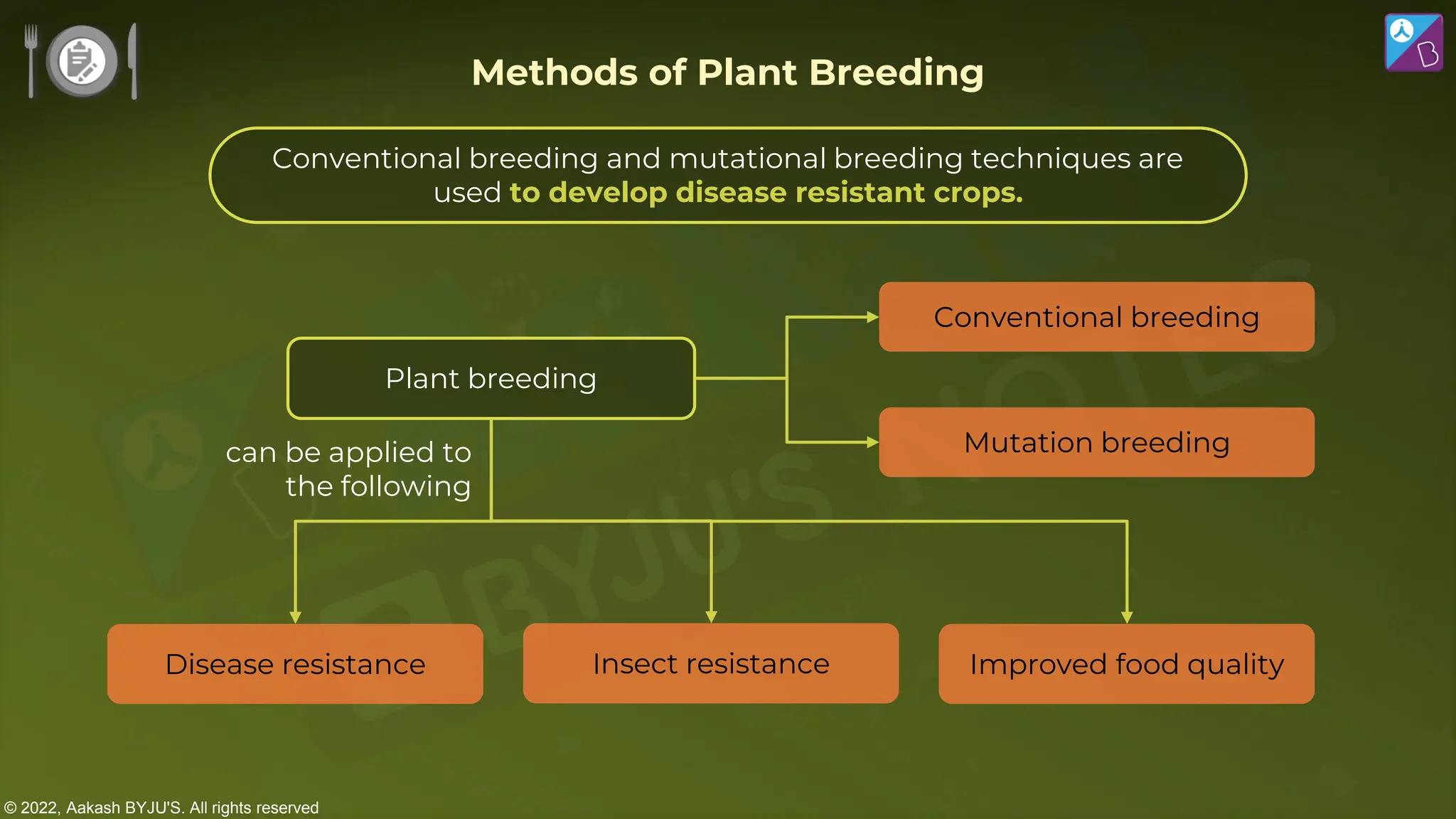
