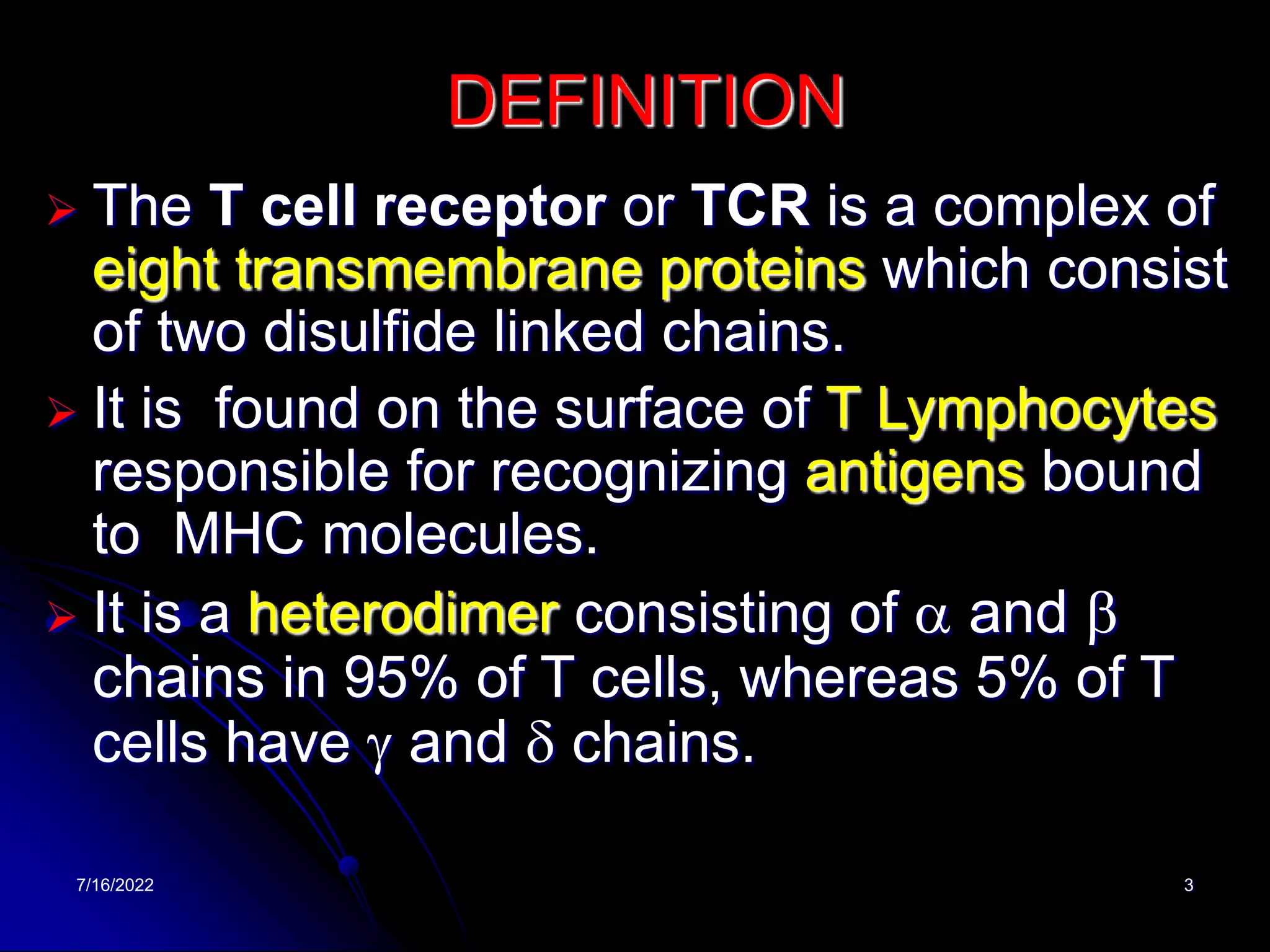
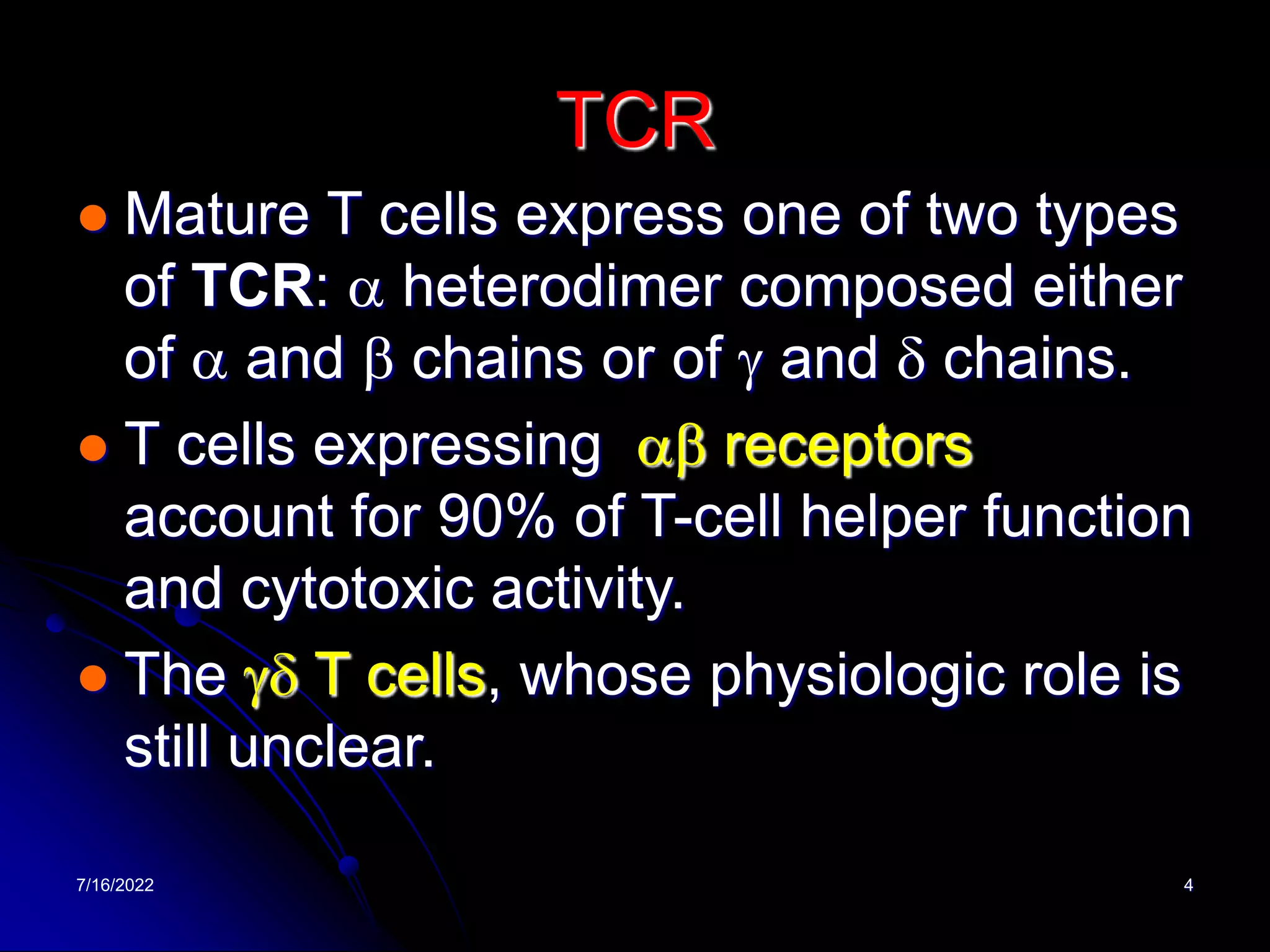
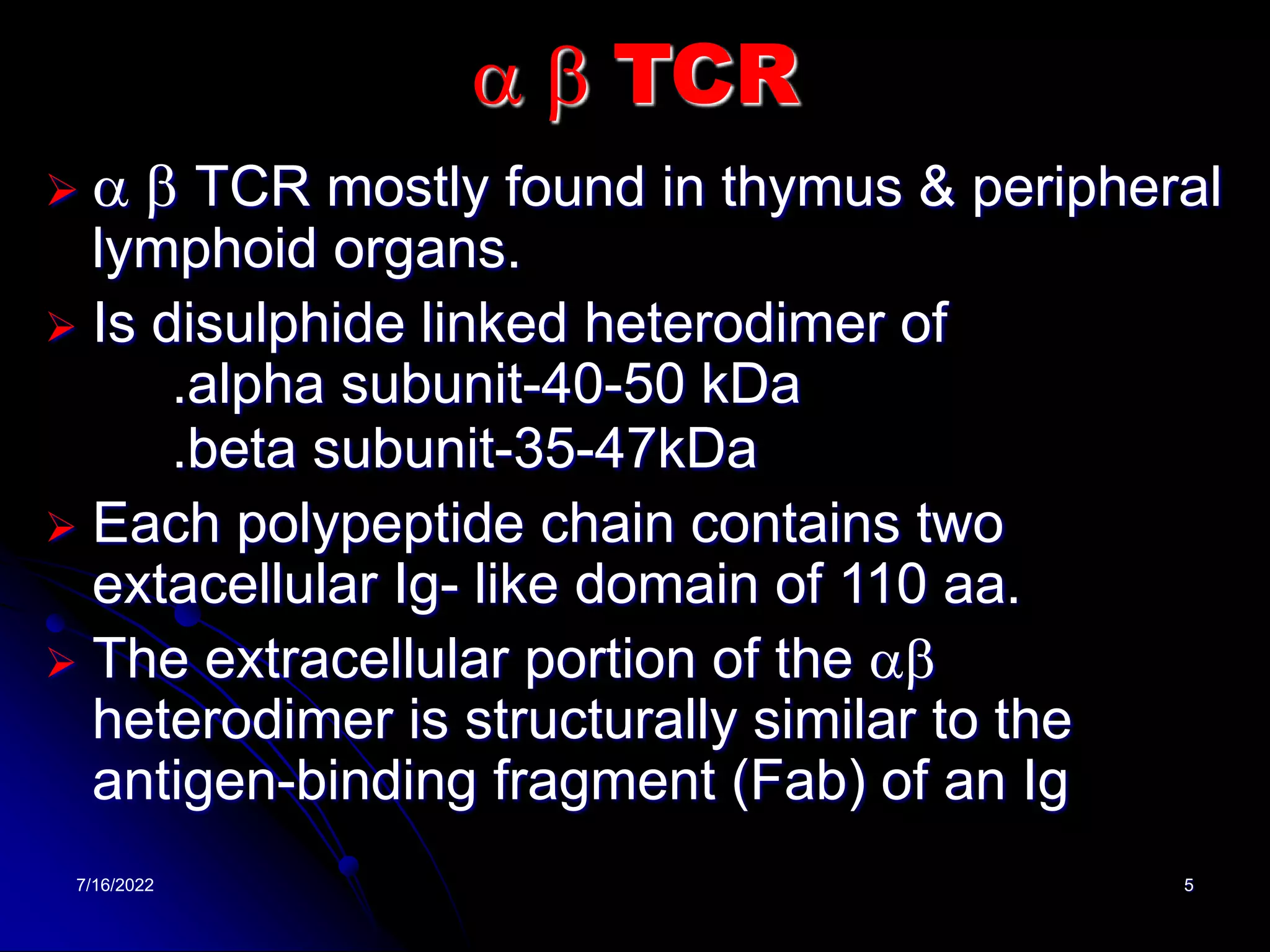
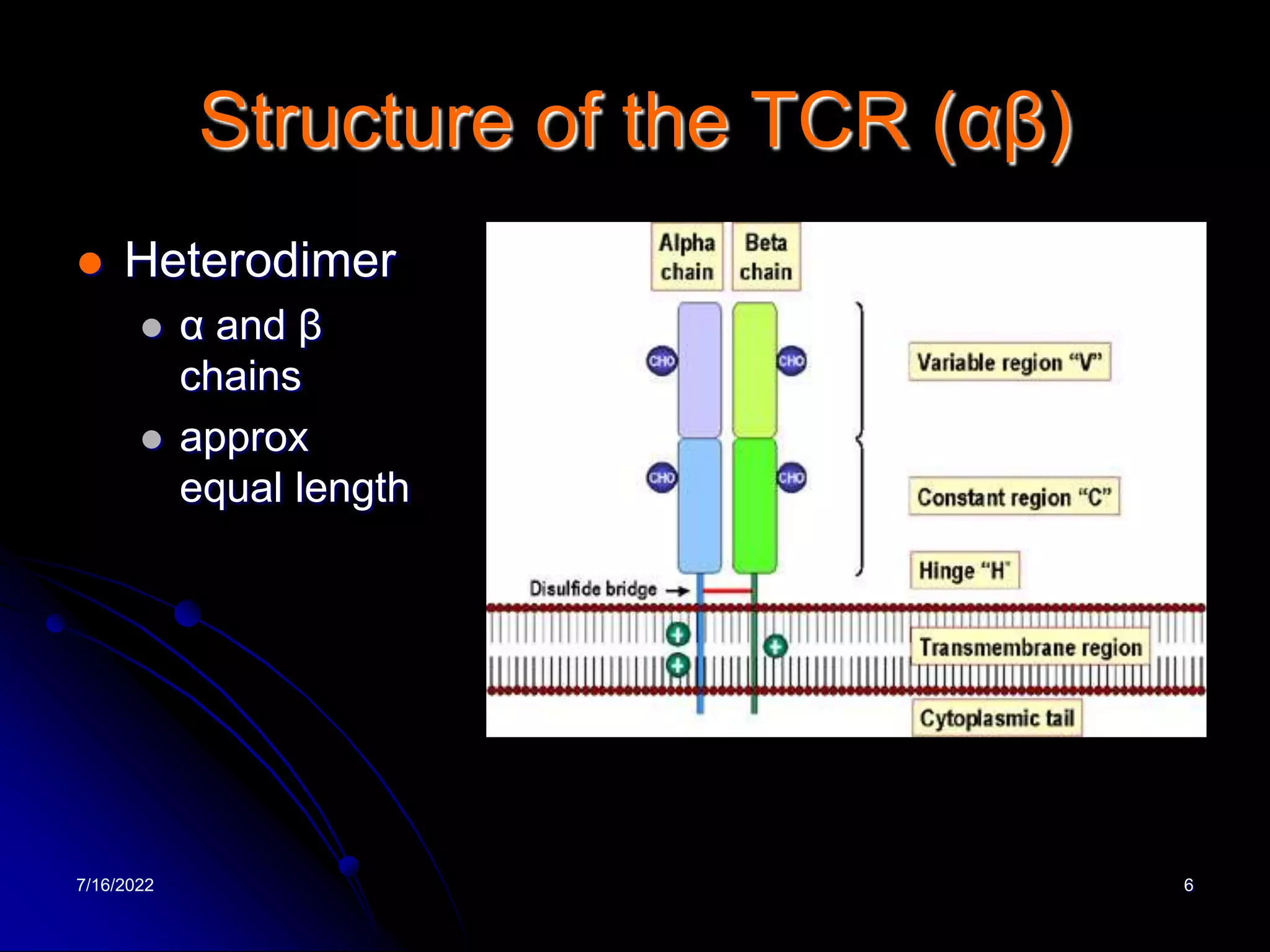
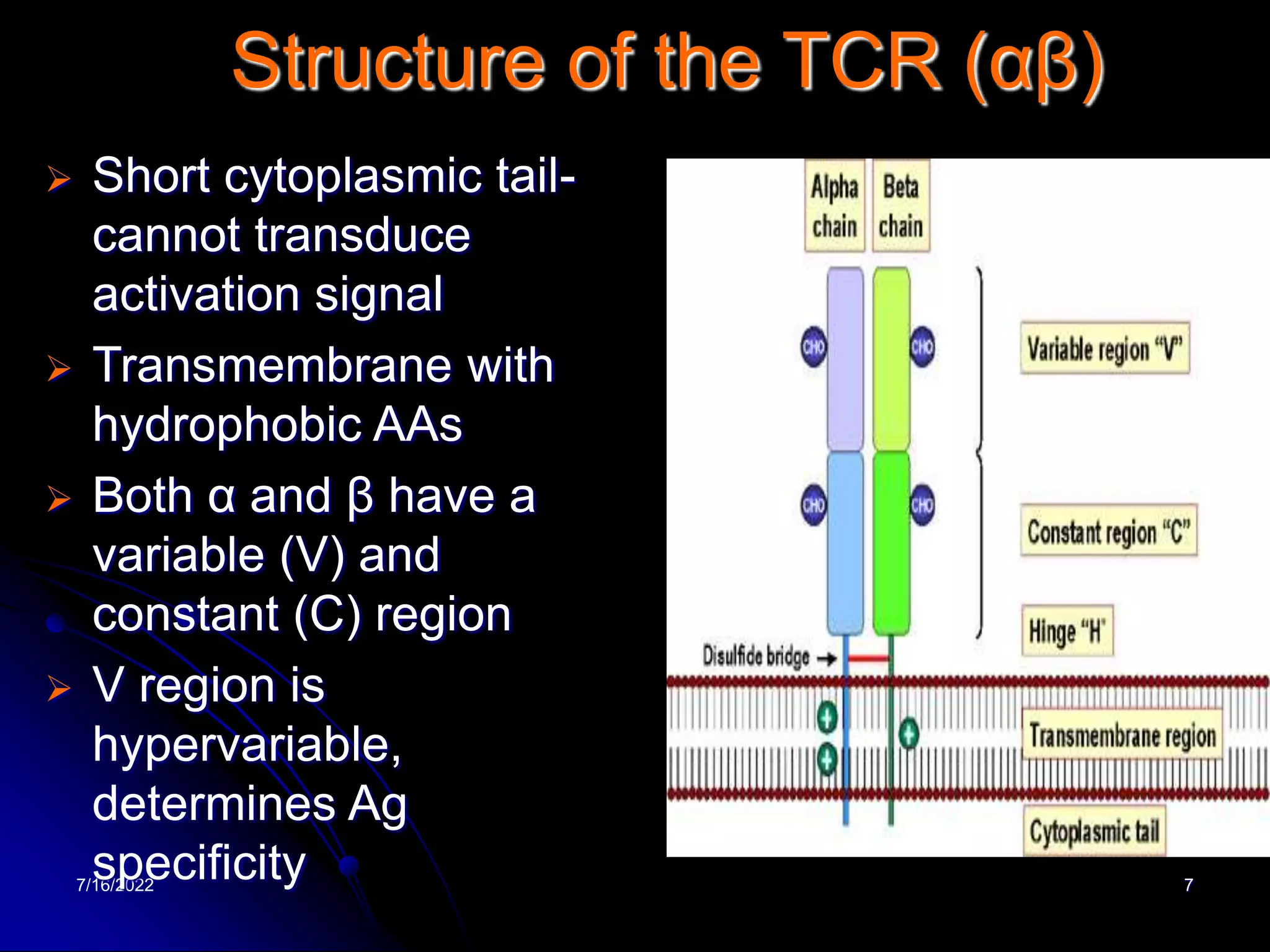
