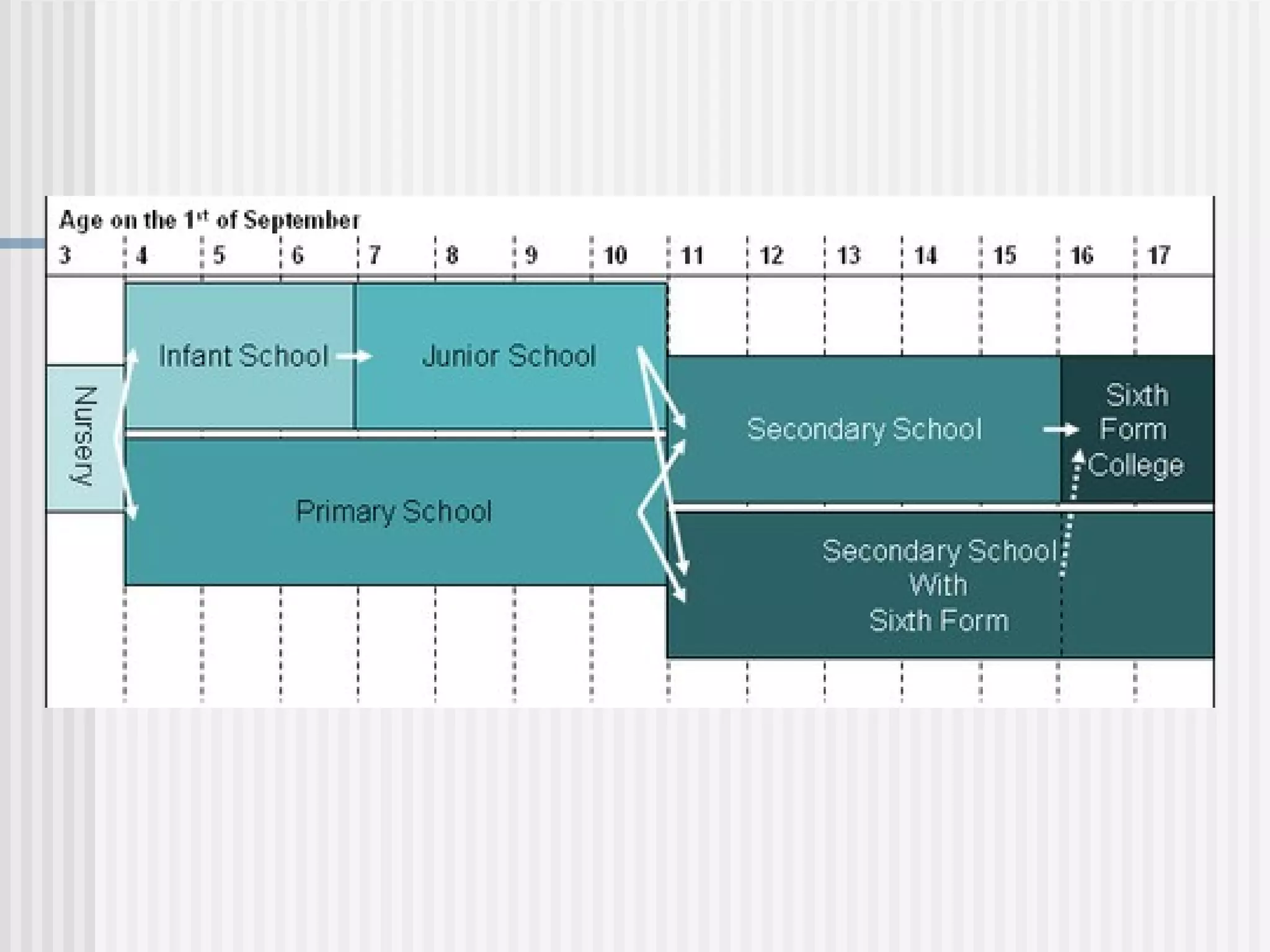
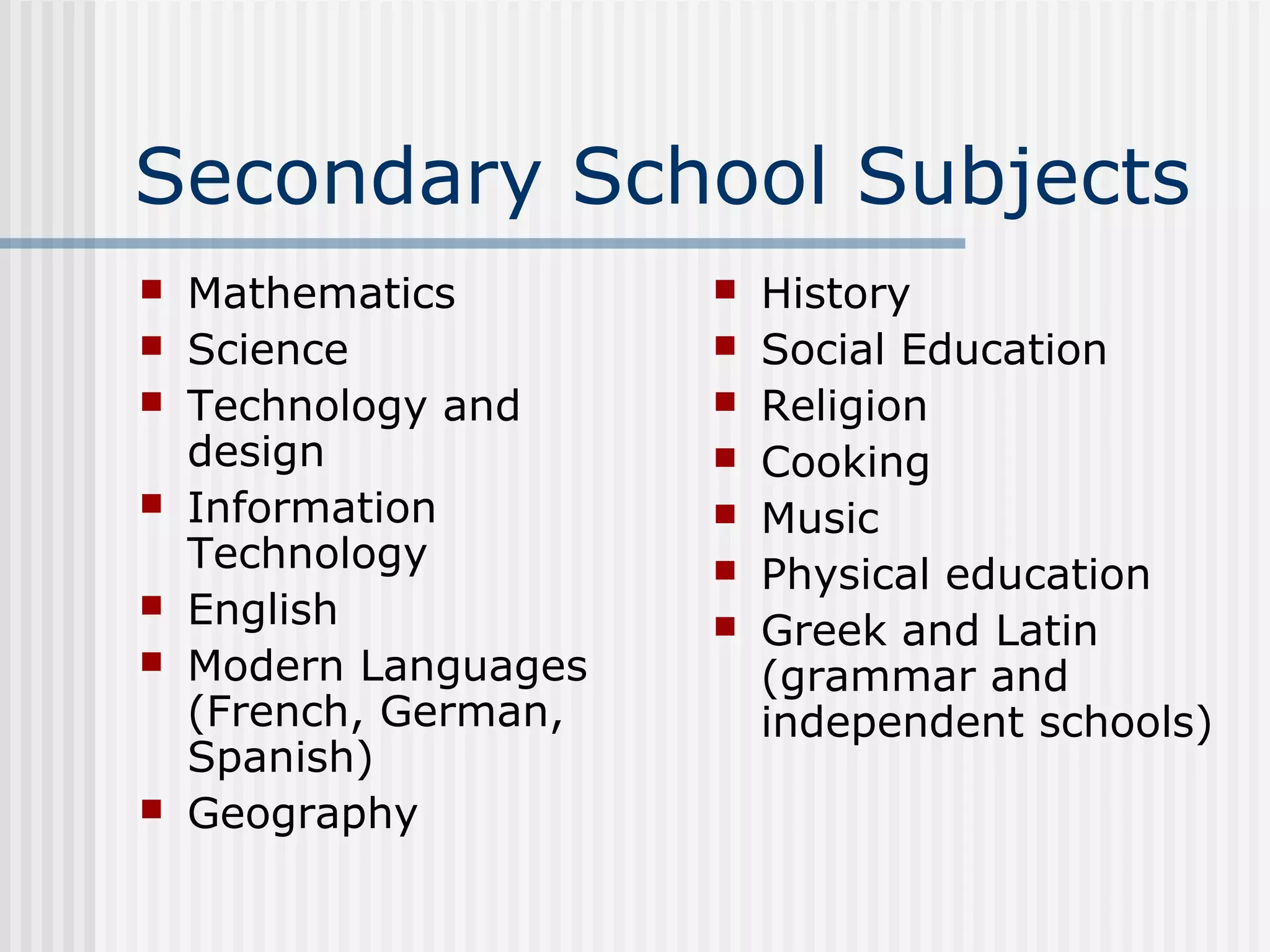
The education system in Britain has three main levels: school education from ages 5-16, further education from 16-18 to prepare for university or a vocation, and higher education offered at over 200 universities. School education follows the National Curriculum. Further education involves exams like A-Levels or Scottish Highers. University degrees include Bachelor's (3 years), Master's (1-2 years), and Doctorates (3-5 years). In 2000, more student visas were awarded to Chinese citizens than any other country.