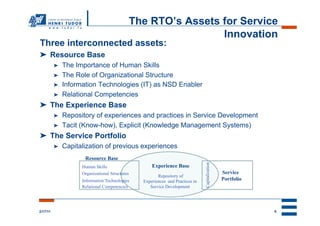
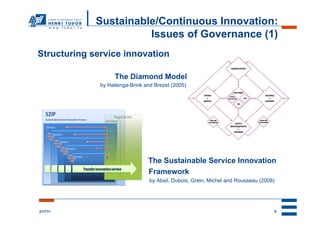
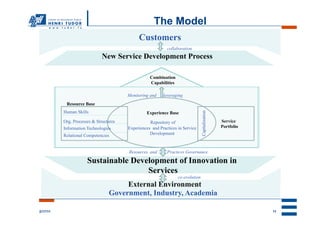
The document proposes a conceptual model for sustainable service innovation at research and technology organizations (RTOs). The model depicts the dual perspective of sustainable development in service innovation, accounting for both sustainable/continuous innovation through effective governance of resources and capabilities, as well as sustainable/responsible innovation regarding environmental, economic and social responsibility. The model illustrates how RTOs can leverage their resource base, experience base, and service portfolio through the new service development process and collaboration with customers and external stakeholders to achieve sustainable innovation.