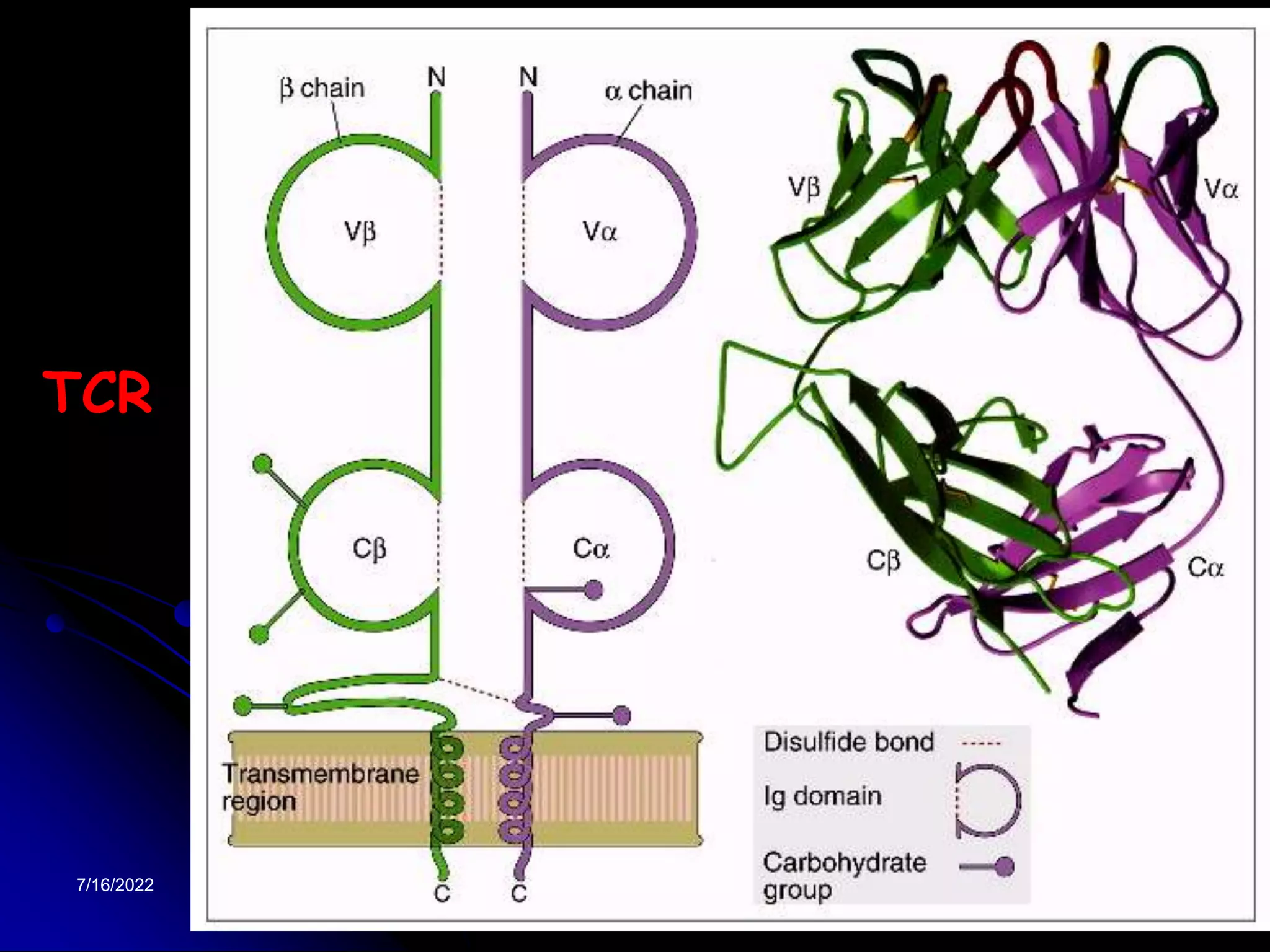
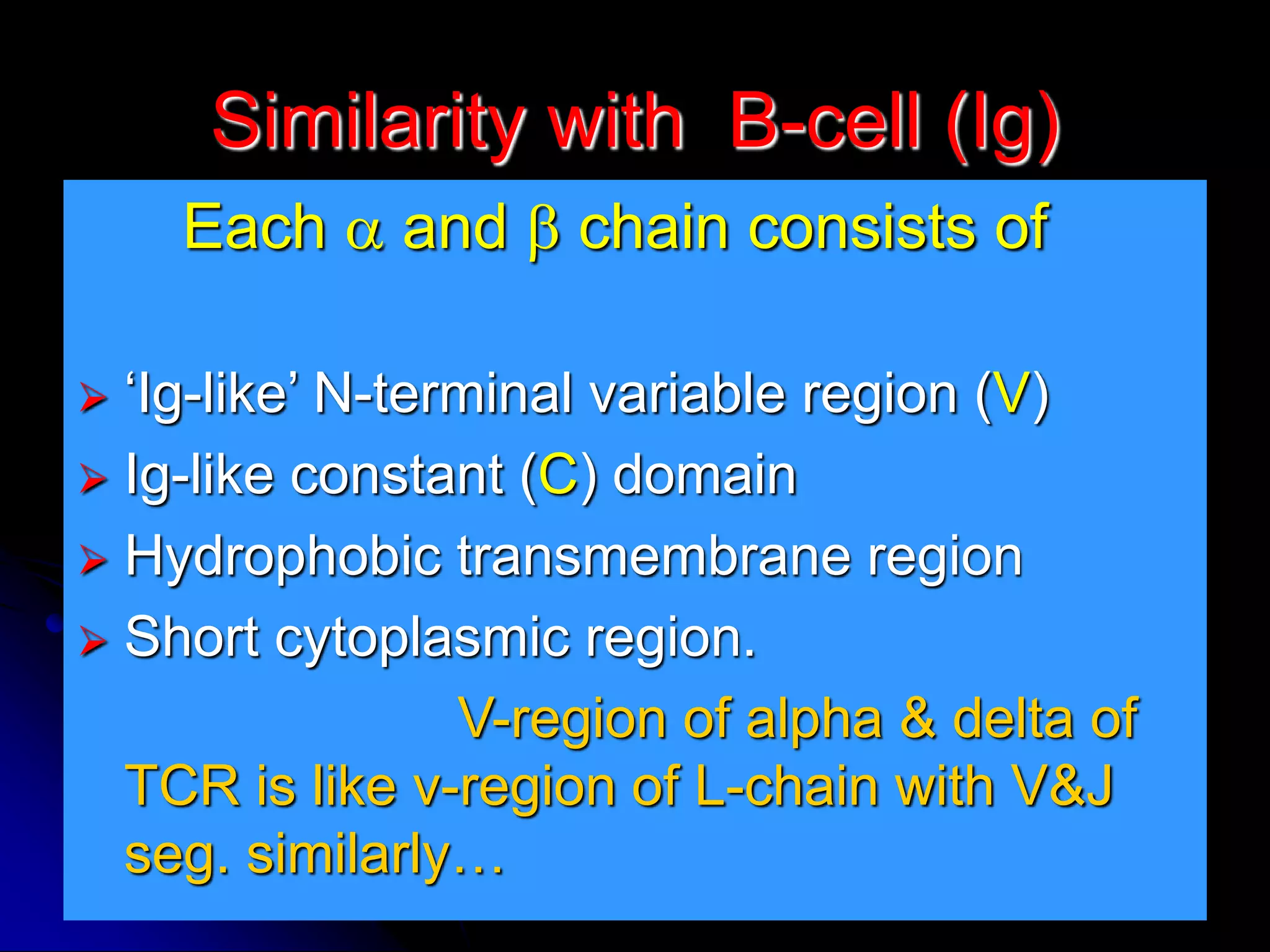
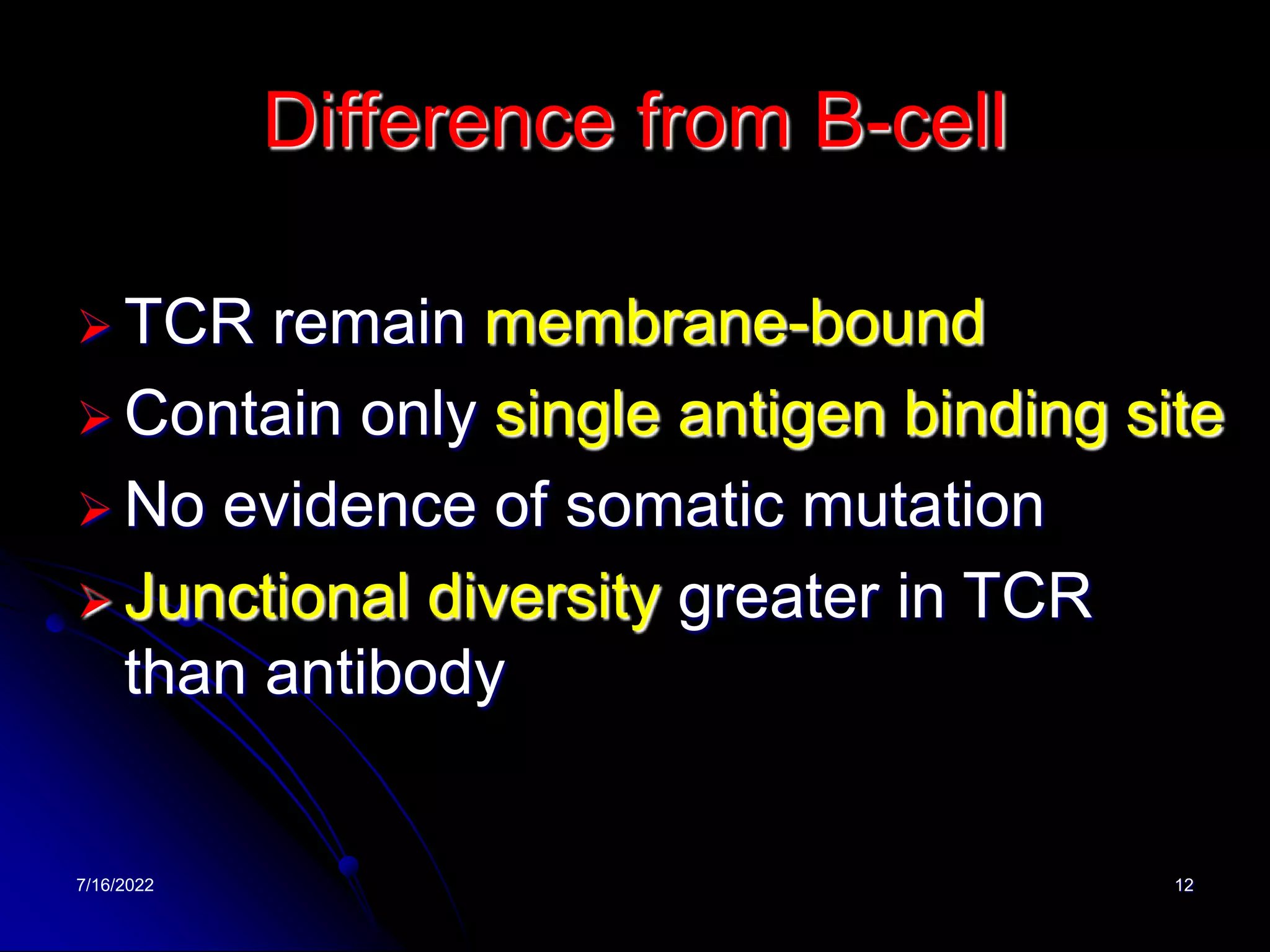
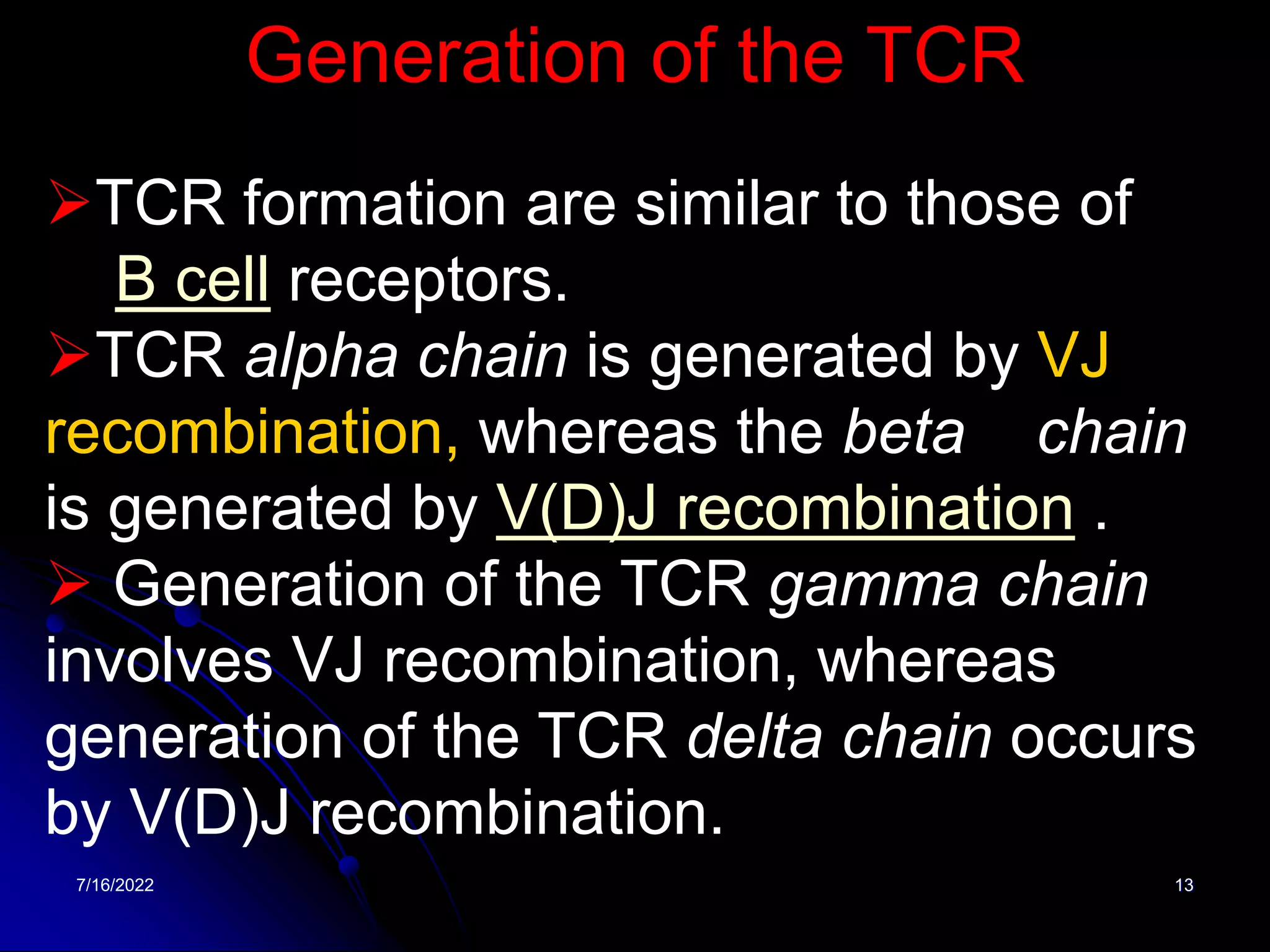
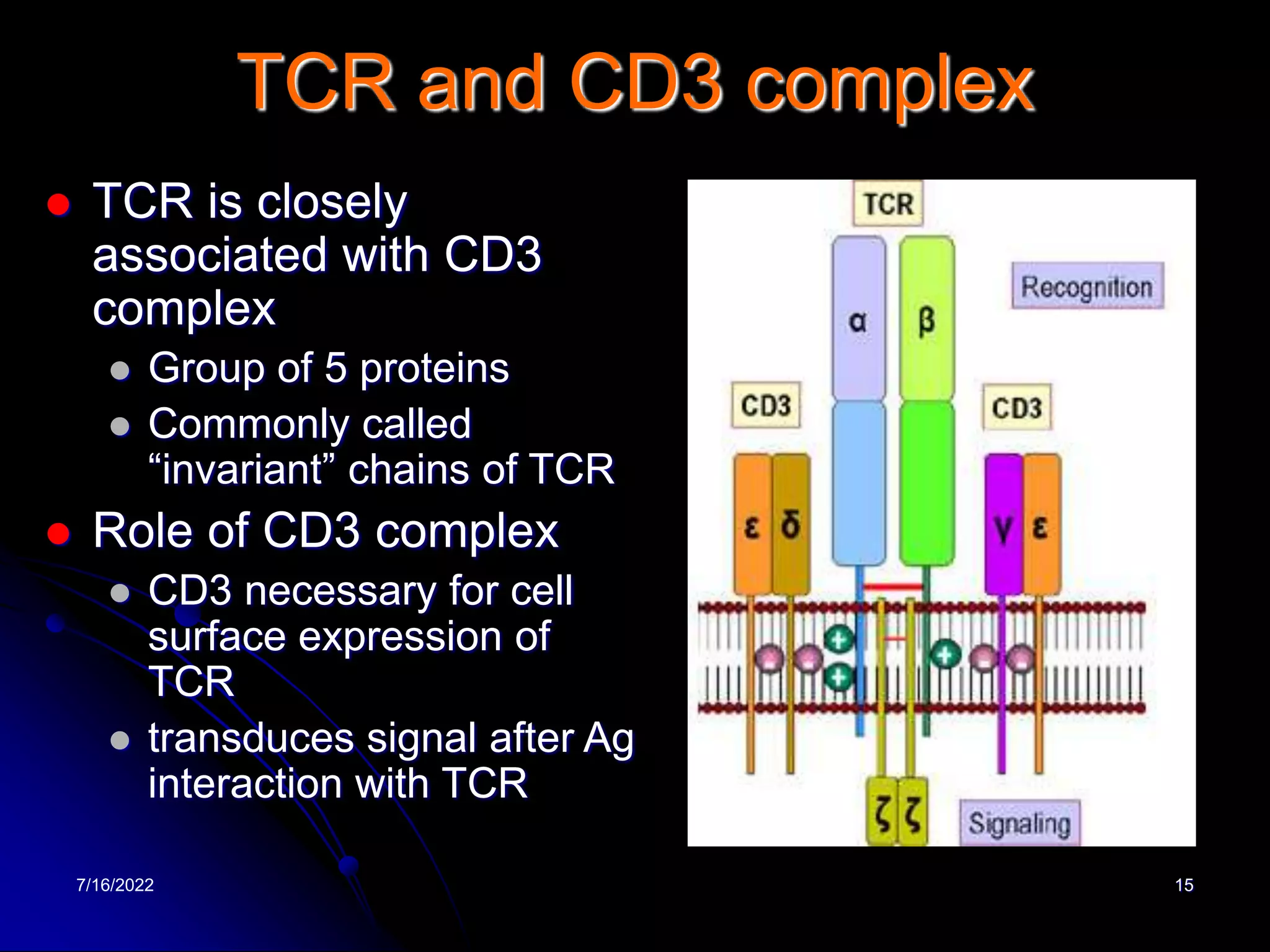
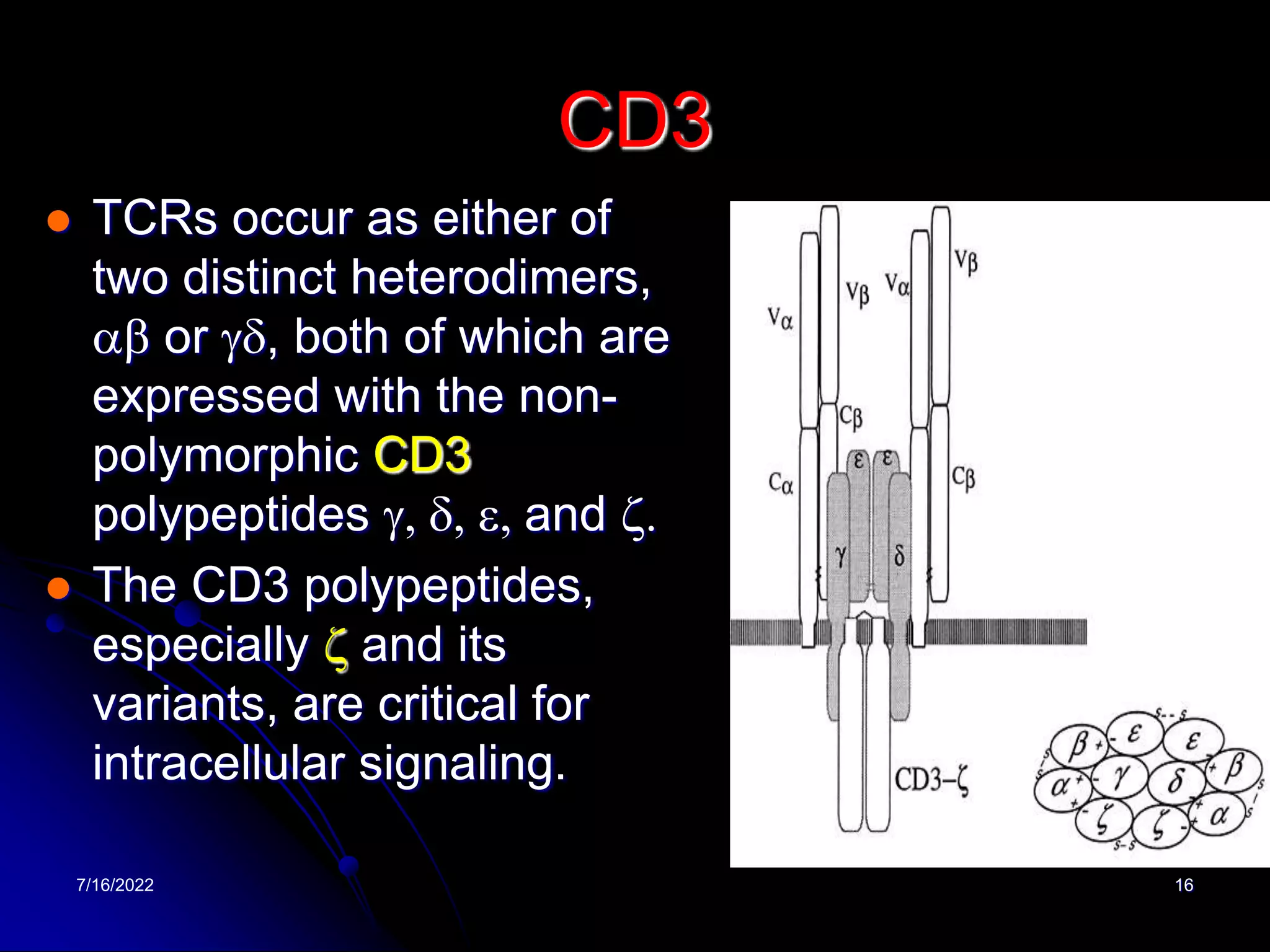
