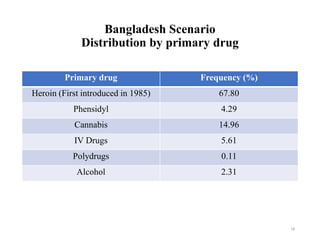
The document discusses substance abuse, detailing definitions, classifications, warning signs, and the impact of drug addiction on health, family, and society, particularly in the global and Bangladeshi context. It highlights the risk factors for drug dependence, the demographics of substance users, and the management and prevention strategies, including treatment facilities available in Bangladesh. Overall, the document emphasizes the urgent need for awareness, effective public policy, and rehabilitation to combat substance abuse.