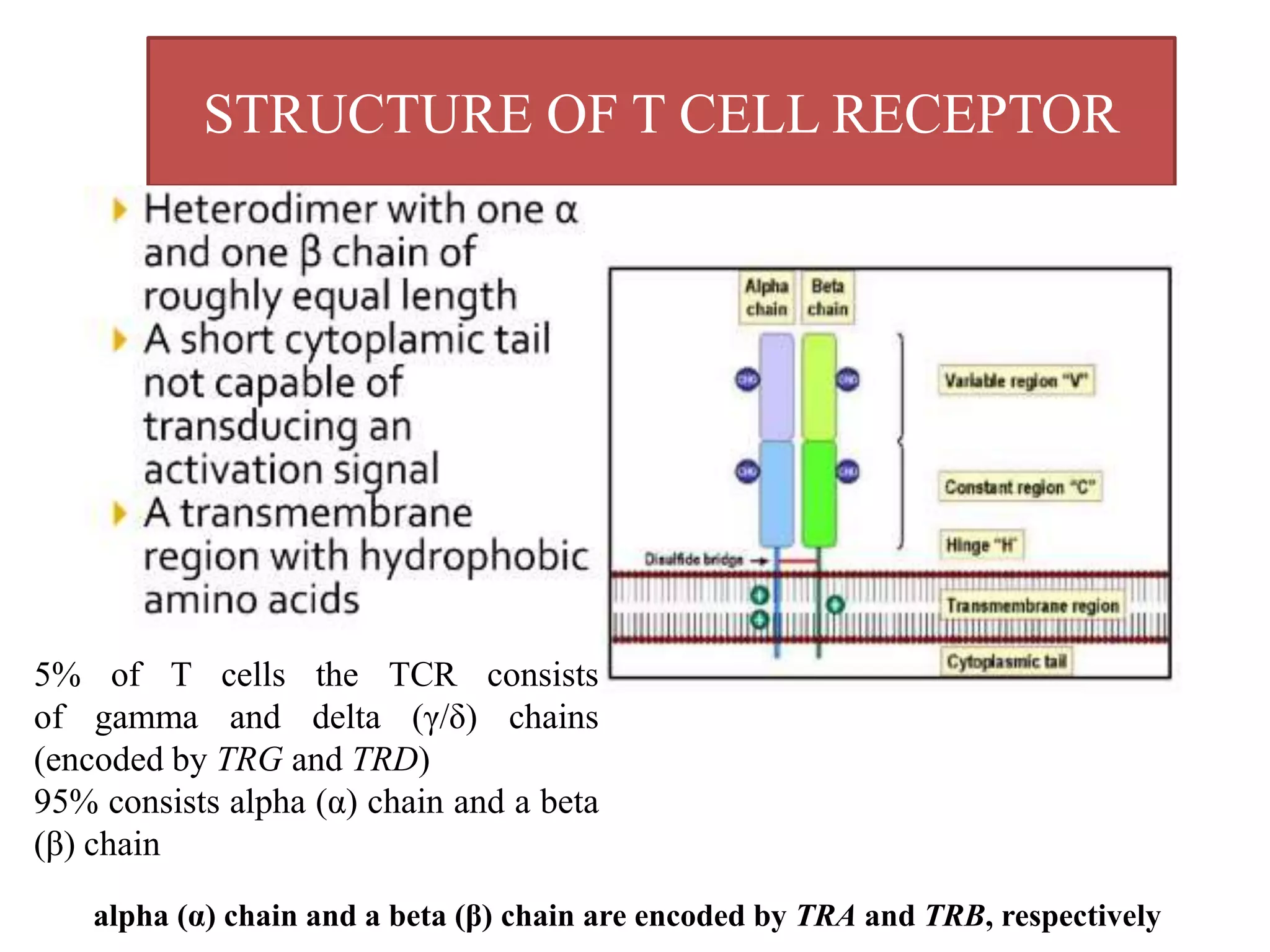
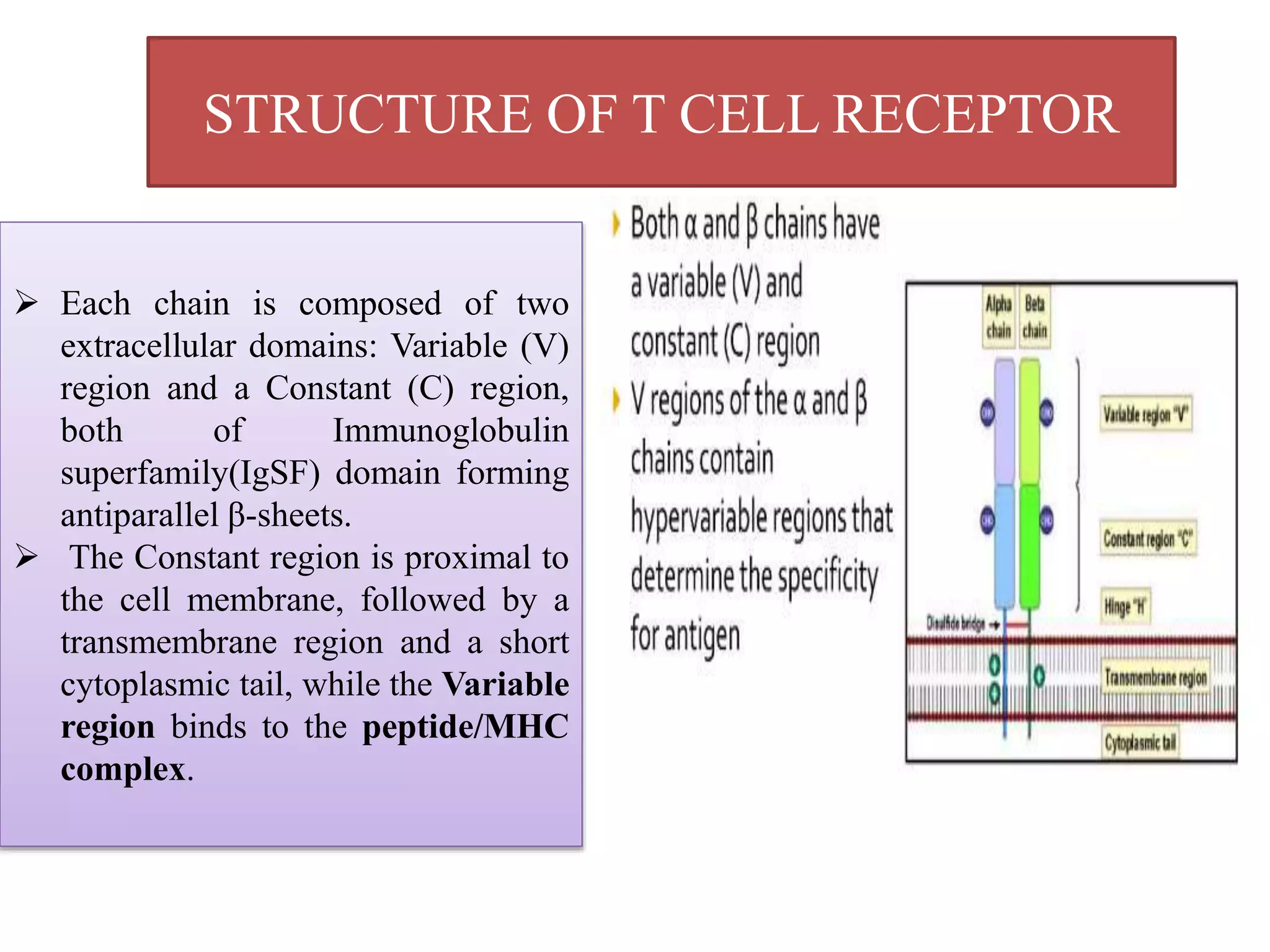
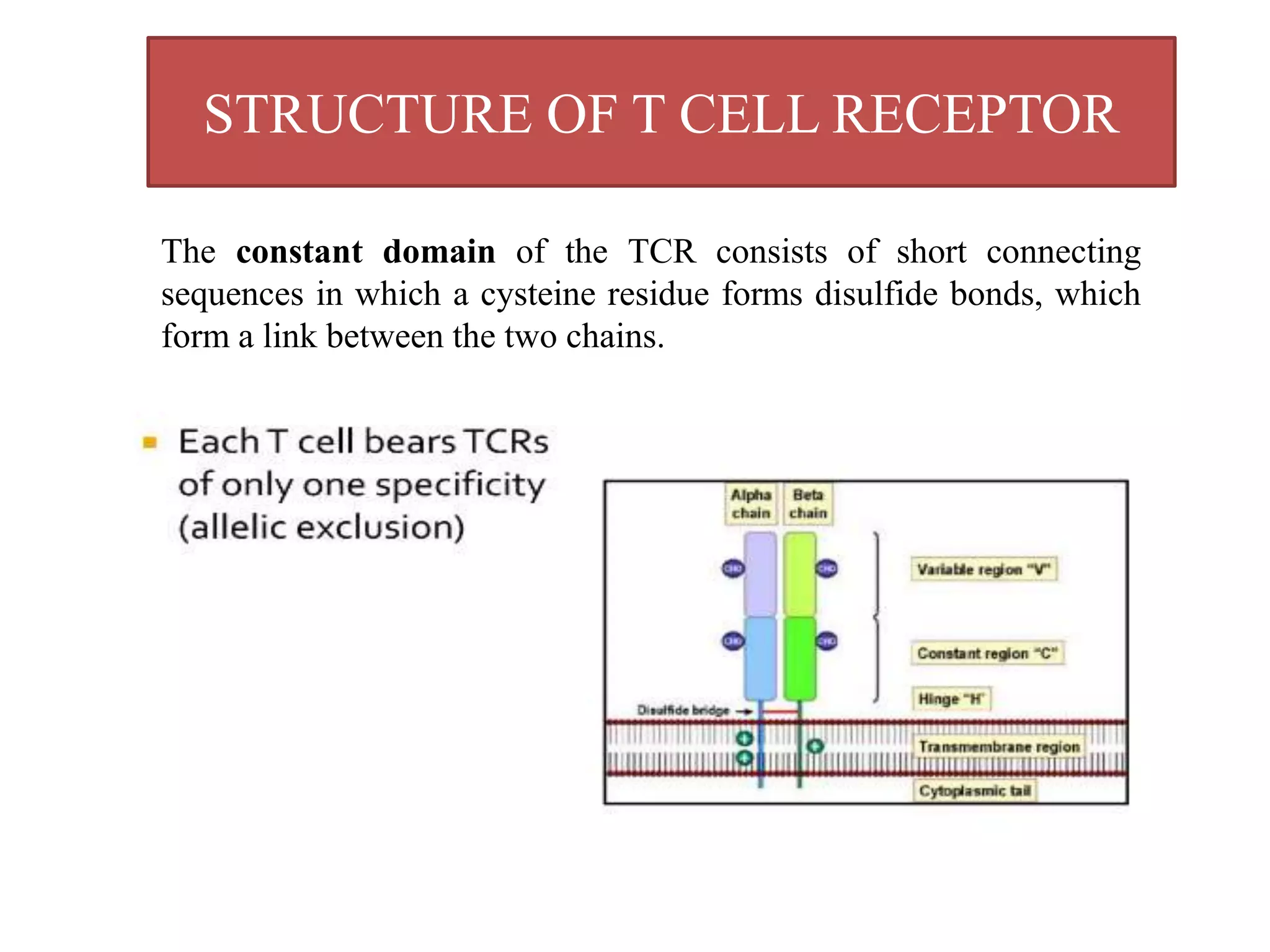
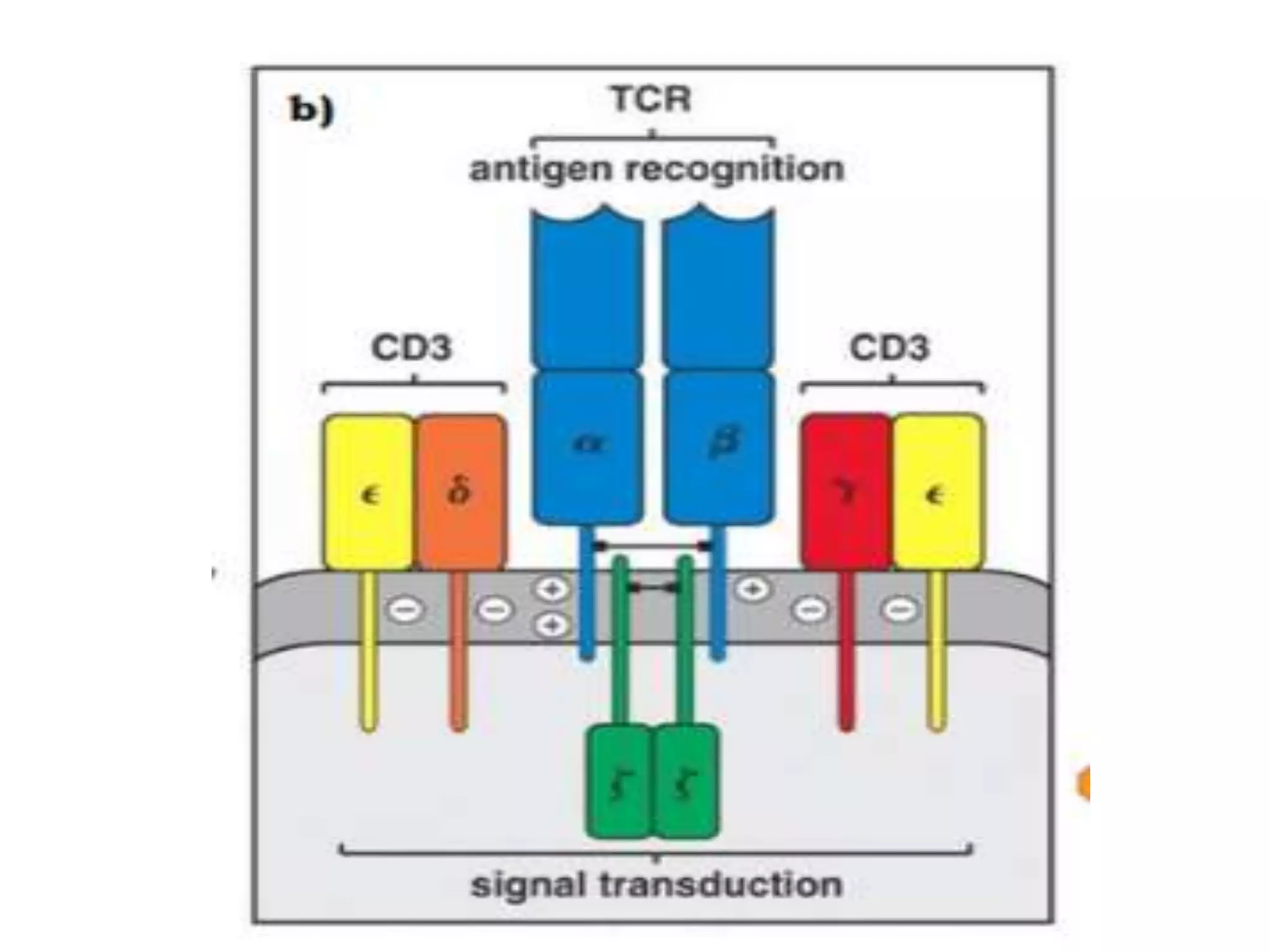