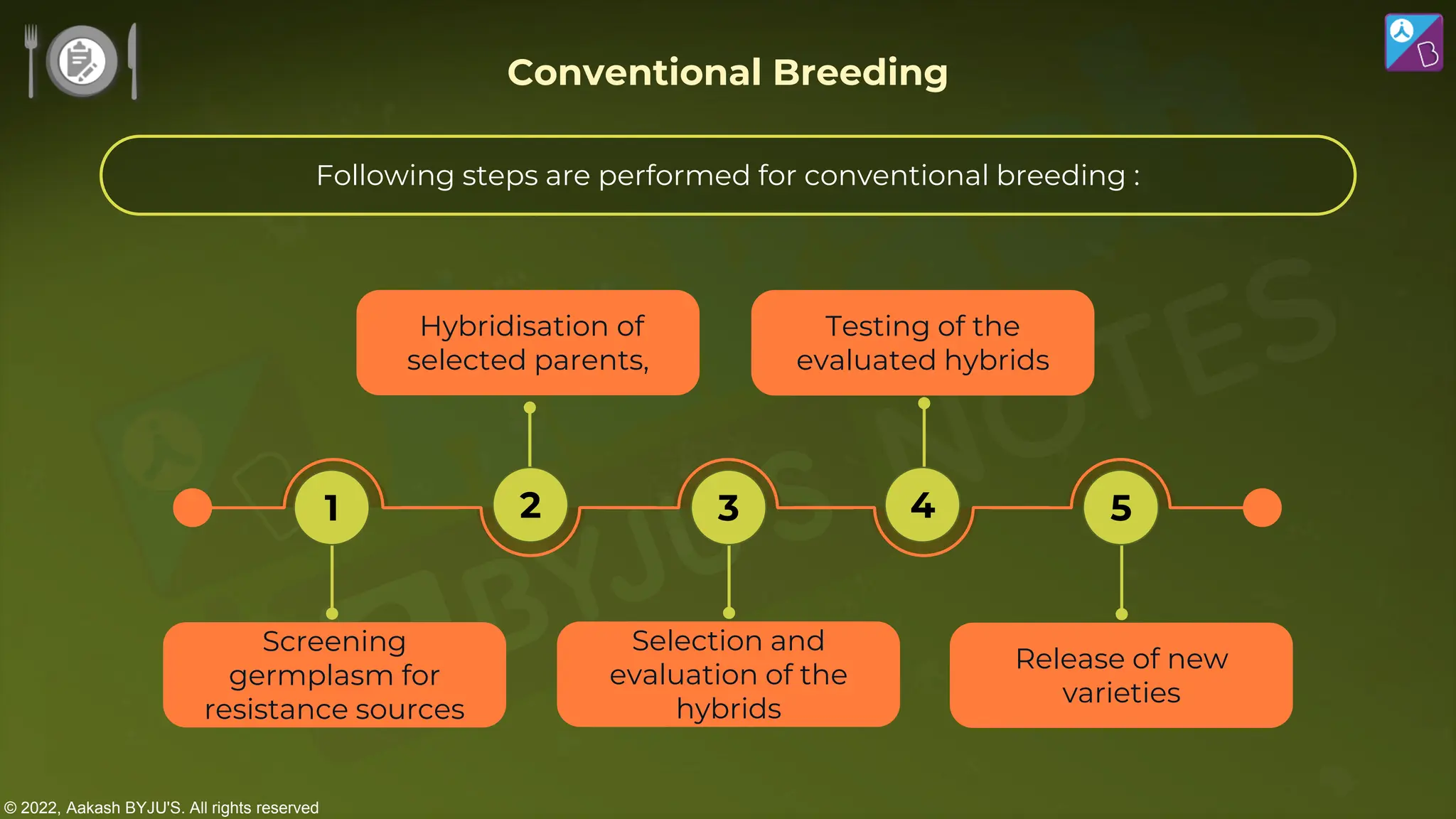
