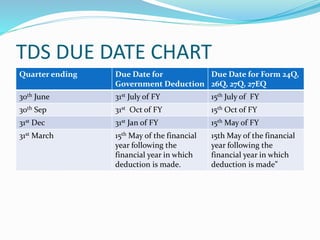
This document provides information on various tax due dates in India, including for income tax, service tax, VAT, advance tax, and tax deducted at source (TDS). It also outlines the annual and event-based compliance requirements for limited liability partnerships (LLPs) registered in India.