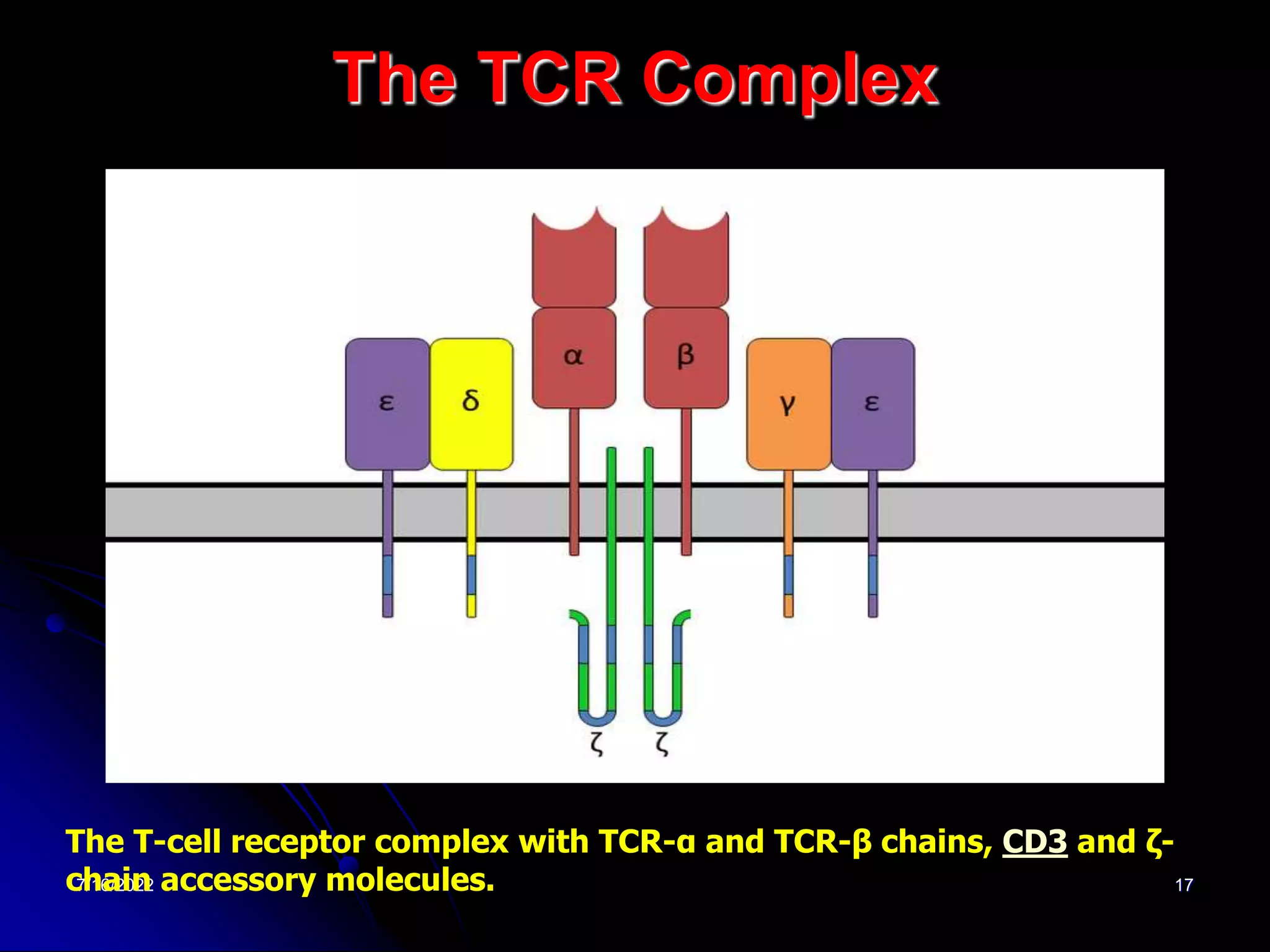
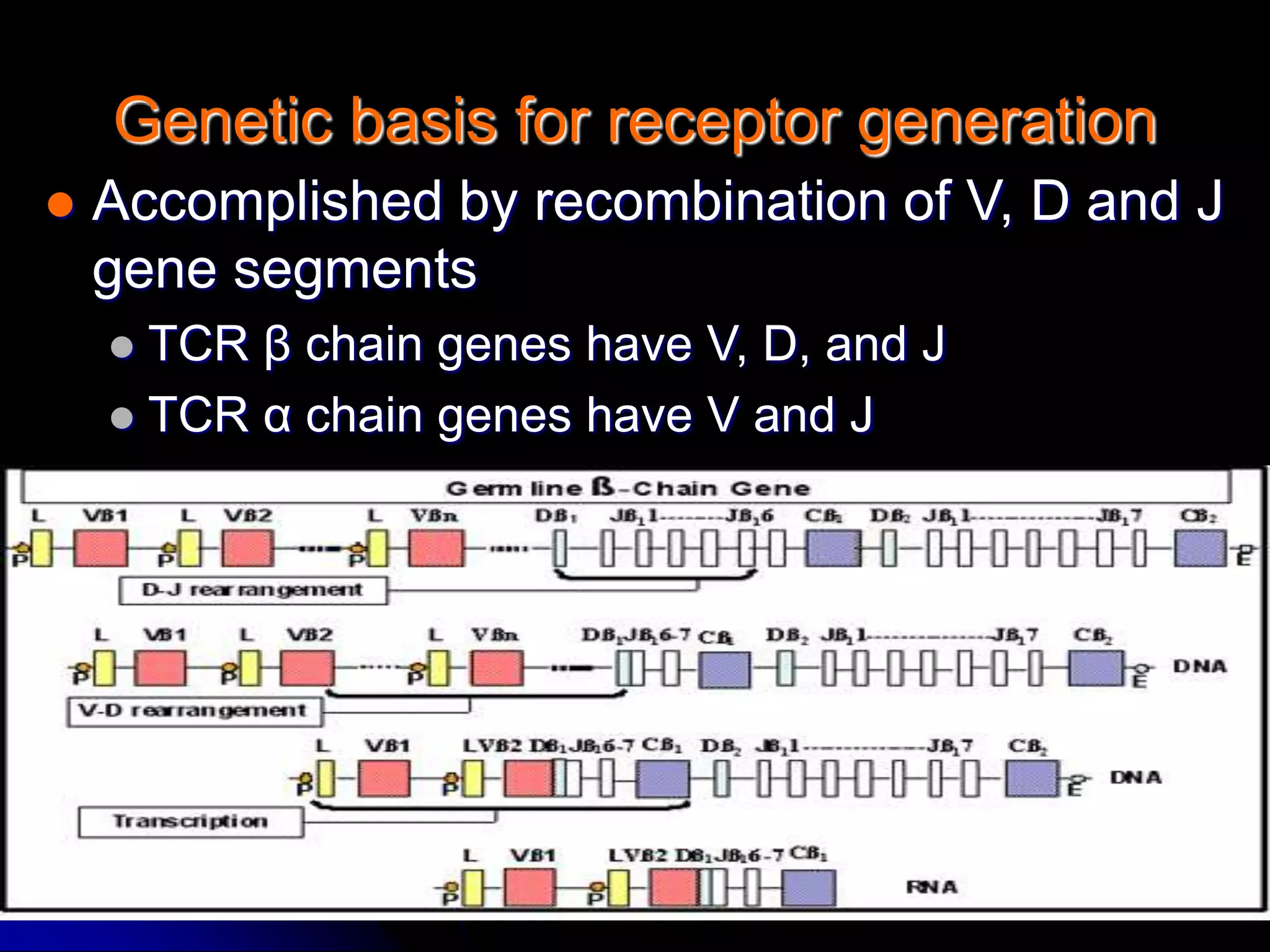
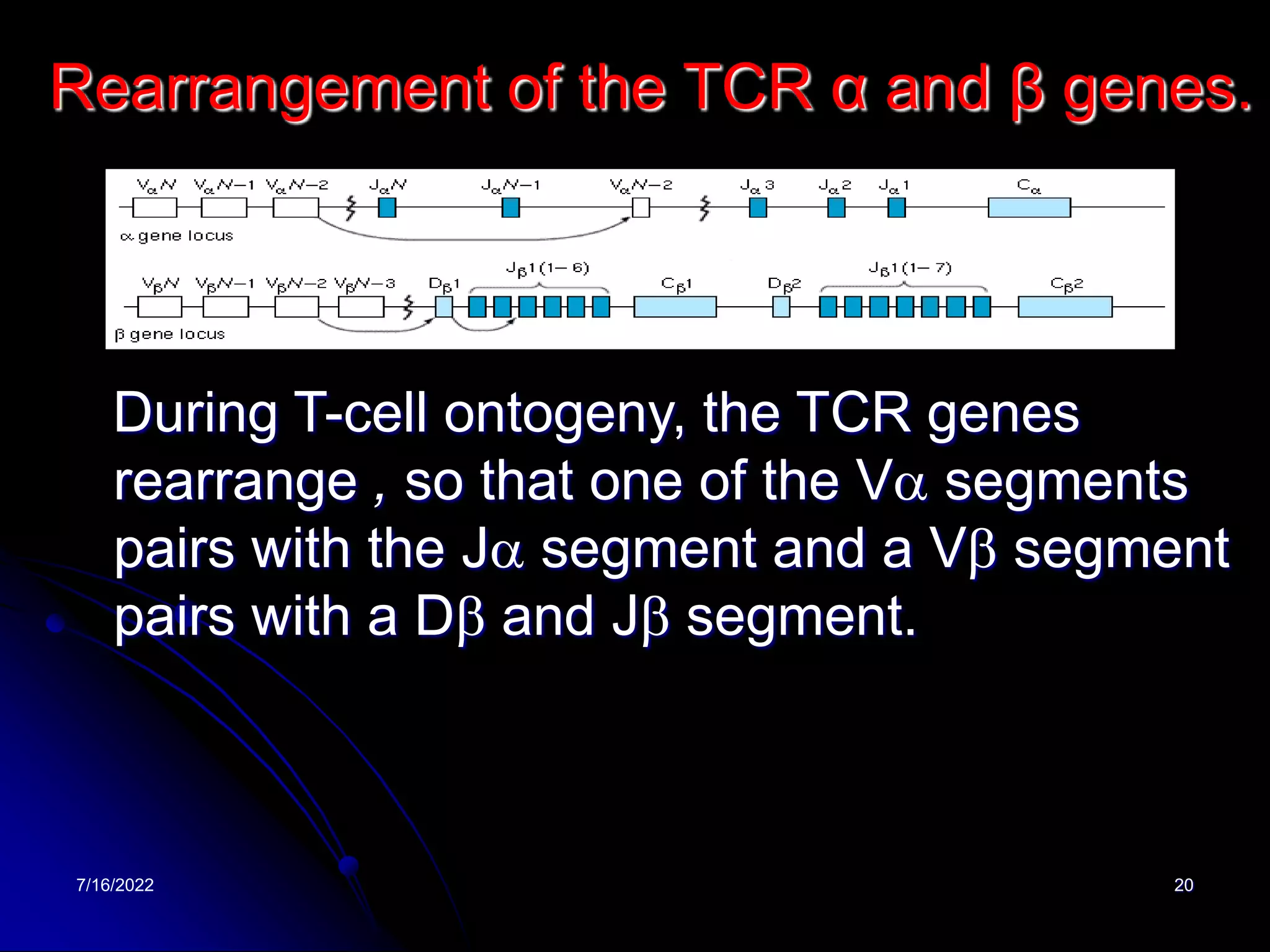
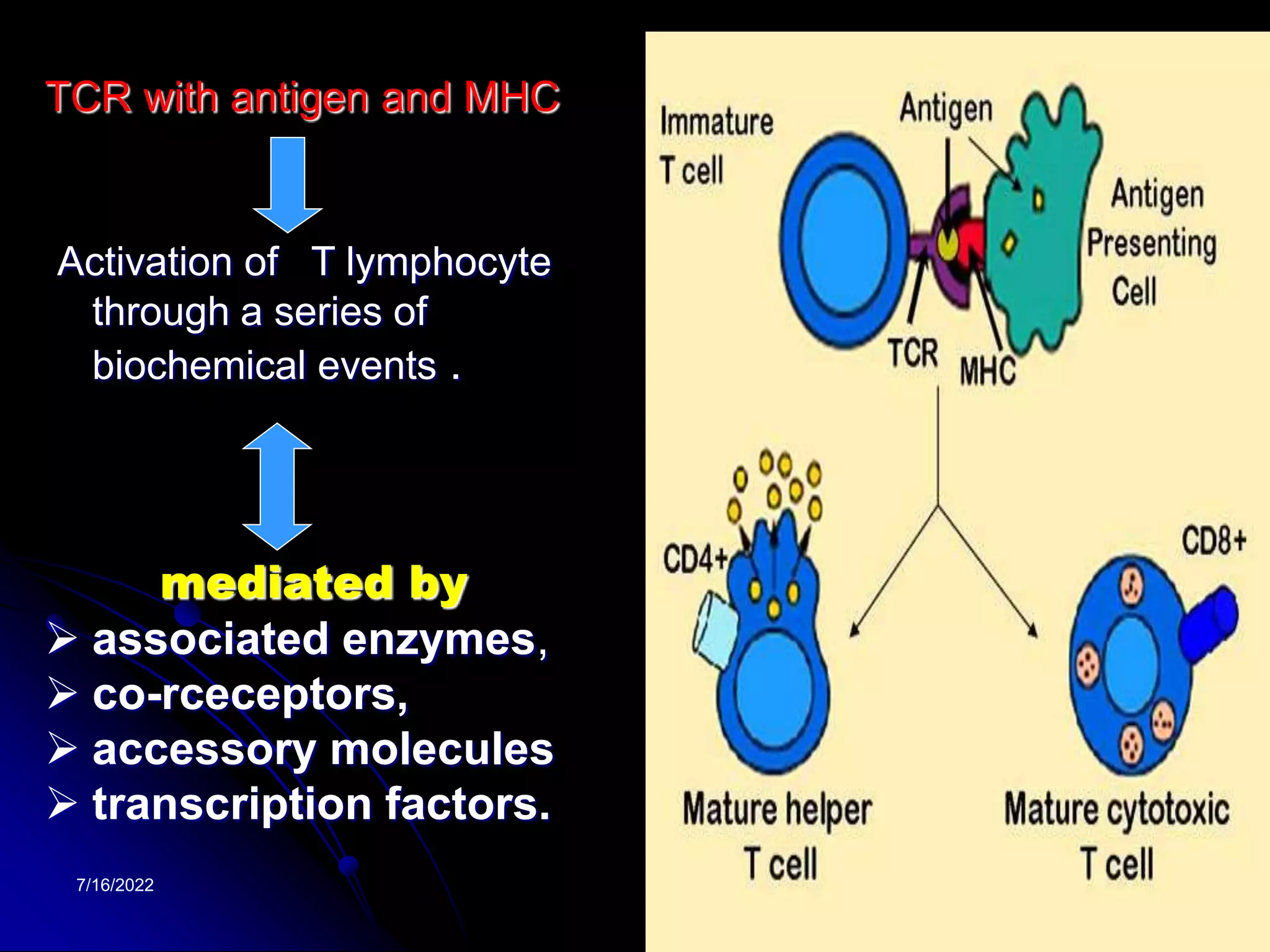
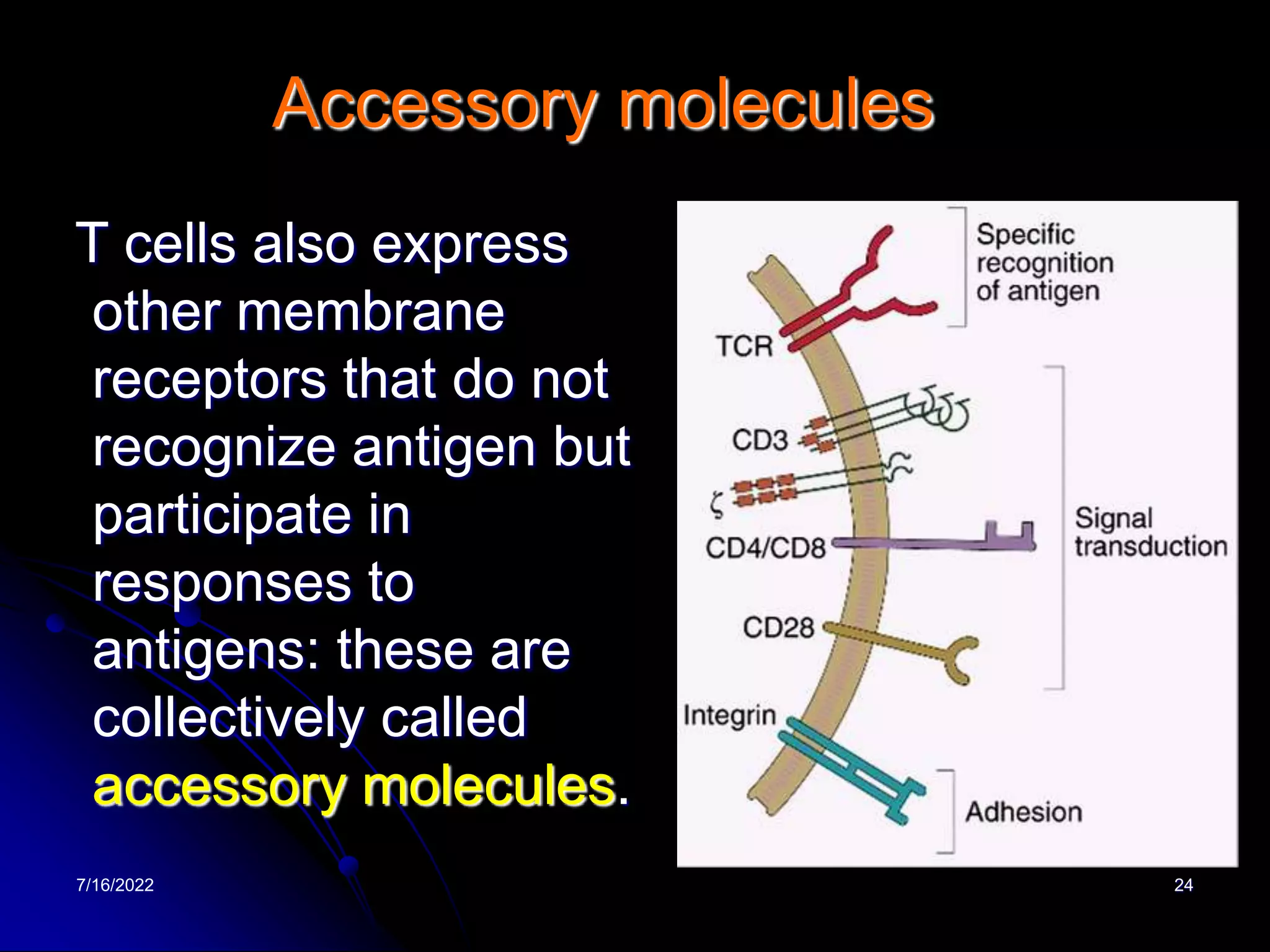