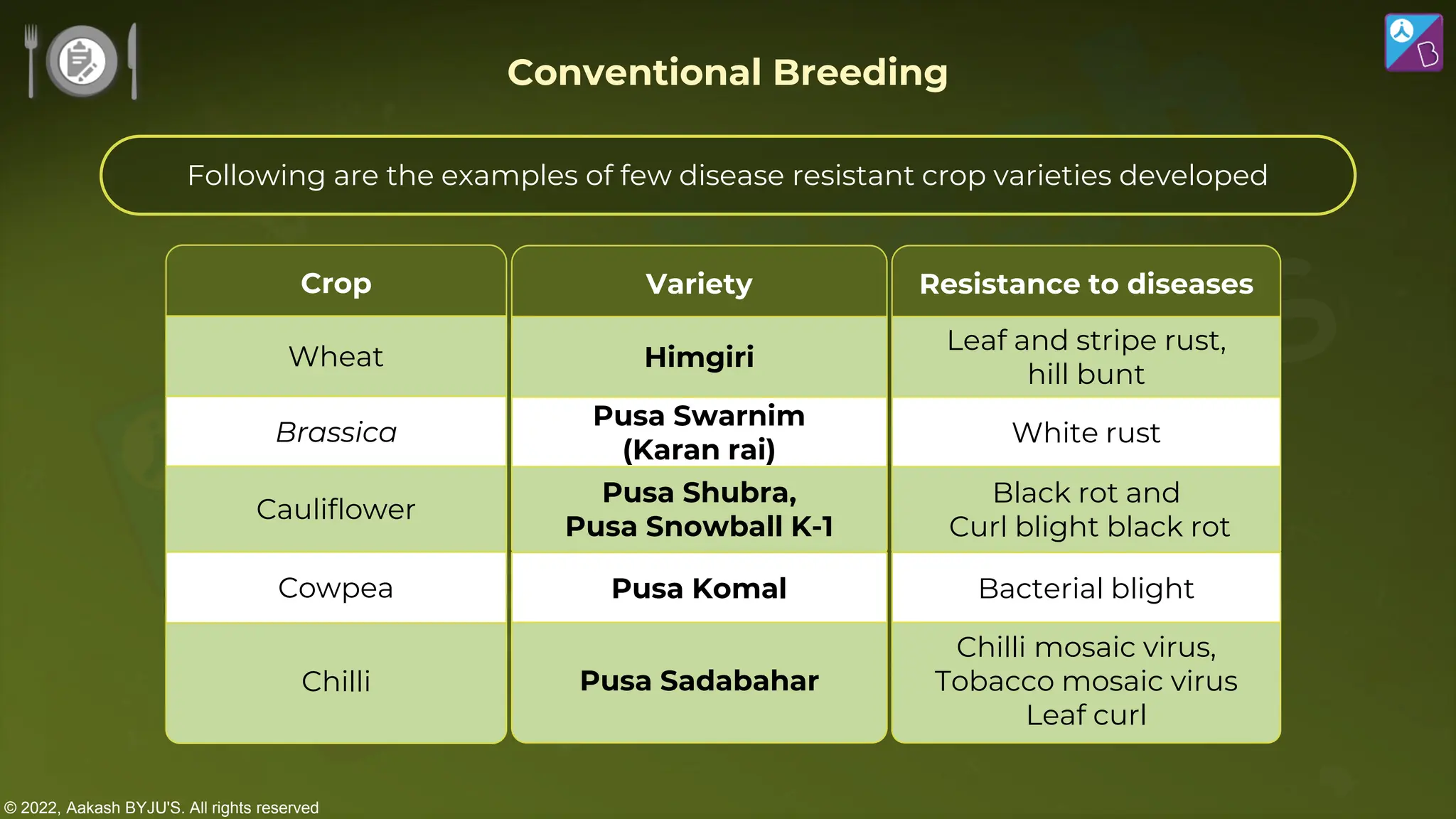
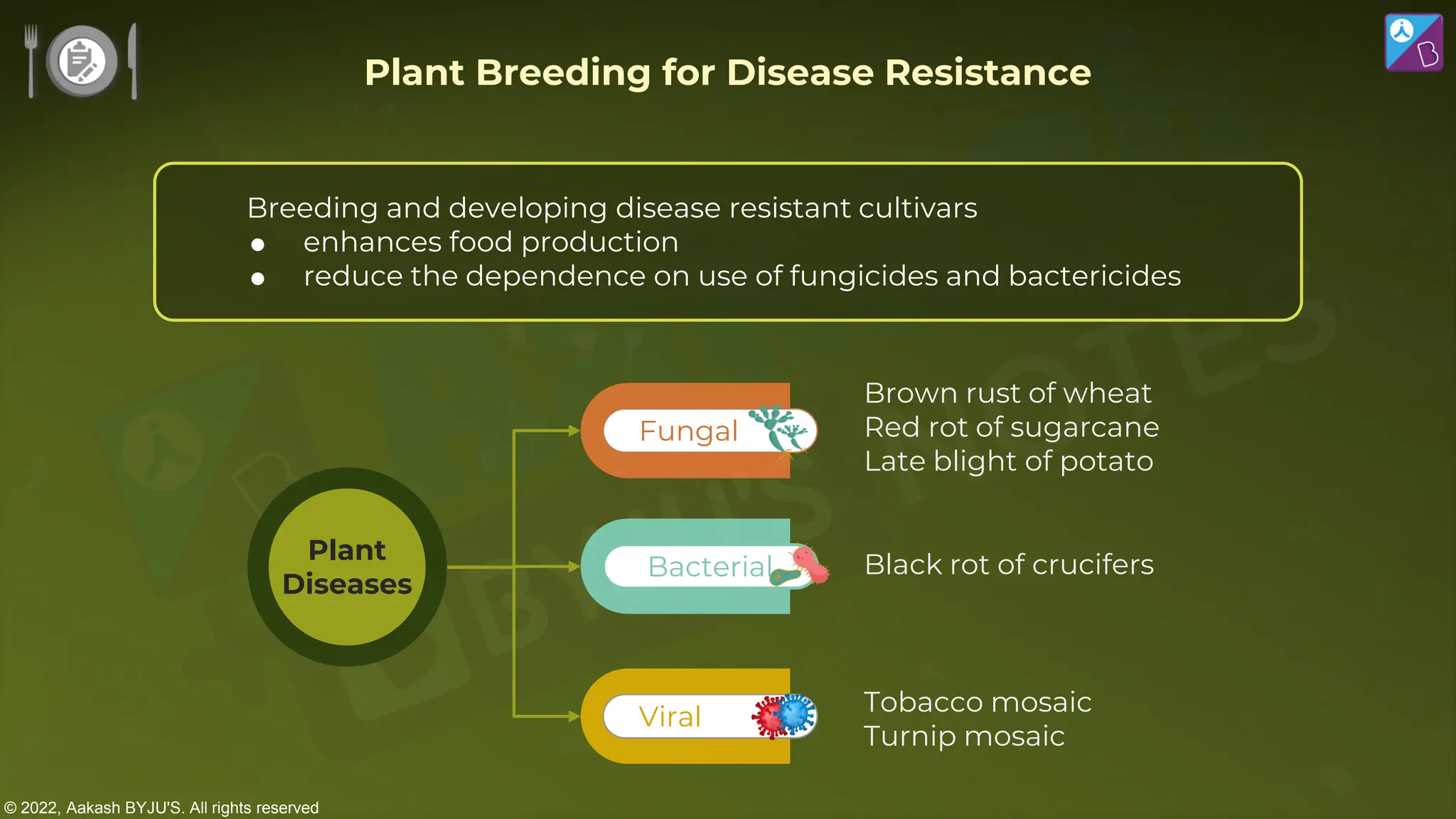
