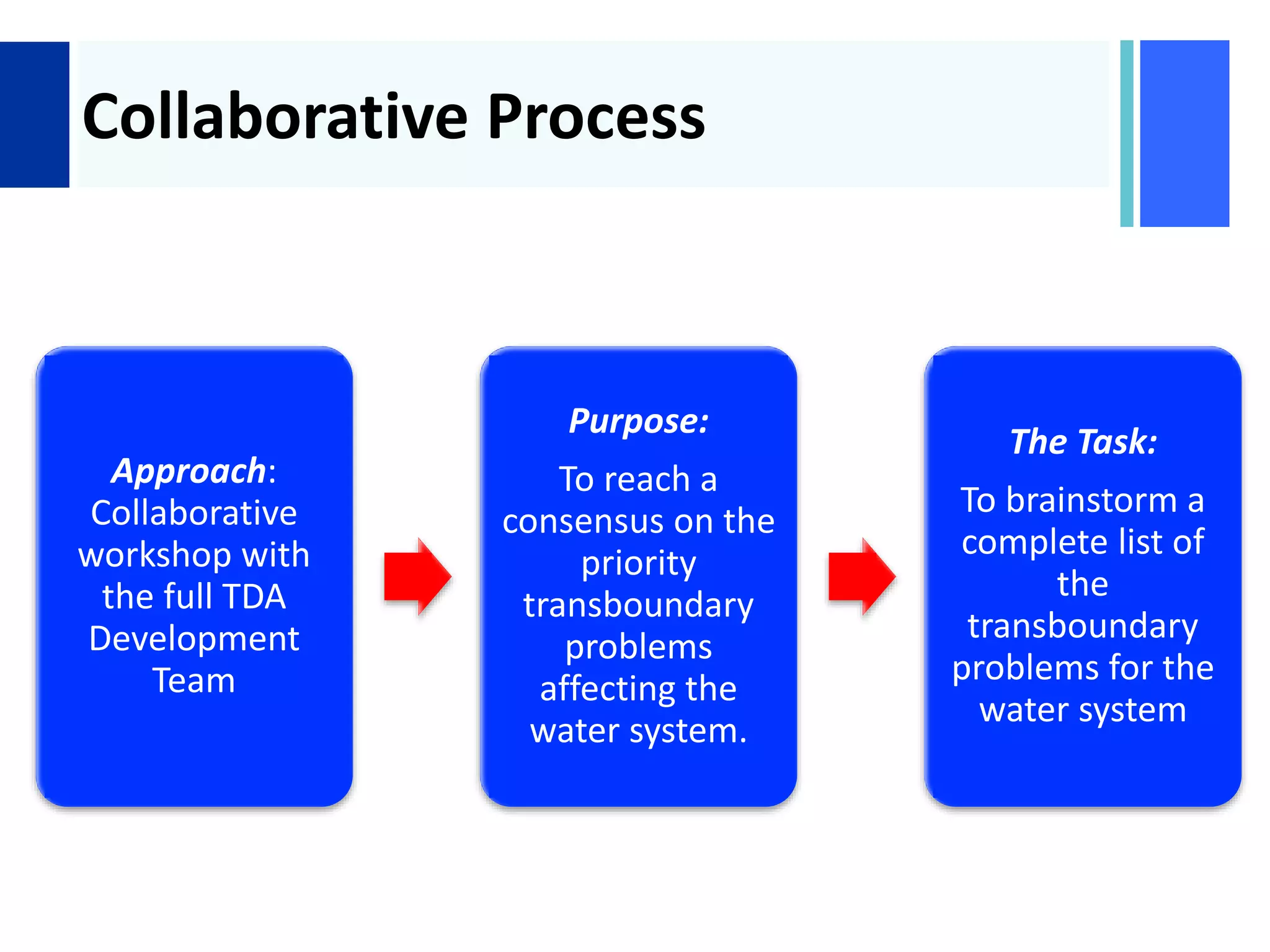
The goal is to develop a consensus among the full TDA development team on the highest priority transboundary problems affecting the water system through an open, collaborative workshop process. Individual input is gathered but the final output is an agreed upon prioritized list.