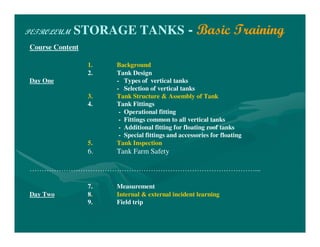
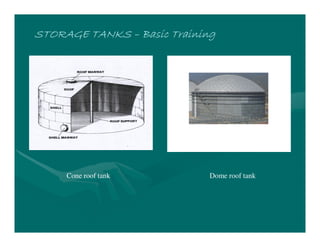
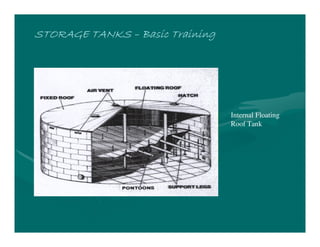
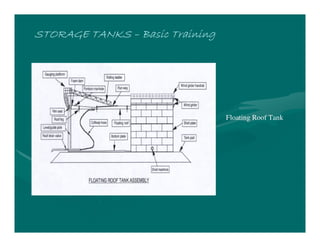
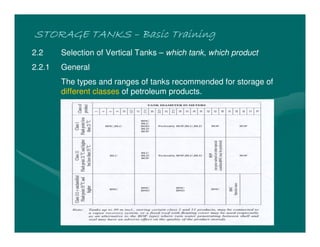
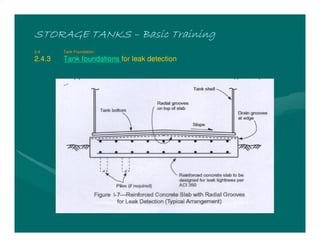
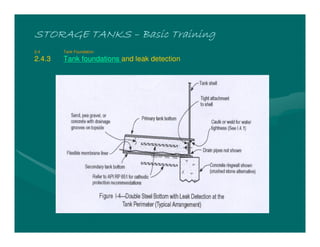
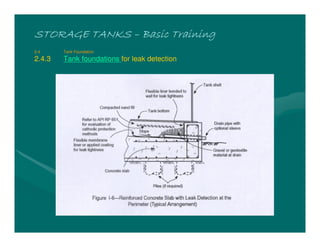
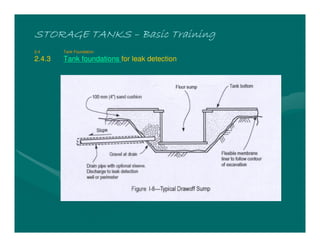
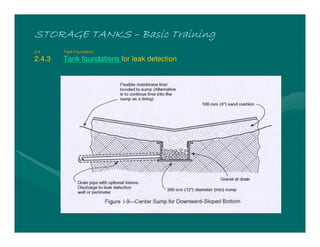
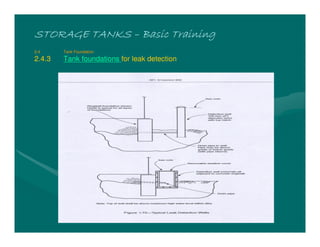
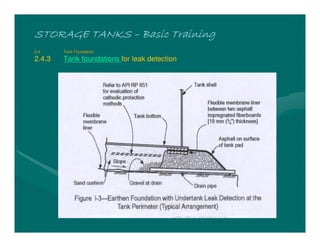
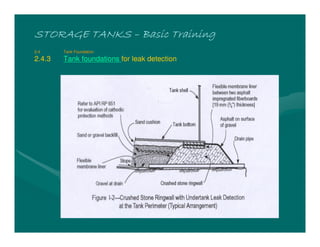
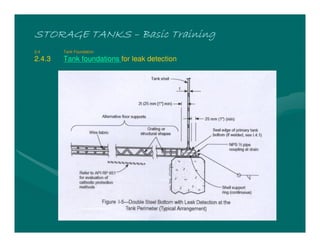
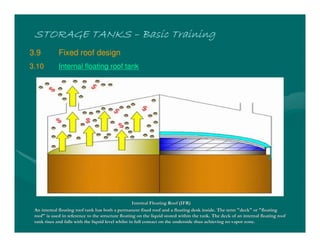
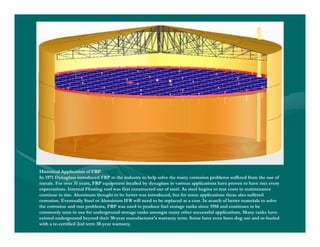
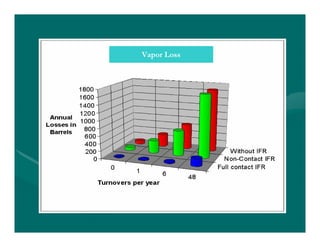
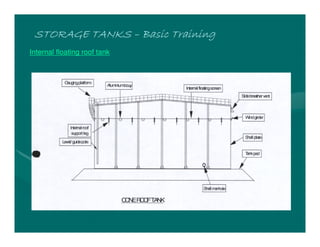
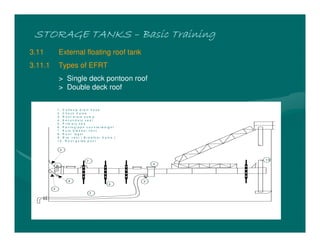
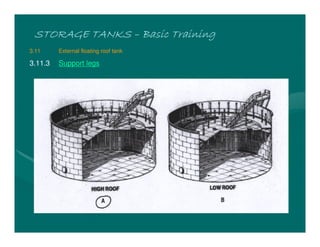
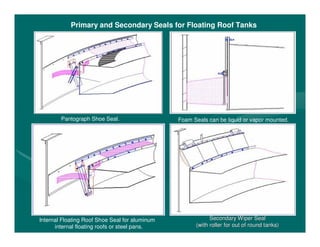
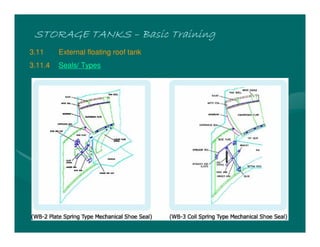