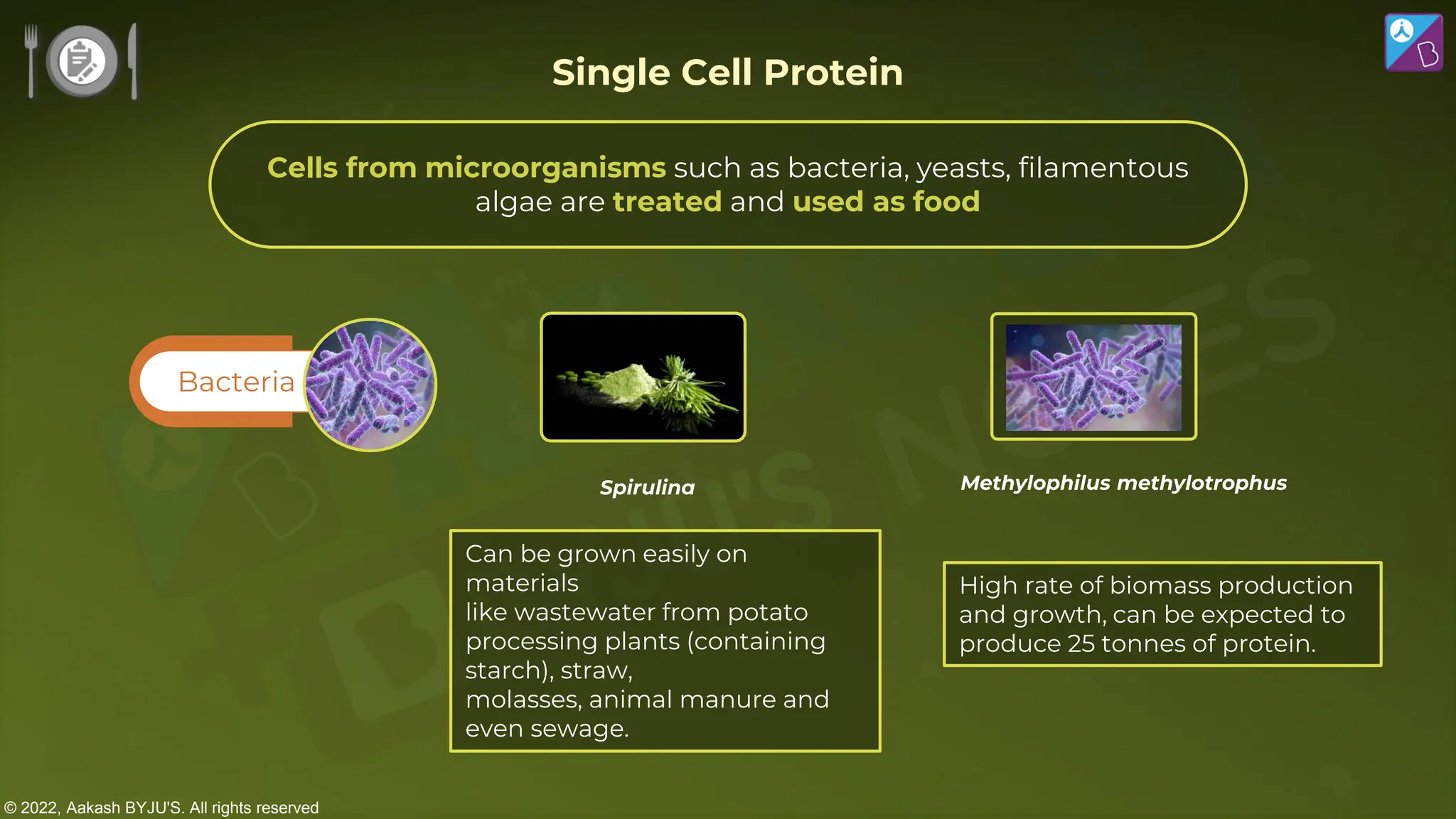
