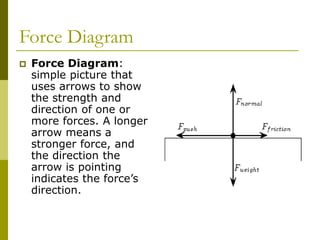
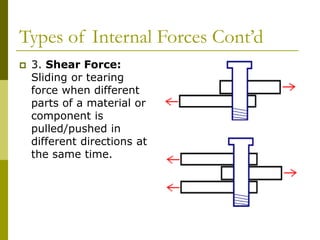
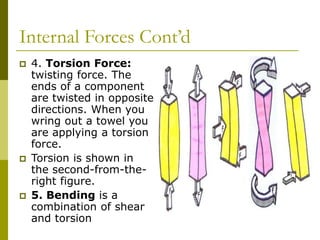
The document explains key concepts of mass and weight, defining mass as the amount of matter in an object and weight as the force of gravity acting on it. It outlines how to calculate weight using the formula fg = mass * g, and discusses the types of forces acting on structures, including external and internal forces, as well as various internal force types such as tension, compression, shear, torsion, and bending. Additionally, it notes the strengths of different materials when faced with these forces during structure design.