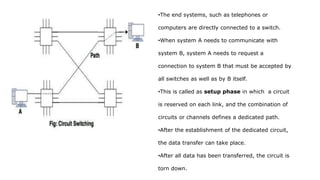
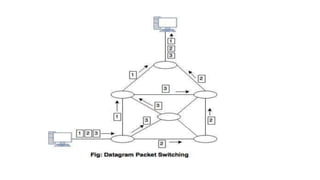
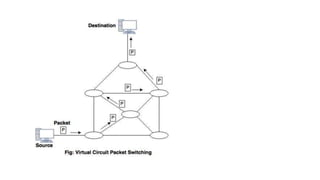
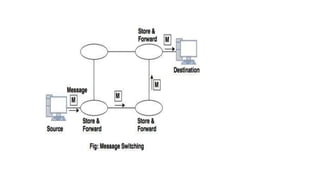
There are three common switching techniques: circuit switching, packet switching, and message switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated communication path between nodes before data transfer begins. Packet switching divides messages into packets that are routed independently through the network on a first-come, first-served basis. Message switching routes entire messages independently but can cause delays as messages are stored until the next hop has available resources.