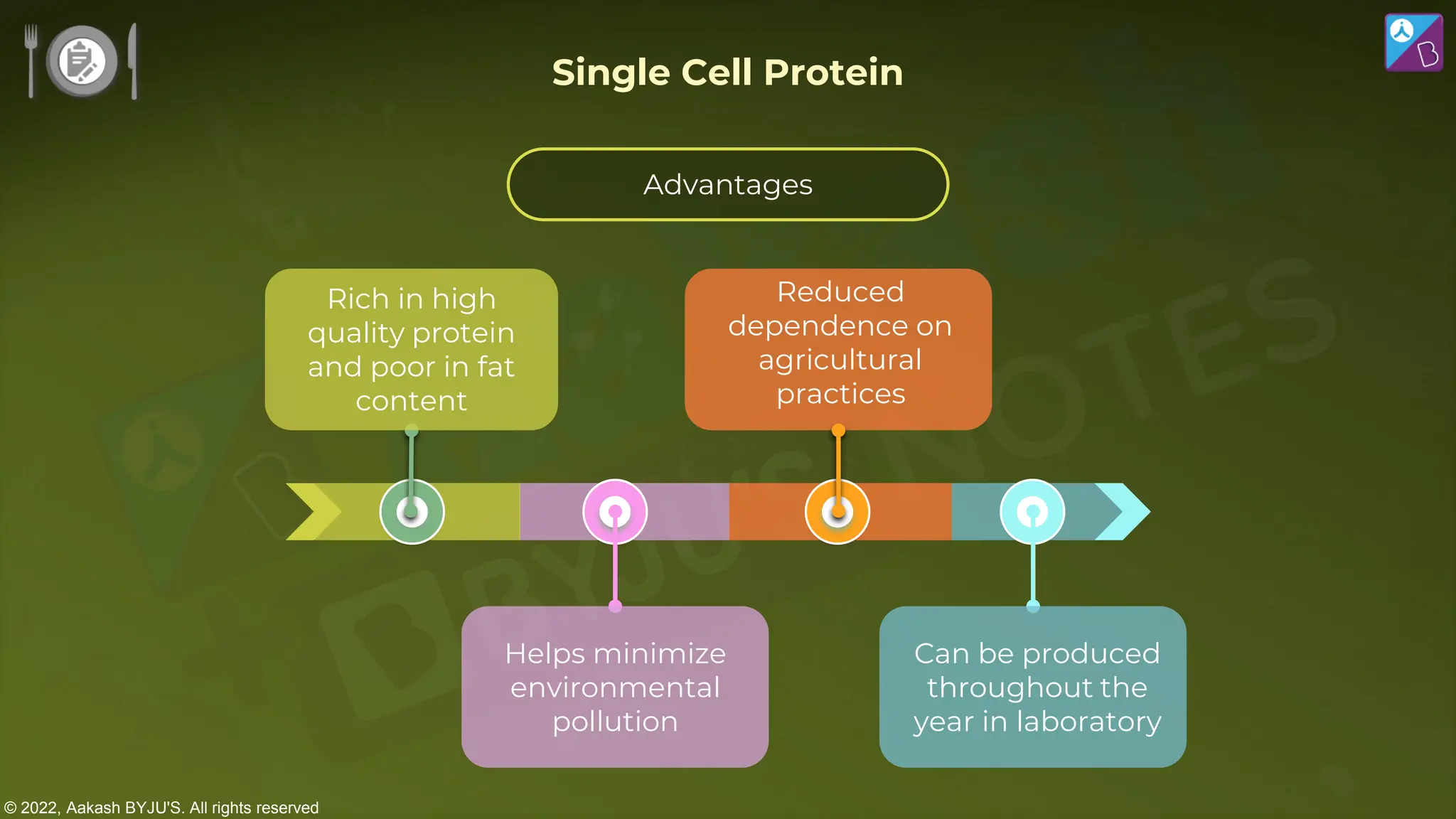