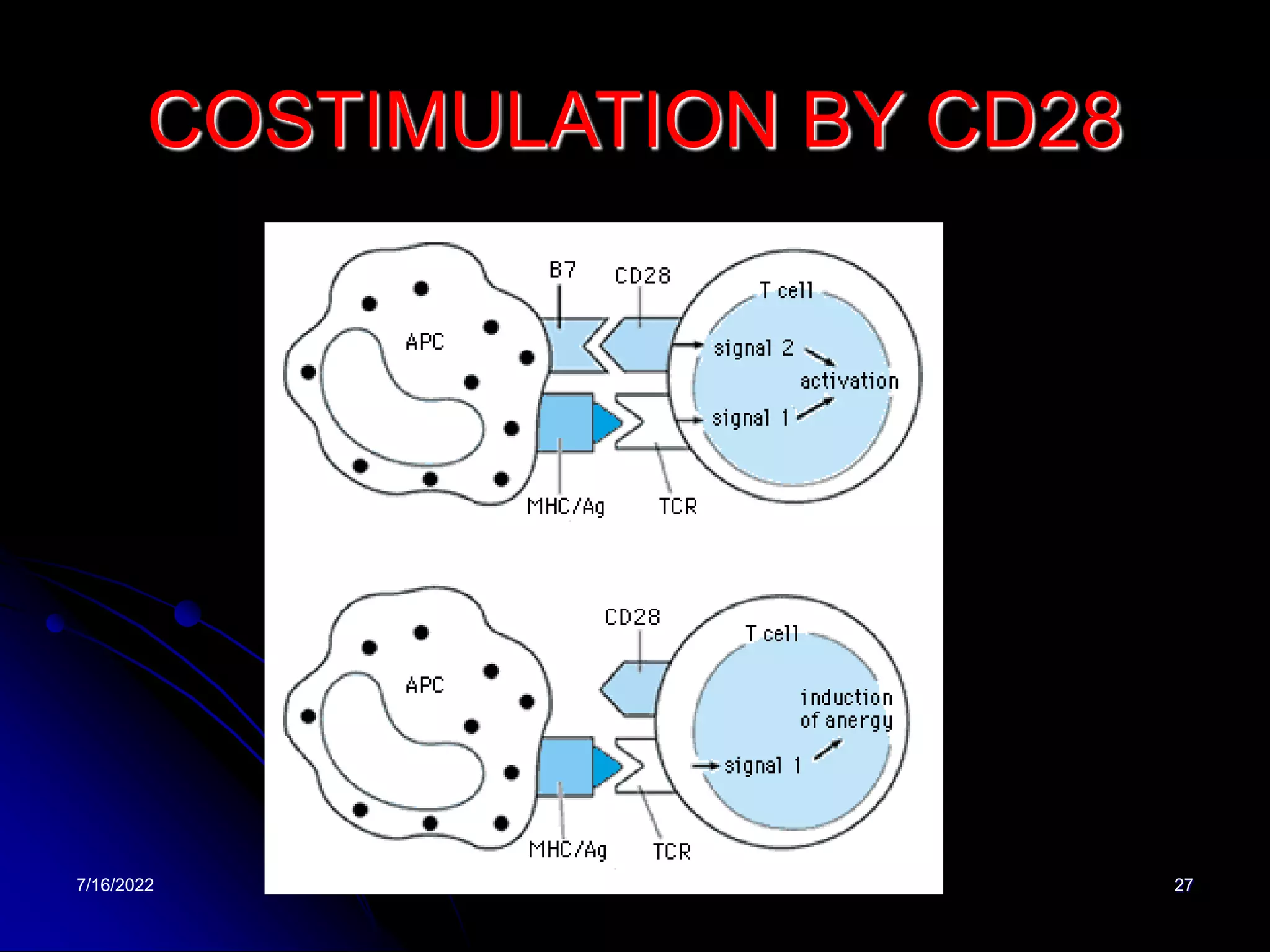
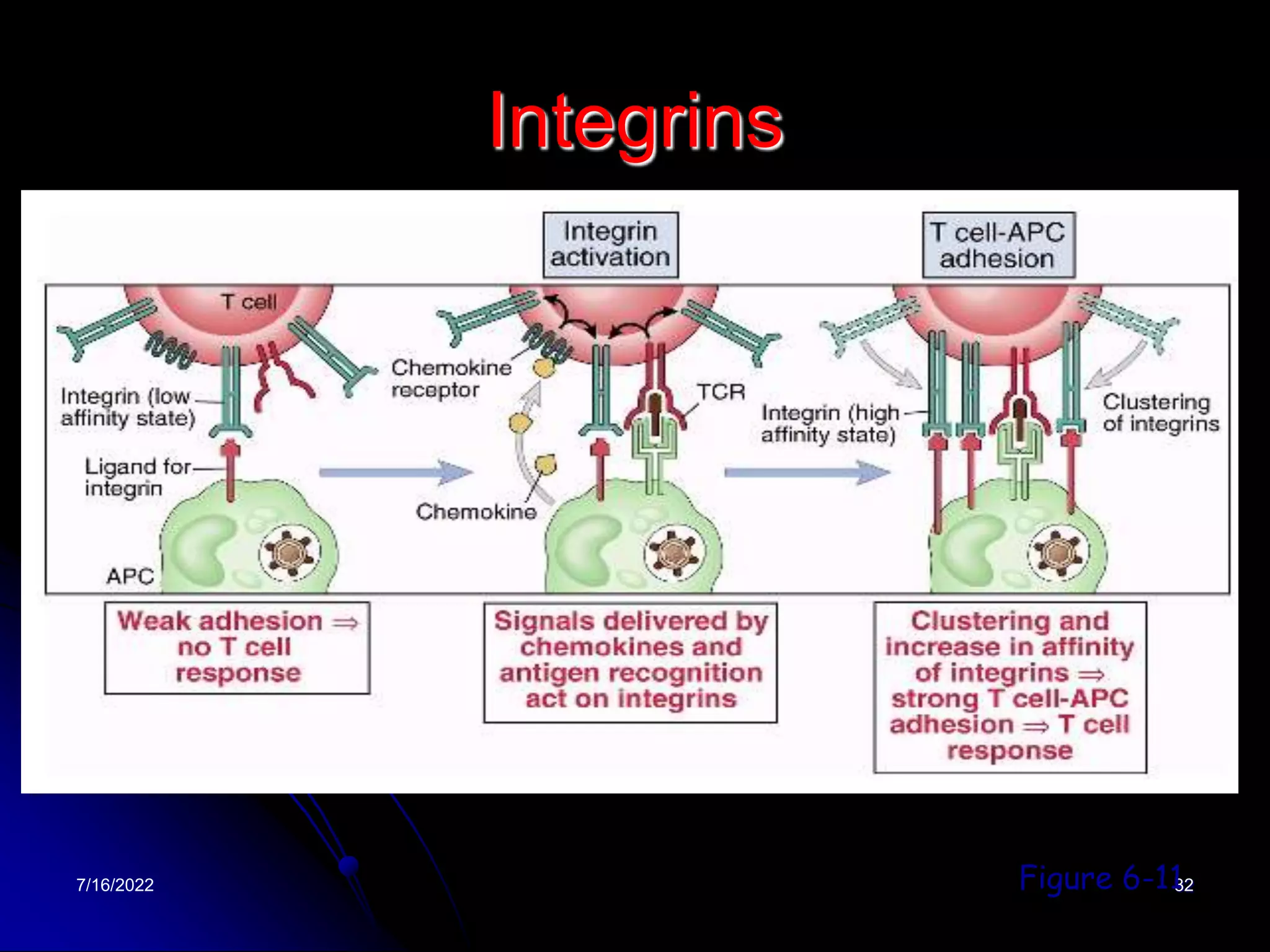
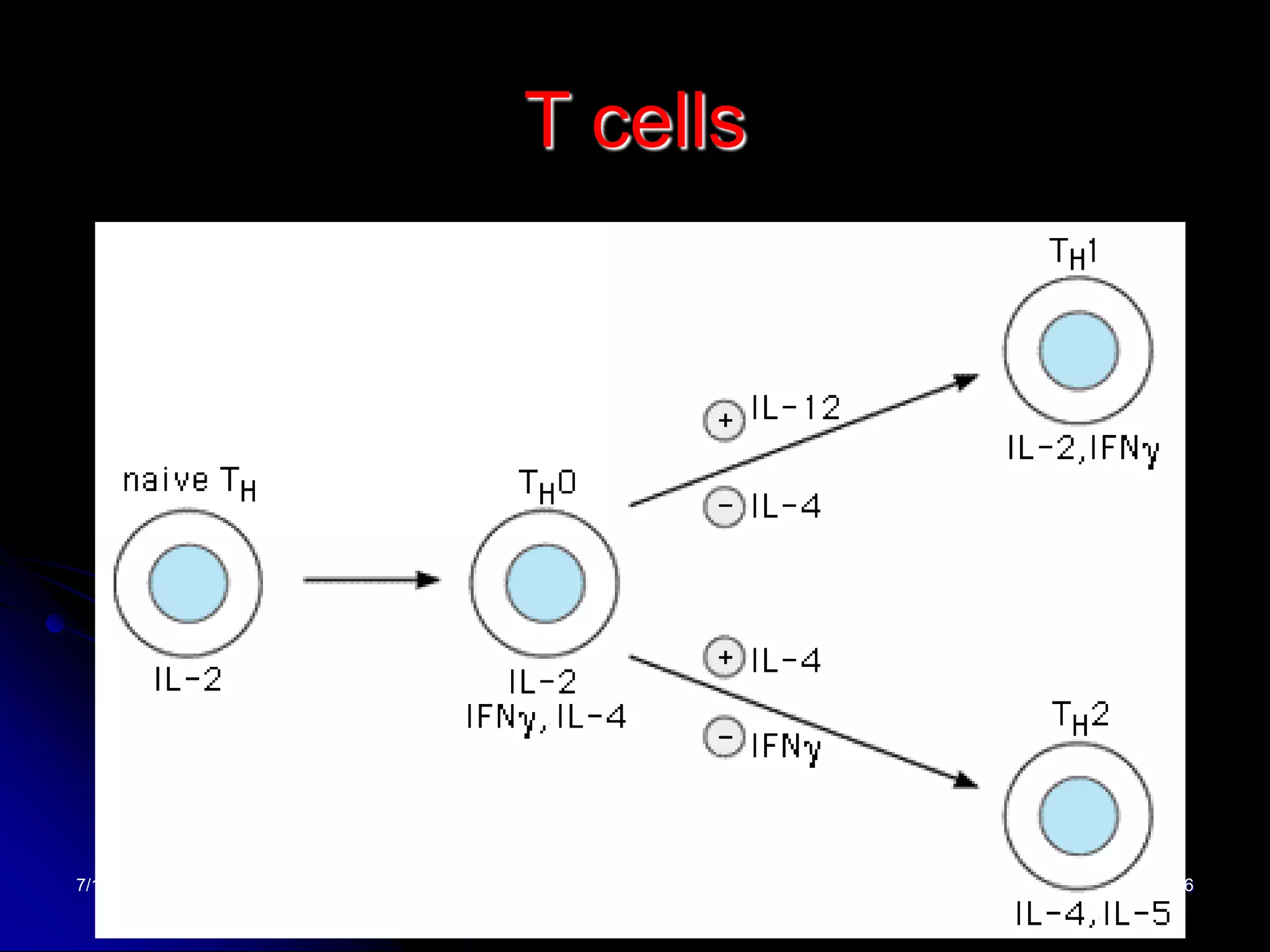
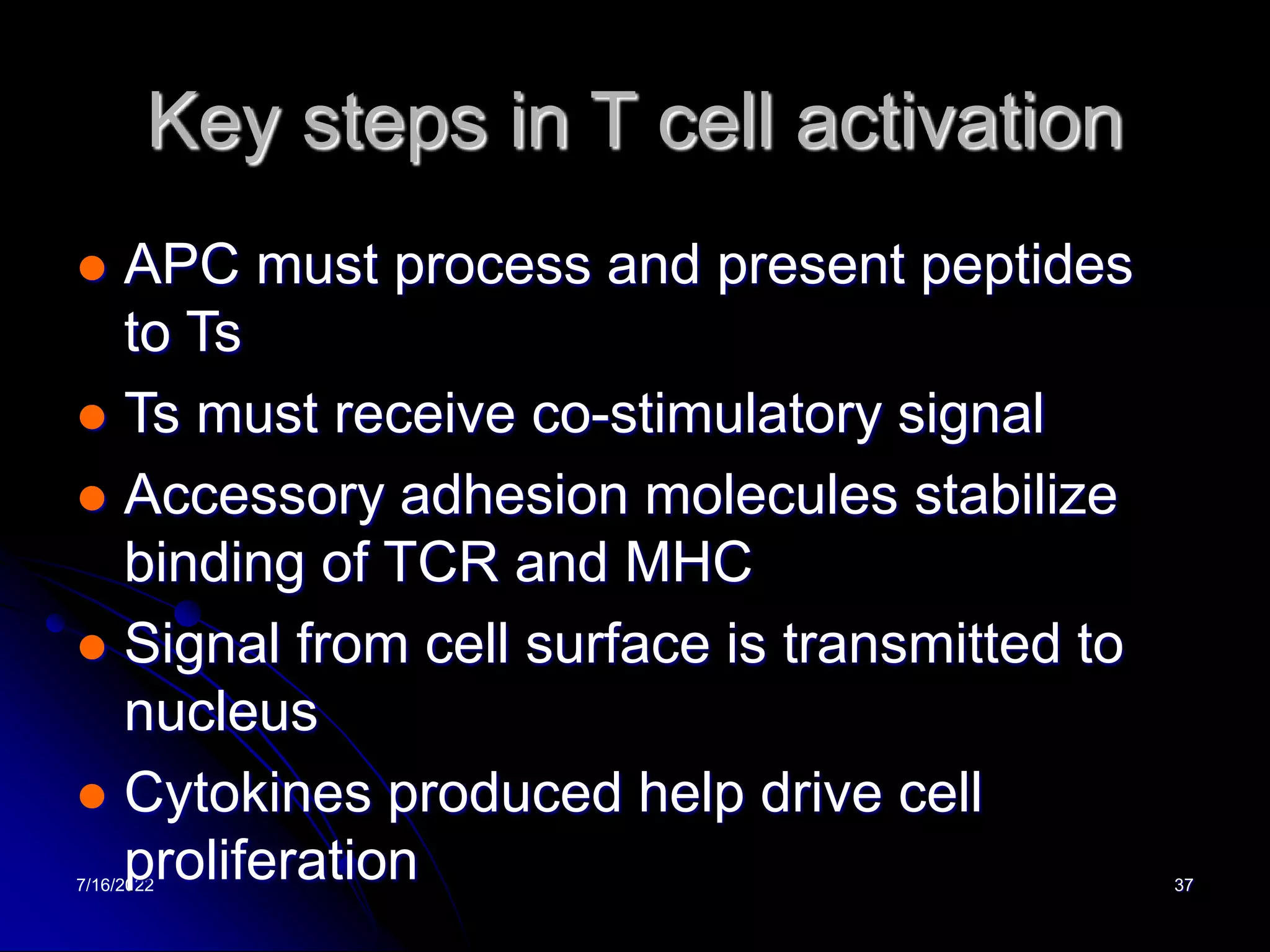
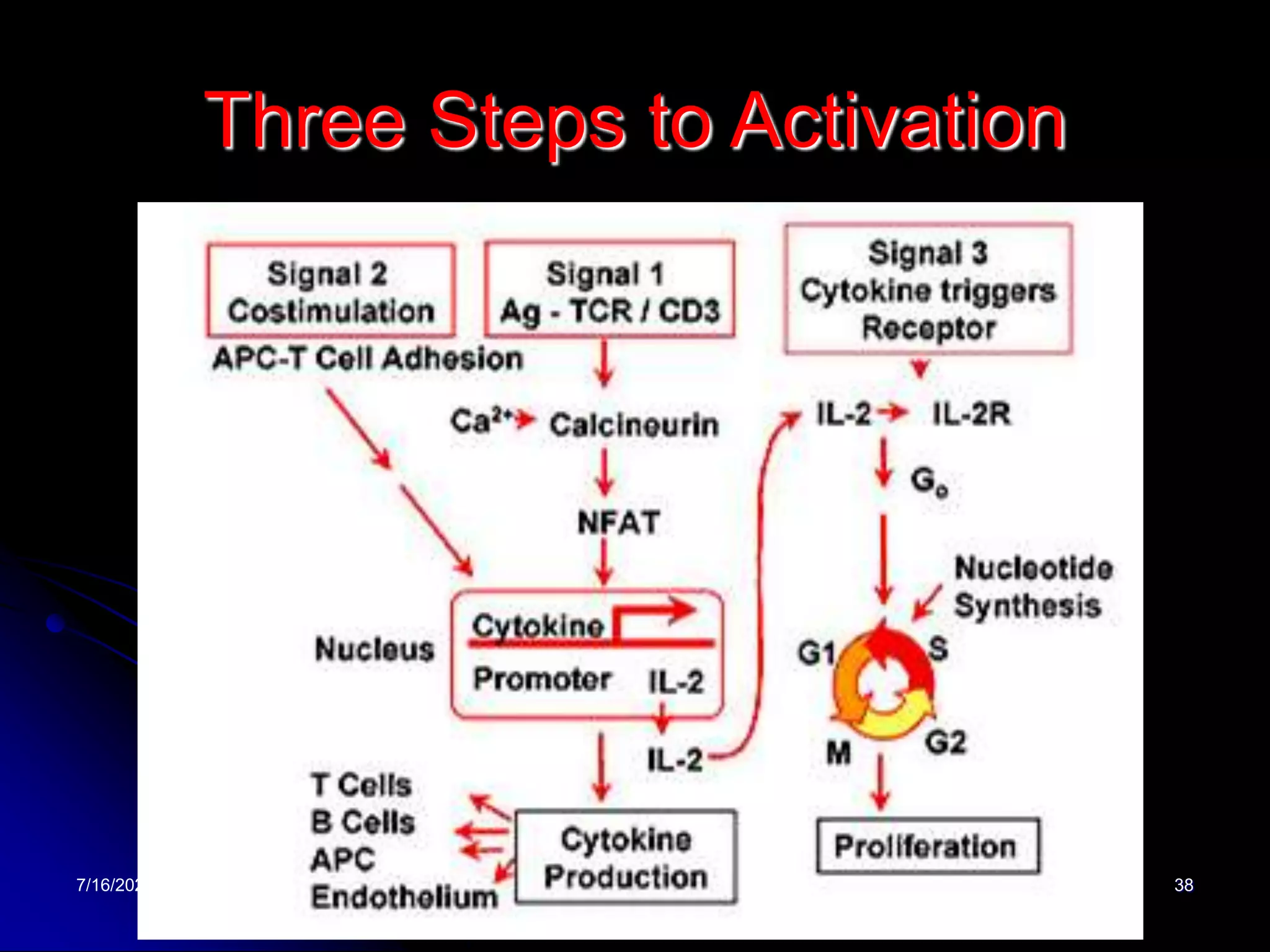