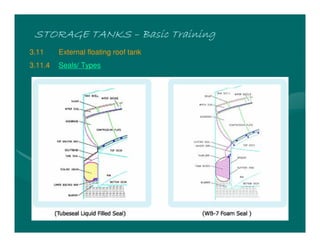
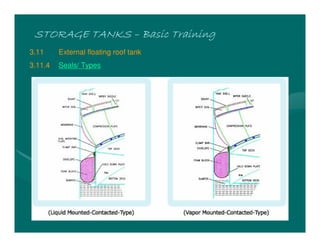
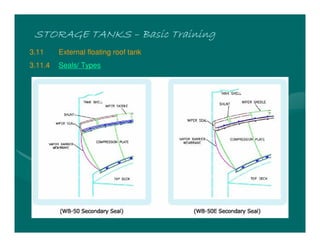
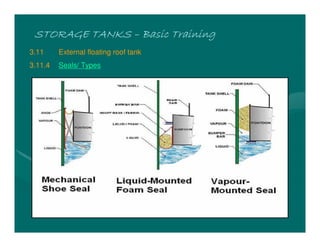
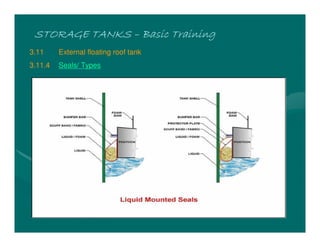
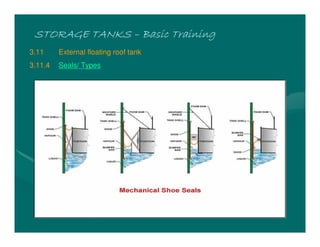
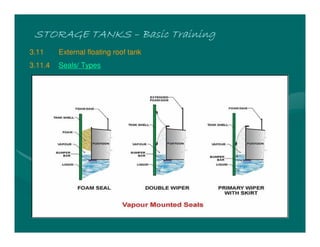
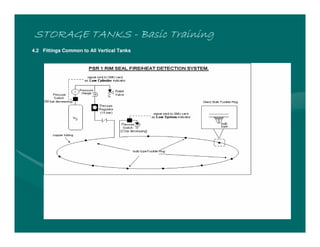
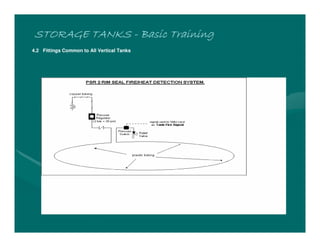
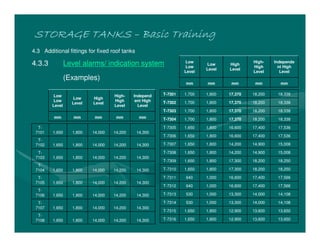
The document provides basic training on petroleum storage tanks, covering aspects such as tank design, types, structures, and safety measures. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining tank integrity to prevent leaks and environmental hazards while detailing various tank types like atmospheric and pressurized storage. The training includes practical elements like tank inspections, stability calculations, and appropriate foundations based on site conditions.