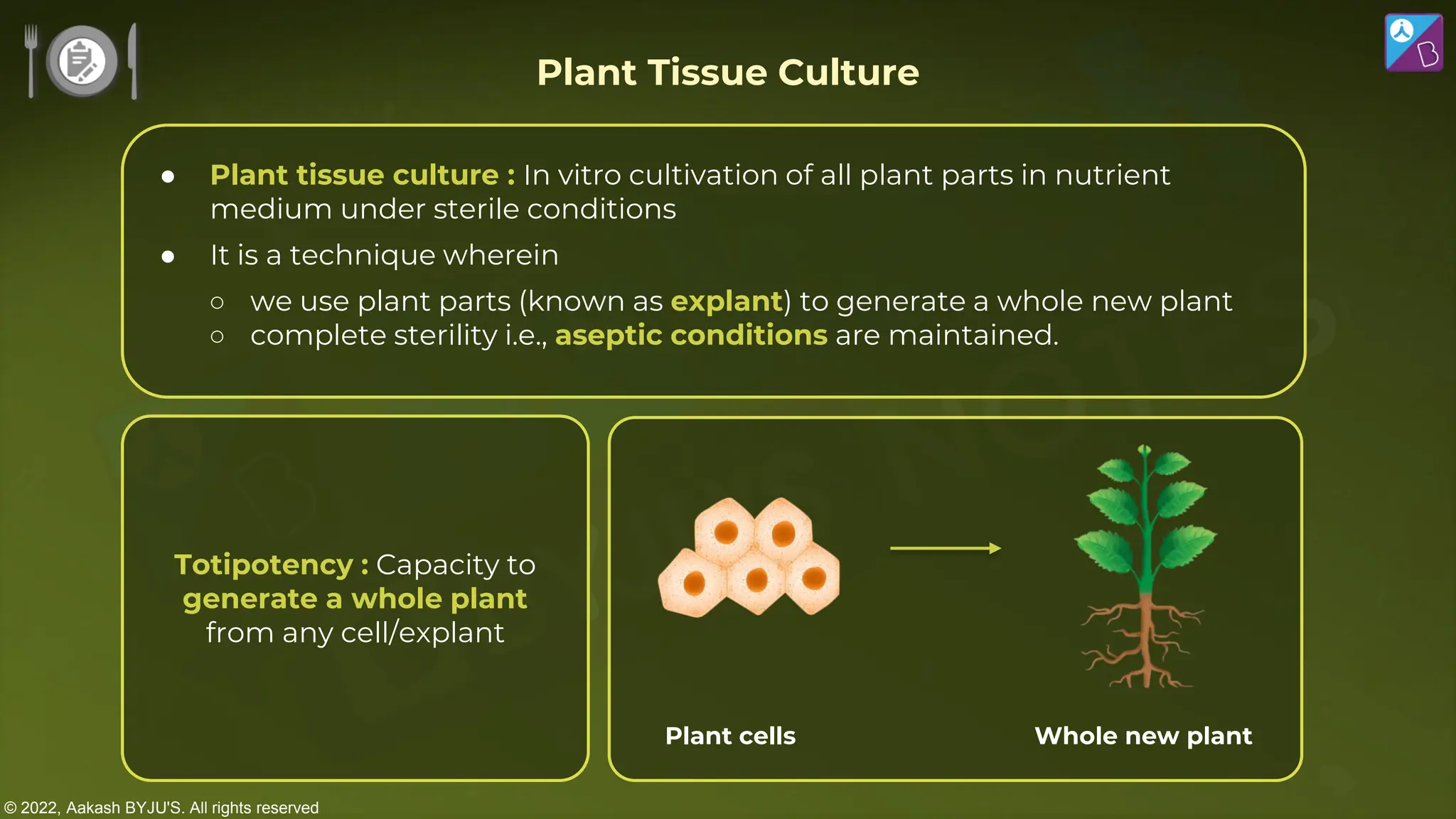
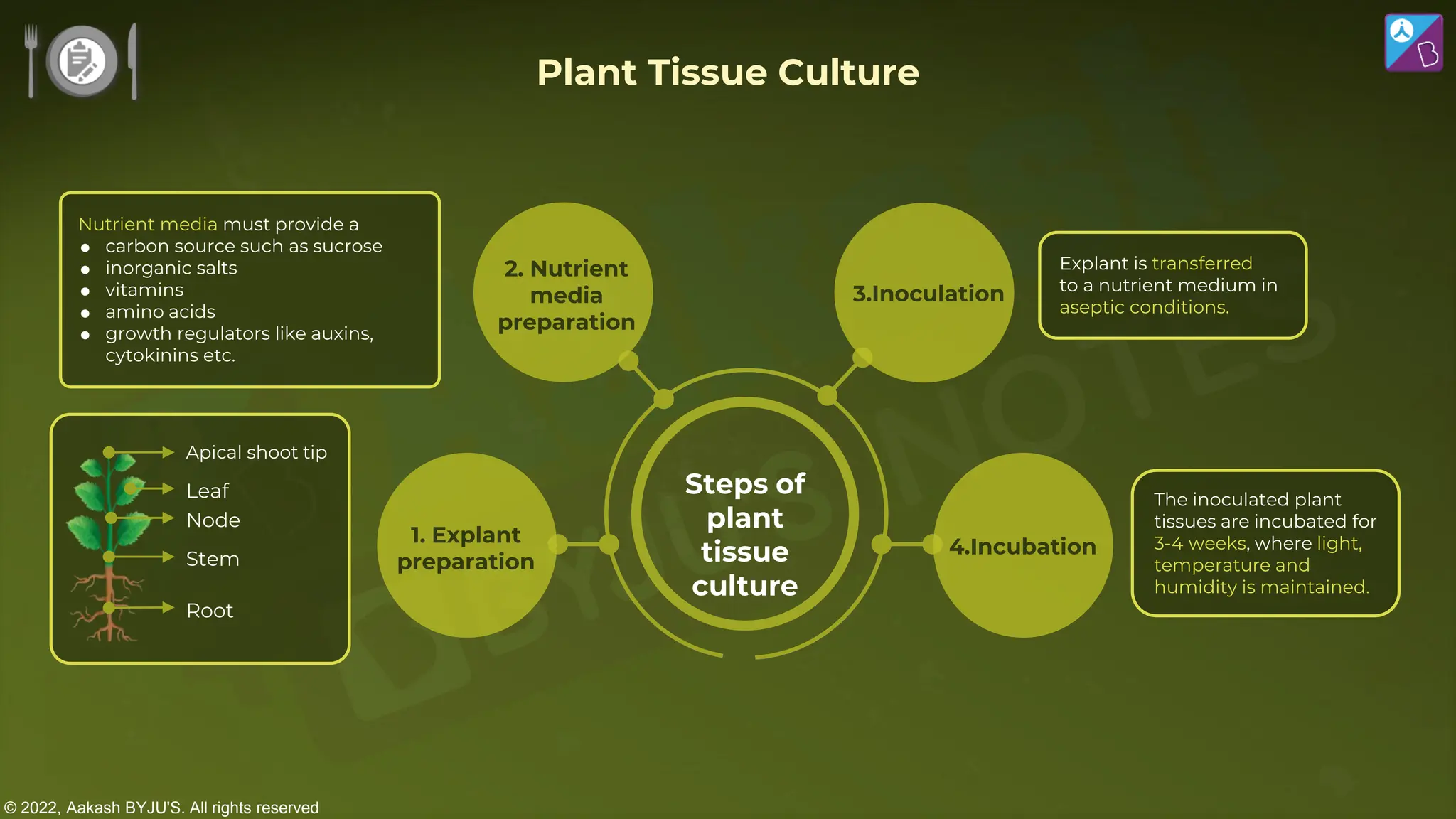