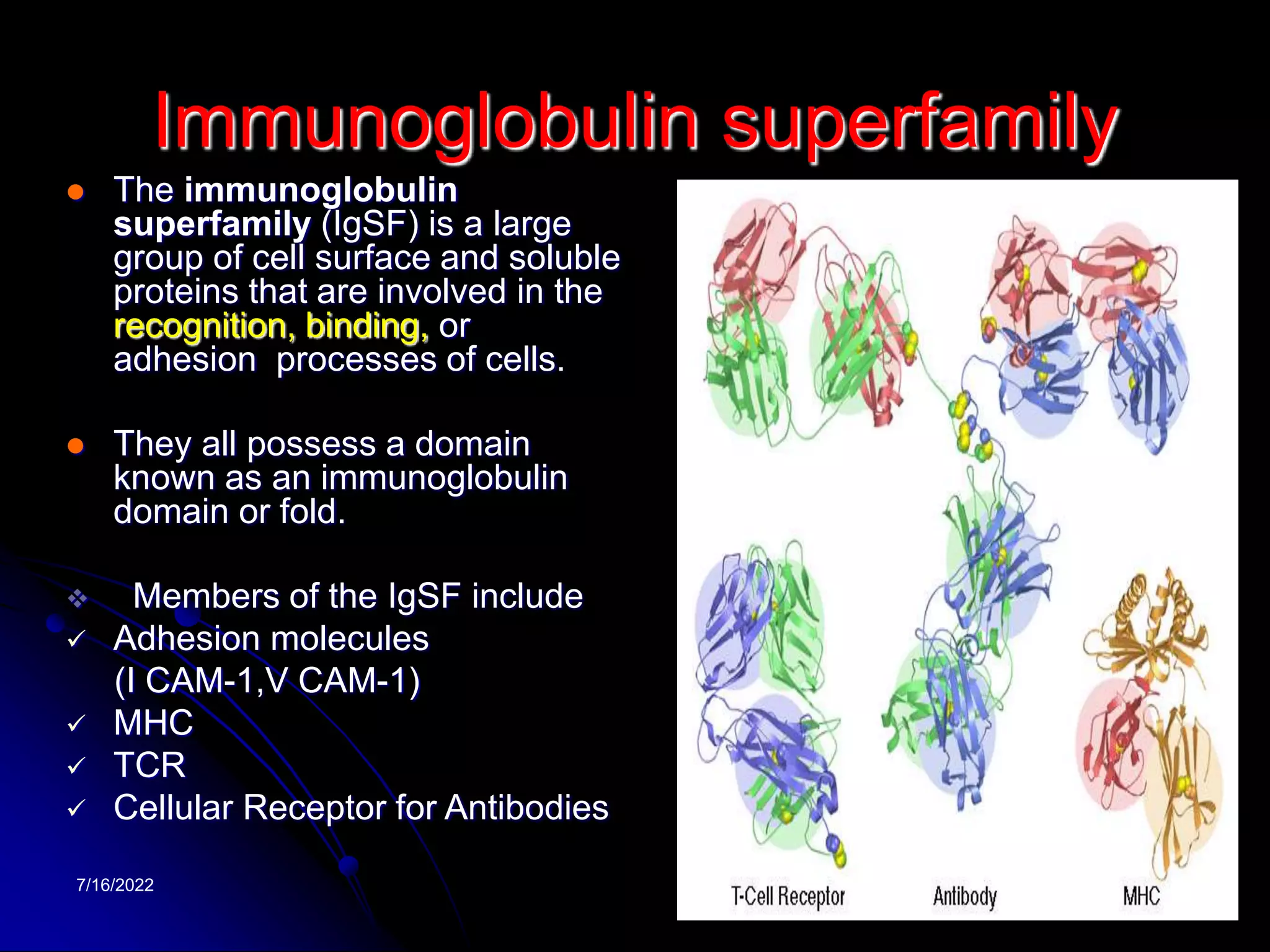
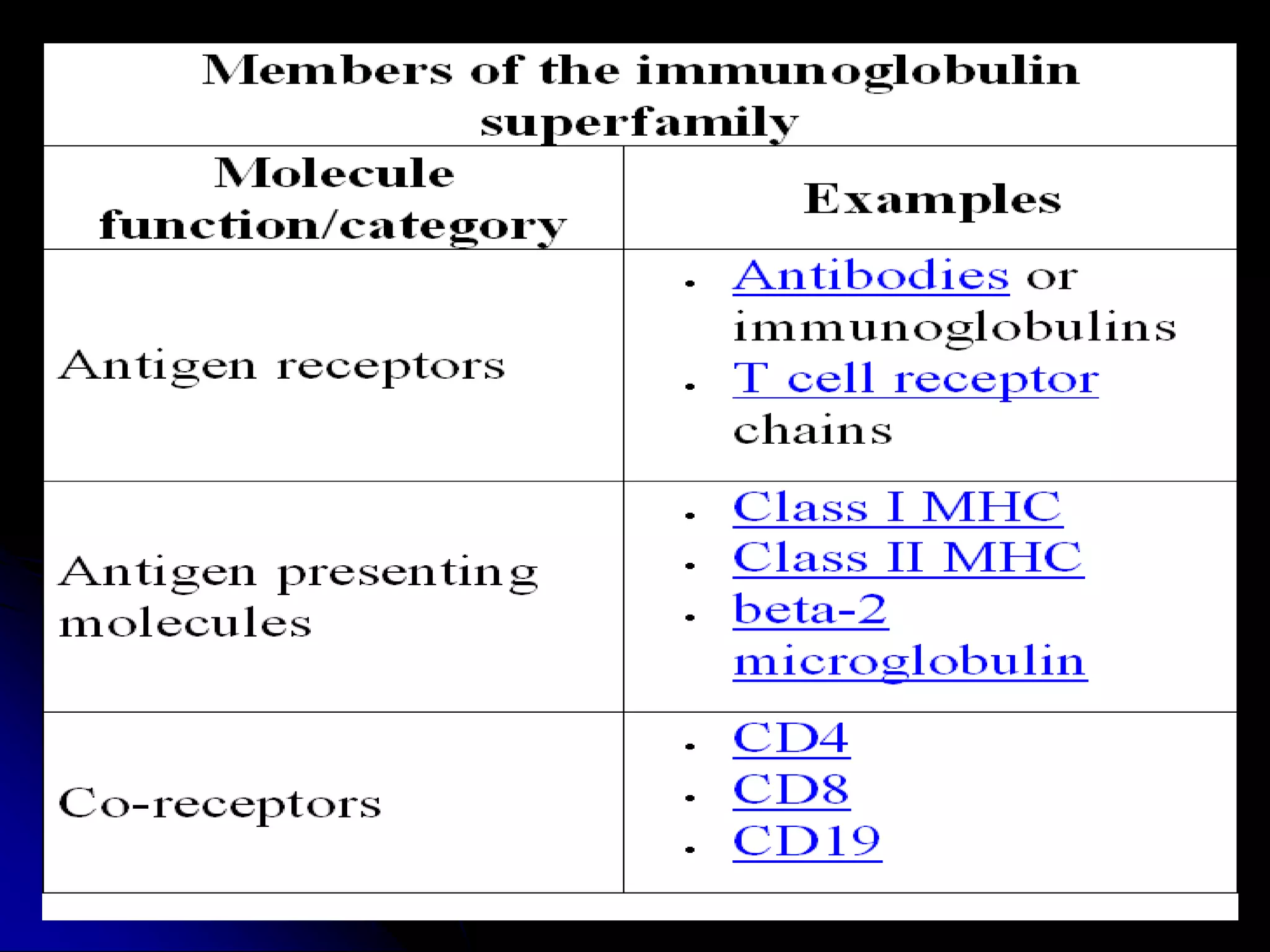
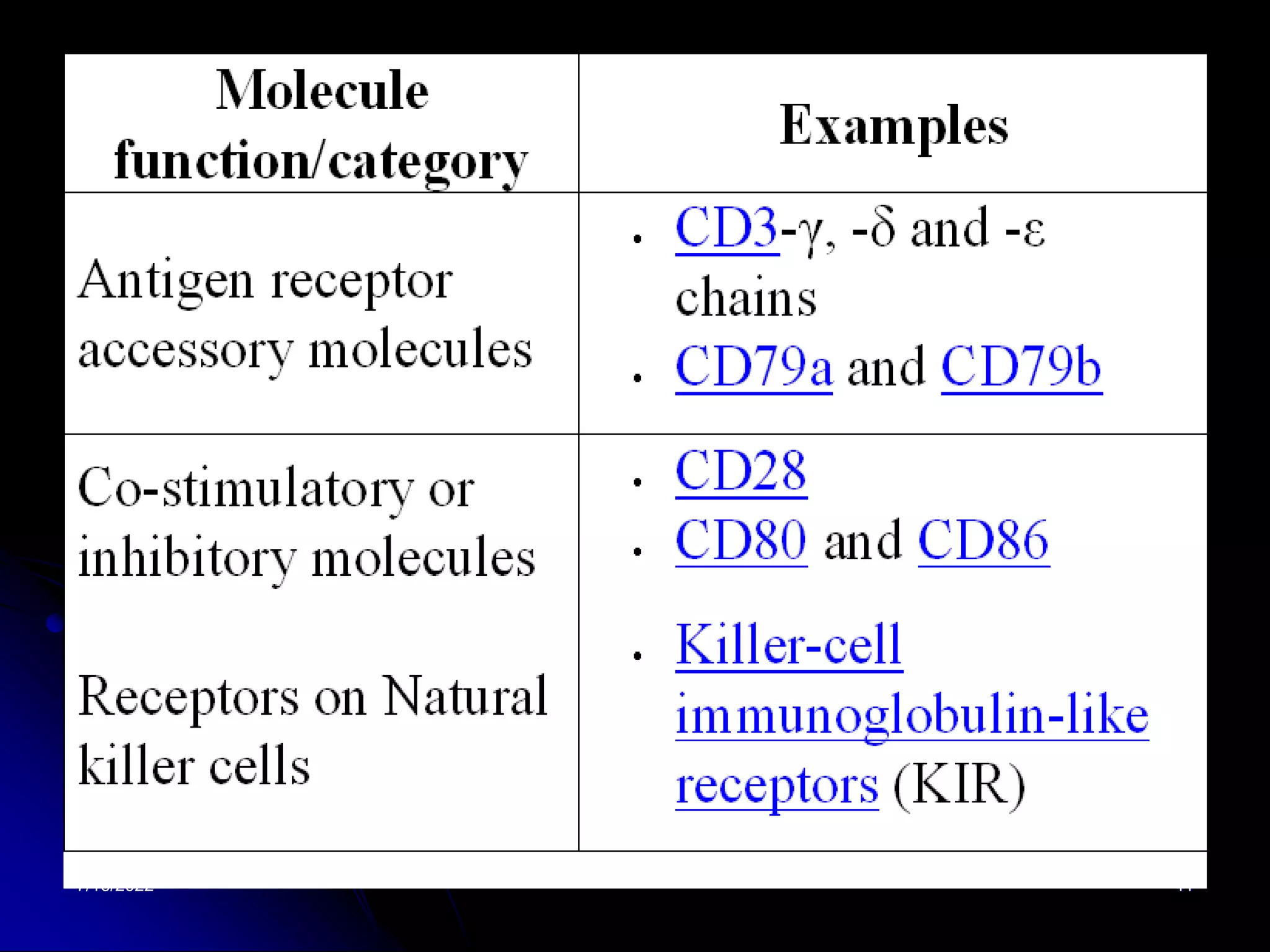
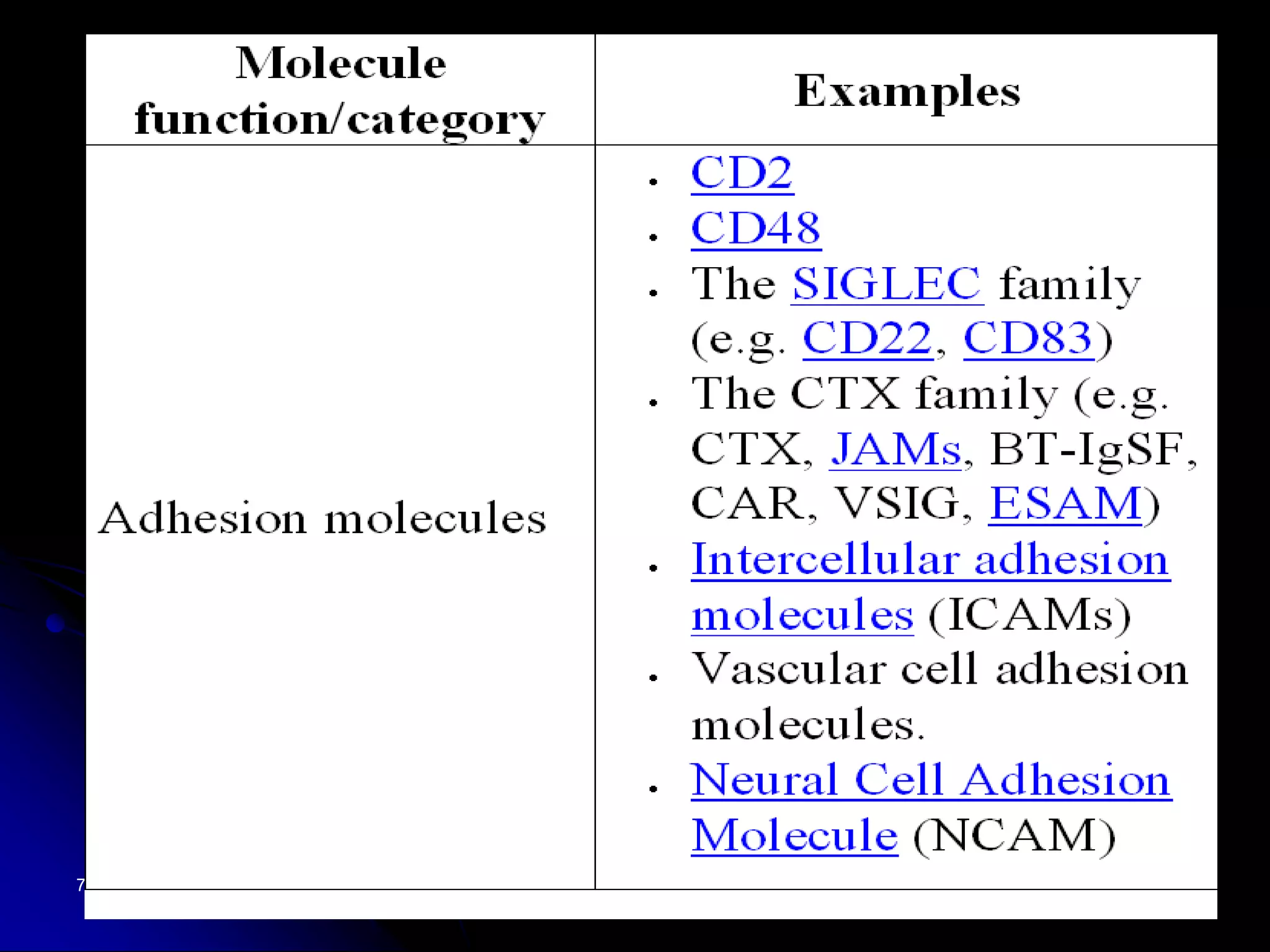
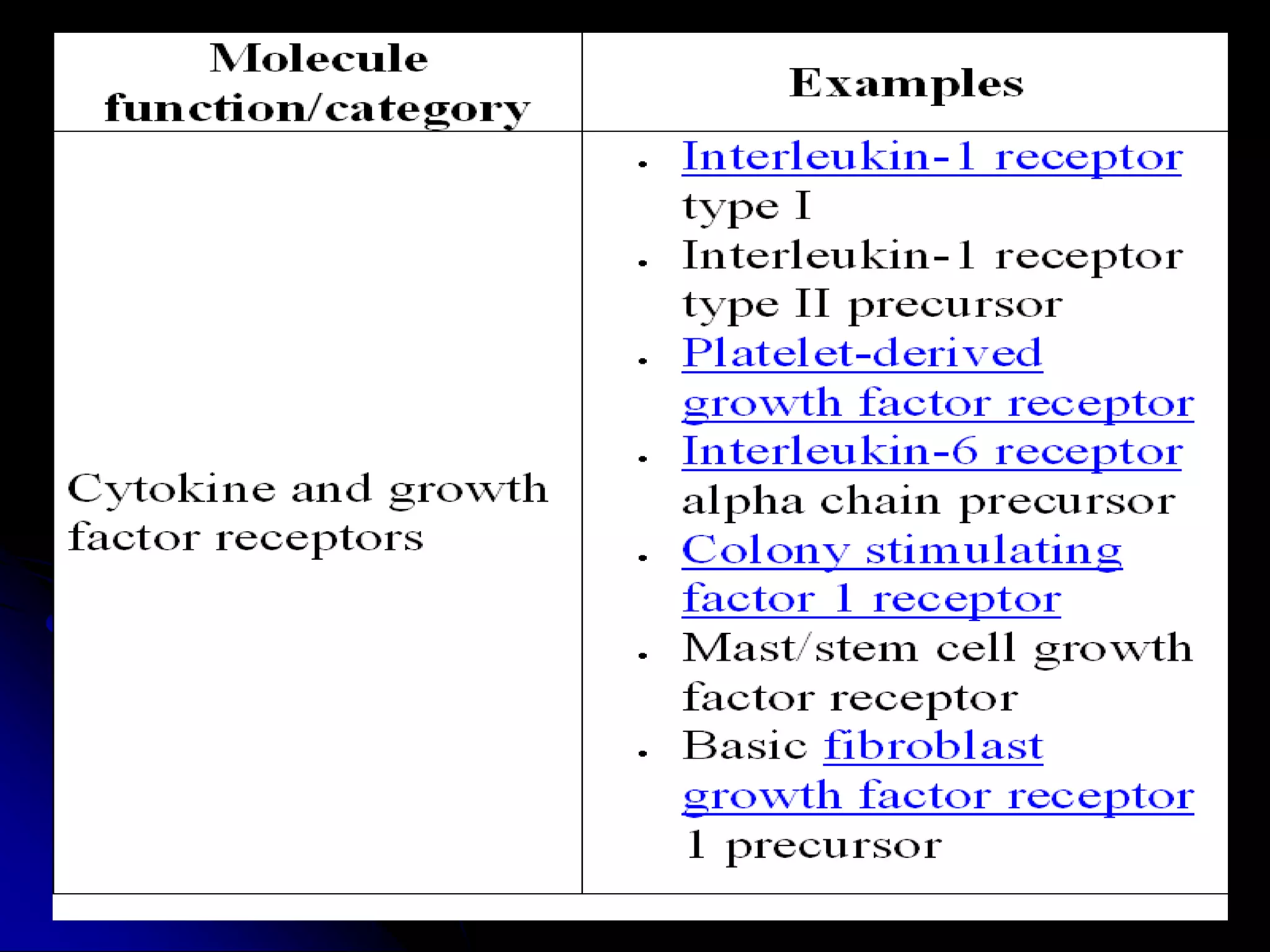
