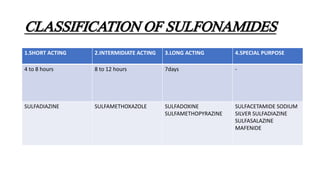
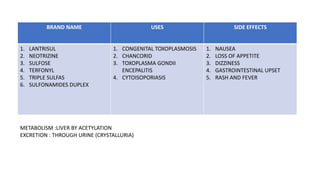
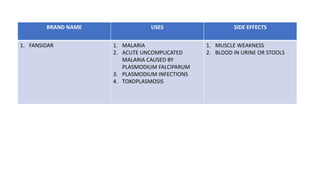
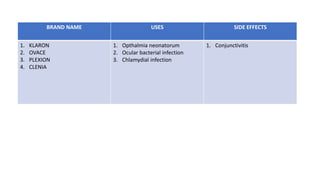
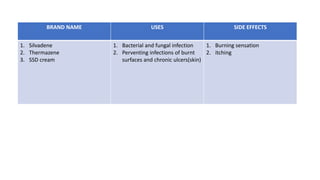
Sulfonamides can be classified as short acting (4-8 hours), intermediate acting (8-12 hours), or long acting (7 days). Common short acting sulfonamides include sulfadiazine and sulfamethopryazine. Sulfamethoxazole is an intermediate acting sulfonamide often used in combination with trimethoprim. Long acting sulfonamides include sulfadoxine and sulfamethopryazine which are used to treat malaria. Special purpose sulfonamides include sulfacetamide sodium used topically for eye infections, and silver sulfadiazine used to prevent infections of burned skin surfaces.