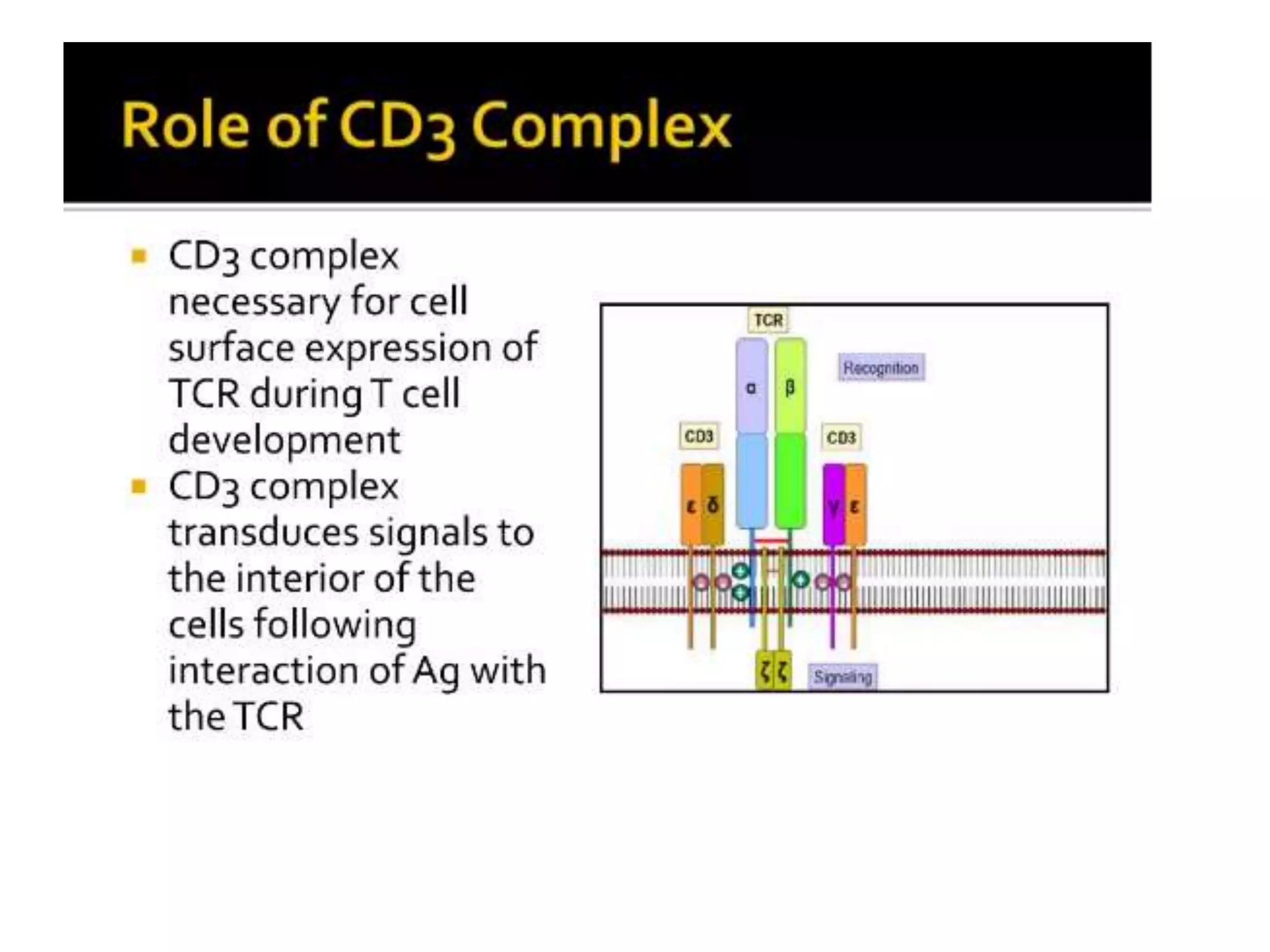
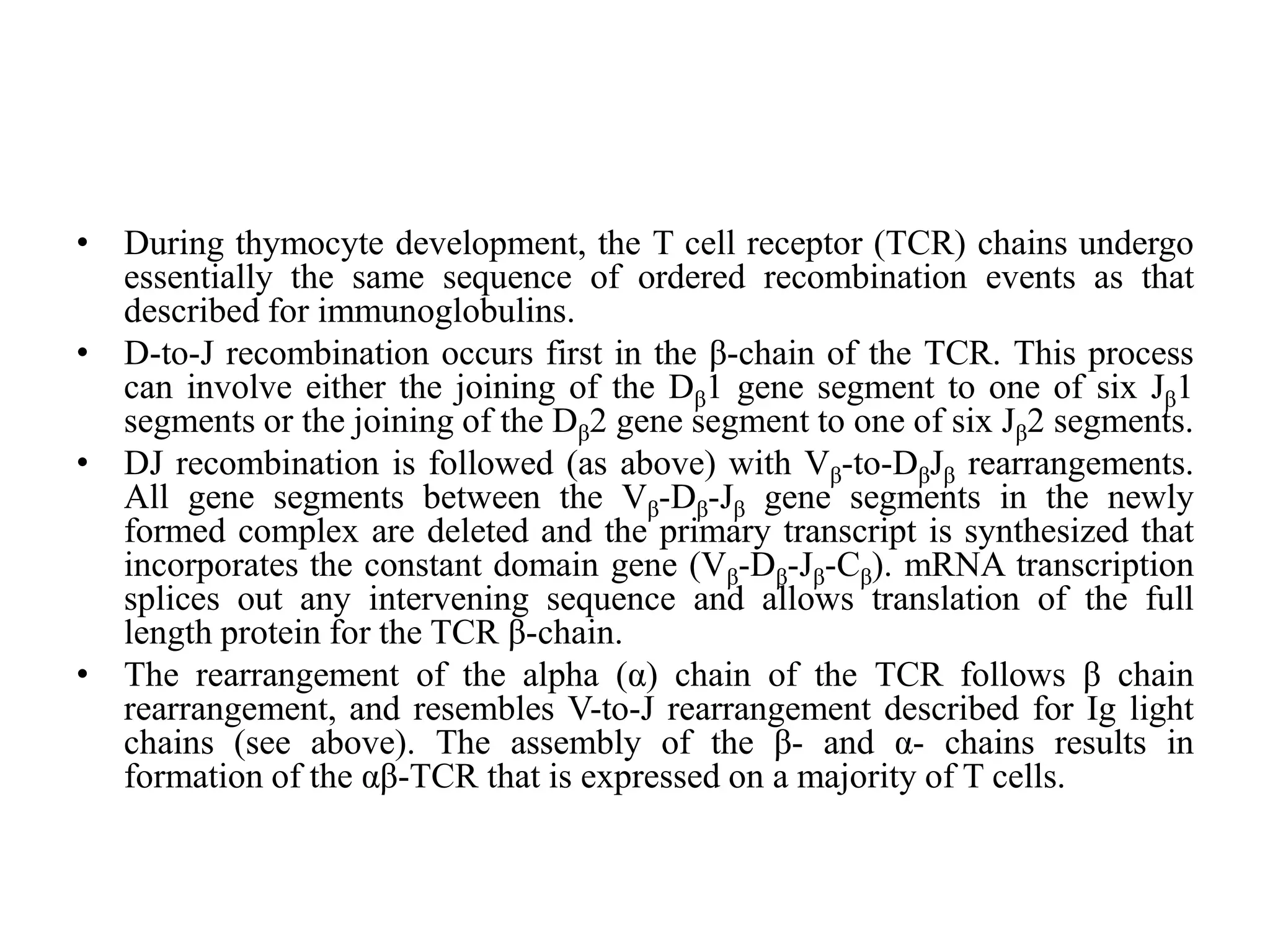
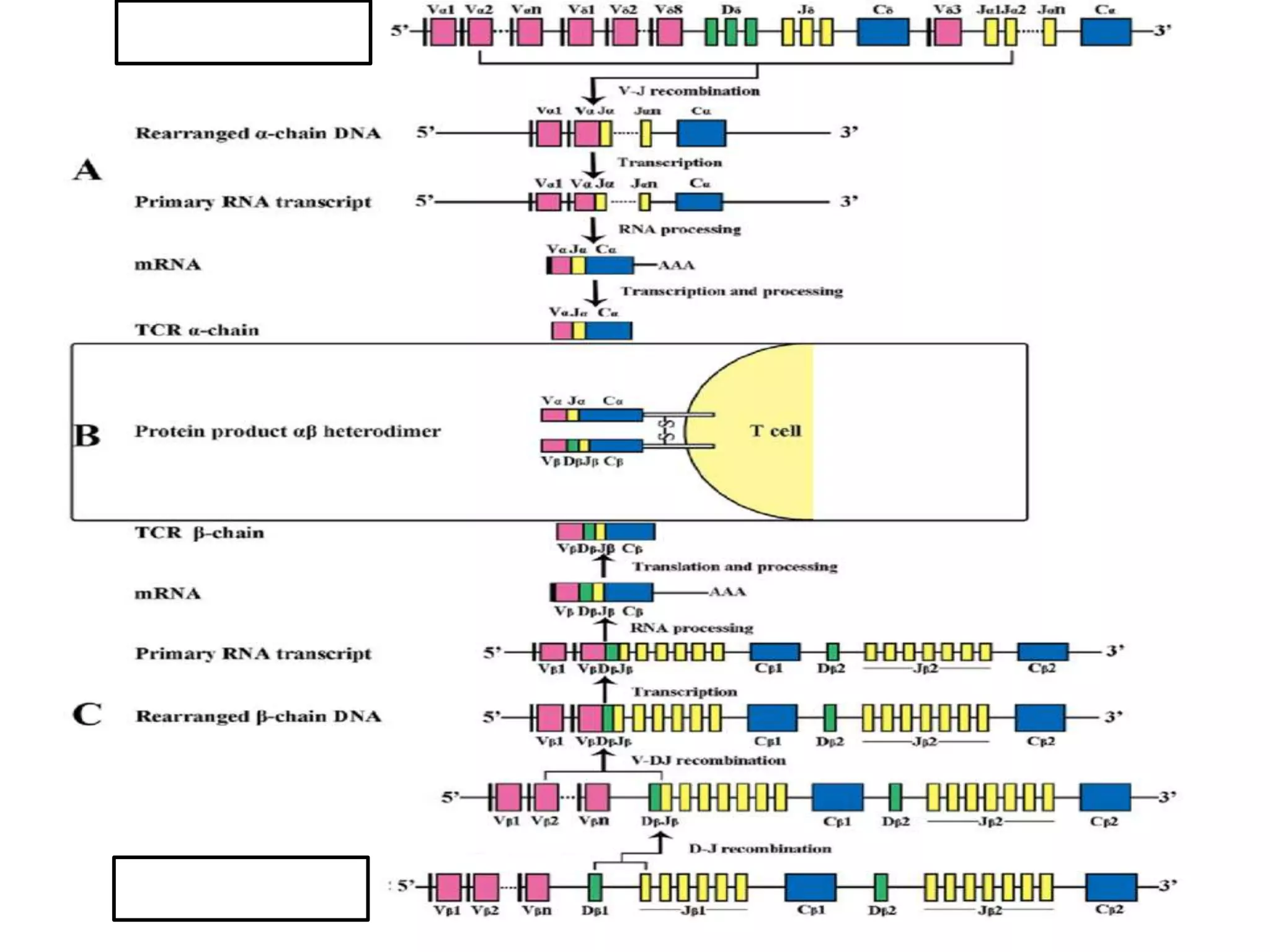
The T cell receptor (TCR) is a protein complex found on the surface of T cells that is responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen bound to MHC molecules. It consists of an alpha and beta chain, with 95% of T cells containing these chains and 5% containing gamma and delta chains instead. Each chain contains a variable region that binds the peptide-MHC complex and a constant region near the cell membrane. The variable regions contain three hypervariable complementarity-determining regions important for antigen recognition. The TCR is associated with CD3 proteins that transmit activation signals into the T cell upon peptide binding. TCR diversity arises from genetic recombination of DNA segments during T cell development.