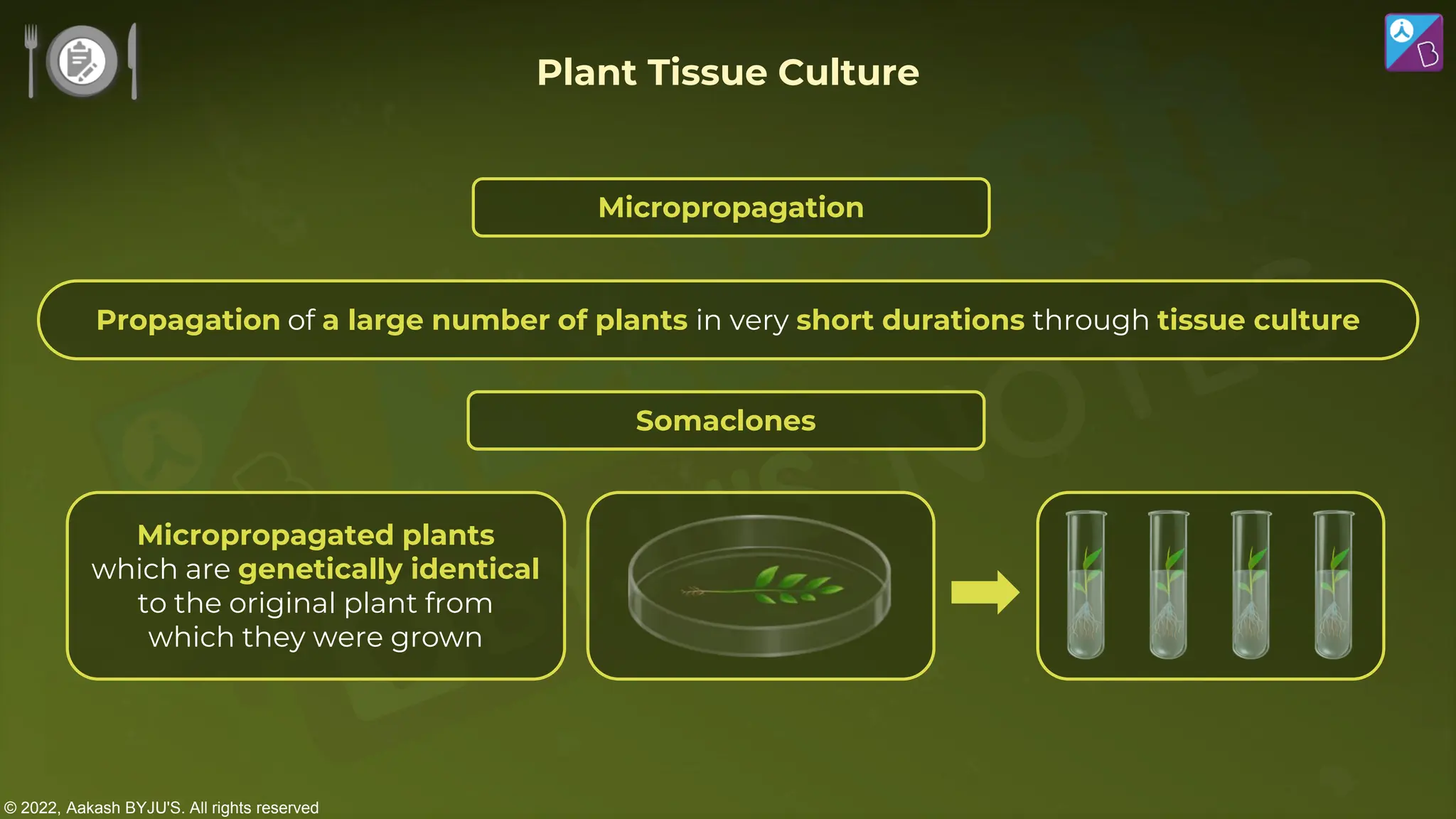