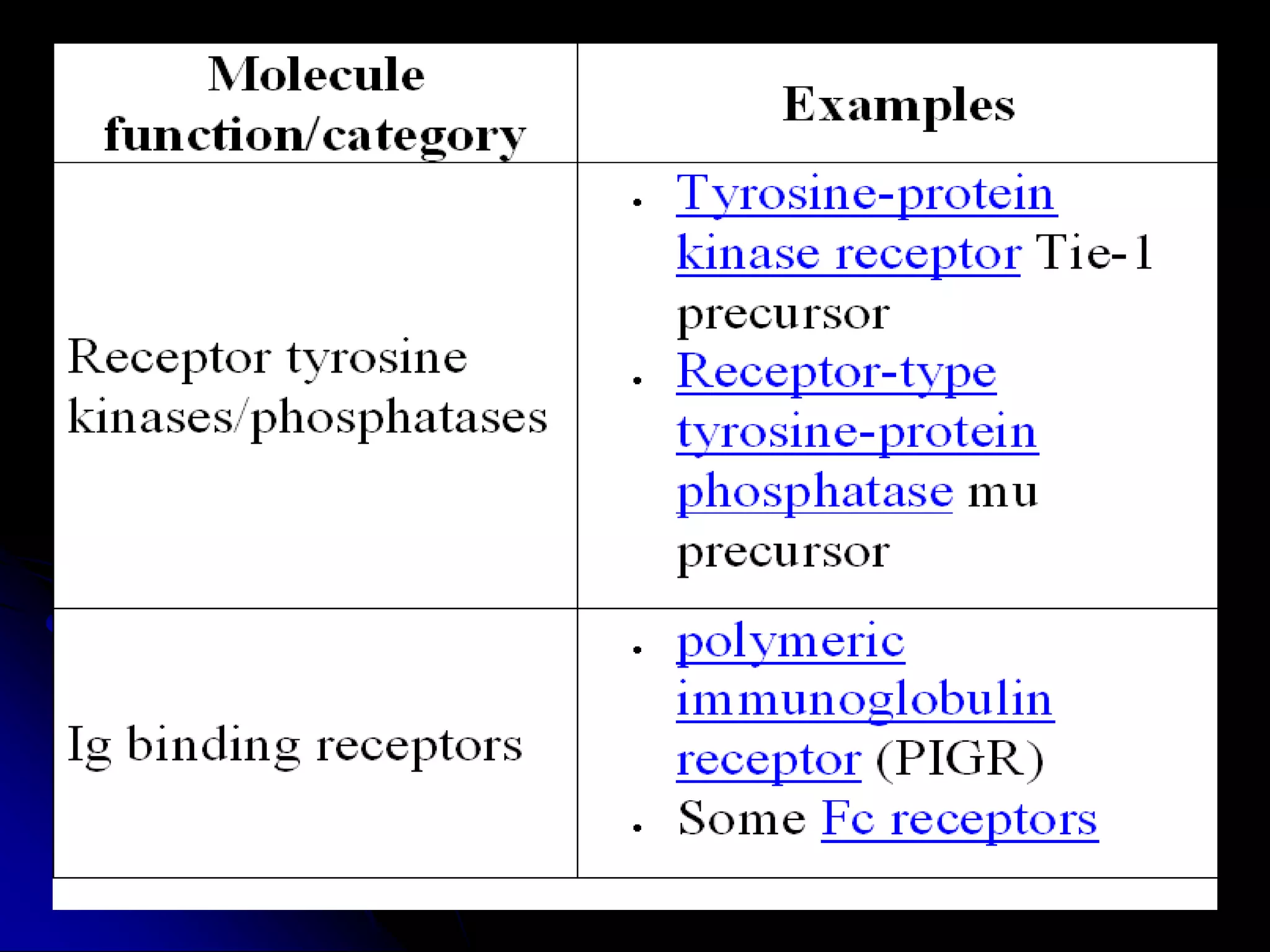
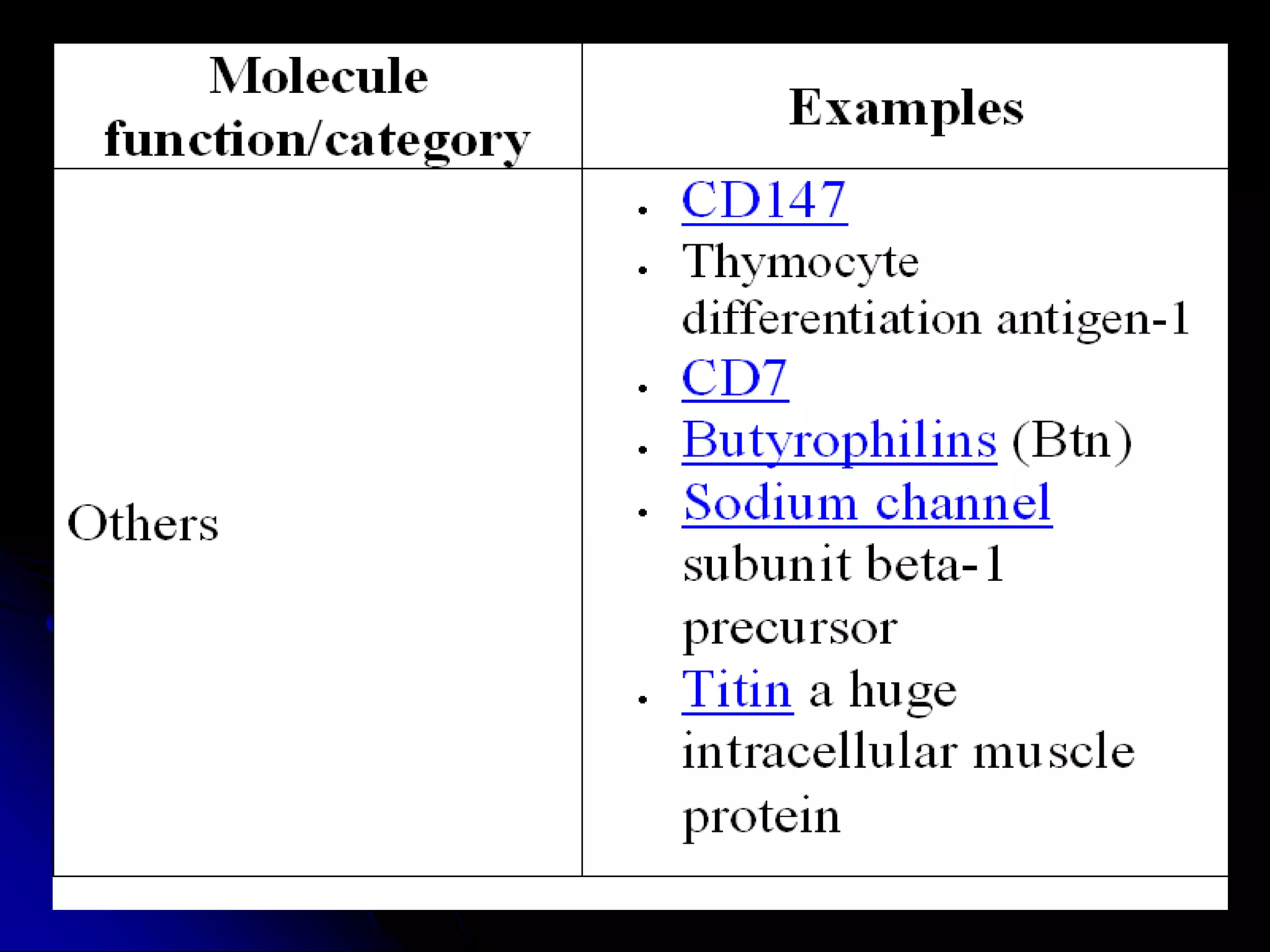
The T cell receptor (TCR) is a heterodimer found on T lymphocytes that recognizes antigens bound to MHC molecules. It consists of either an alpha and beta chain or a gamma and delta chain. The TCR is associated with the CD3 complex consisting of five proteins that are necessary for cell surface expression and signal transduction. TCRs are generated through V(D)J recombination of gene segments and provide diversity to recognize a wide range of antigens. T cell activation requires recognition of antigen-MHC by the TCR along with co-stimulatory signals through molecules like CD28.