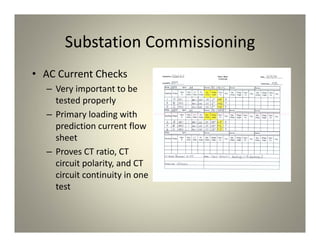
This document discusses substation commissioning, which involves proving the proper operation of newly installed, replaced, modified, or repaired substation equipment before placing it into service. It outlines the commissioning process, including safety procedures, levels of commissioning based on complexity, creating checklists, and testing components like circuit breakers, transformers, relays, and communication systems through steps like DC checks, AC checks, trip checks, and point-to-point testing to ensure all new devices operate as intended before energization. Thorough planning and documentation are emphasized to ensure a successful commissioning.