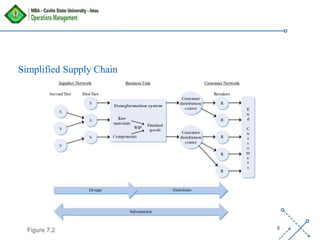
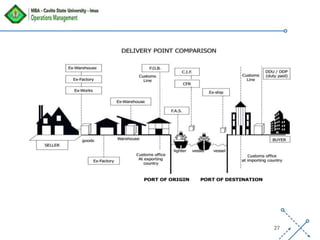
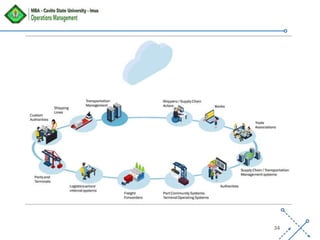
The document discusses supply chain management, emphasizing the integration of suppliers, distributors, and customers to optimize processes from procurement to delivery. Key areas covered include supplier management, procurement versus purchasing, logistics, and the importance of strong relationships with suppliers in a competitive global market. The document outlines effective strategies for managing costs and improving supplier relationships to enhance overall supply chain efficiency.