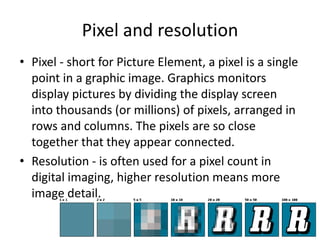
The document discusses key concepts related to digital images including pixels and resolution, vector and raster images, common file formats and their uses, compression techniques, image capture devices, optimizing images, and storage and asset management of digital files. Pixels make up digital images and resolution refers to pixel count, with higher resolution providing more detail. Vector images scale smoothly while raster images lose clarity when scaled. Common file formats include BMP, PNG, GIF, TIFF, JPG, PSD, PDF, EPS and AI, each suited for different image types and uses. Compression reduces file sizes by eliminating unnecessary data or removing marginally important information. Devices like cameras and screen capture tools are used to capture digital images. Optimizing improves efficiency