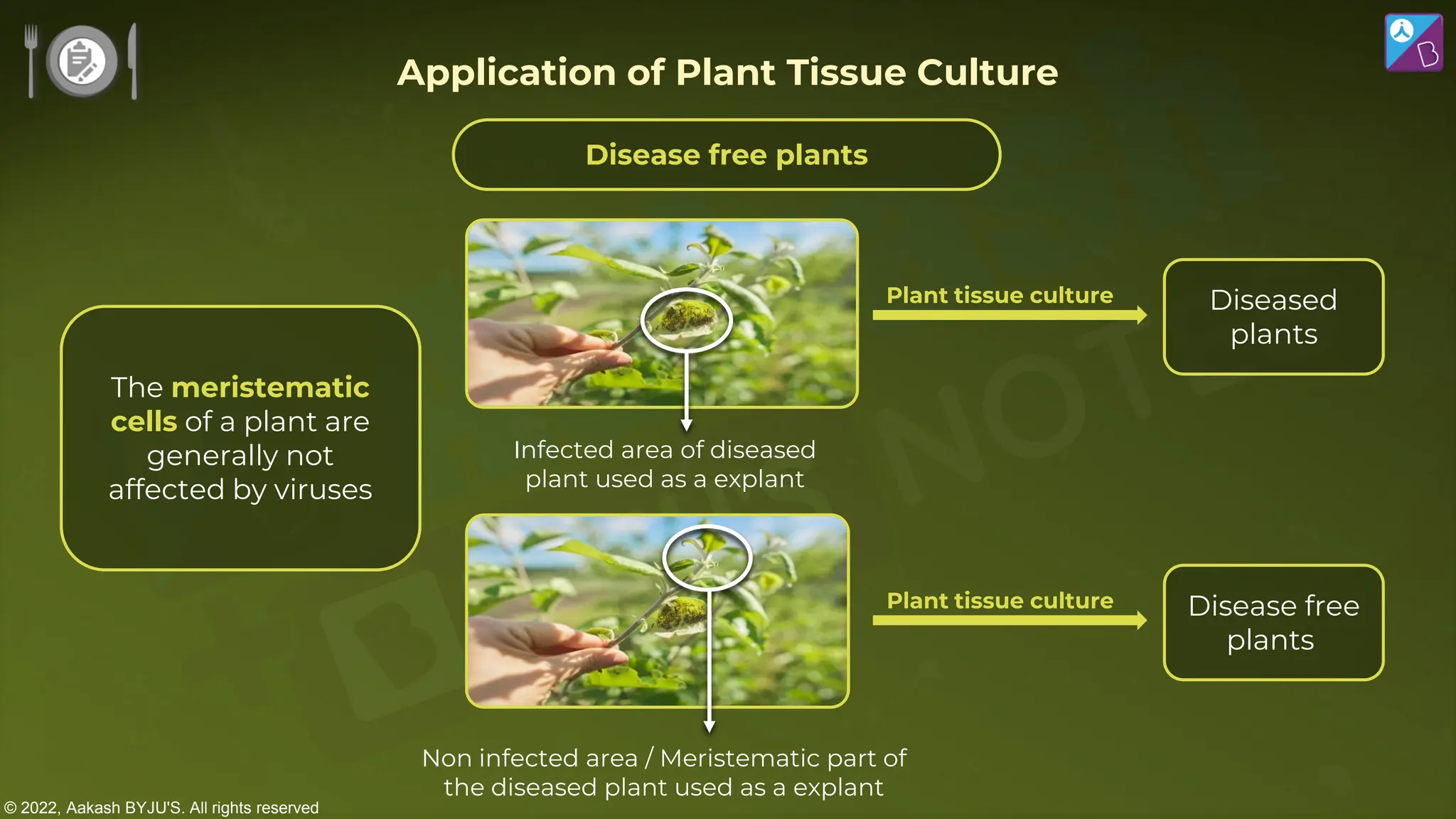
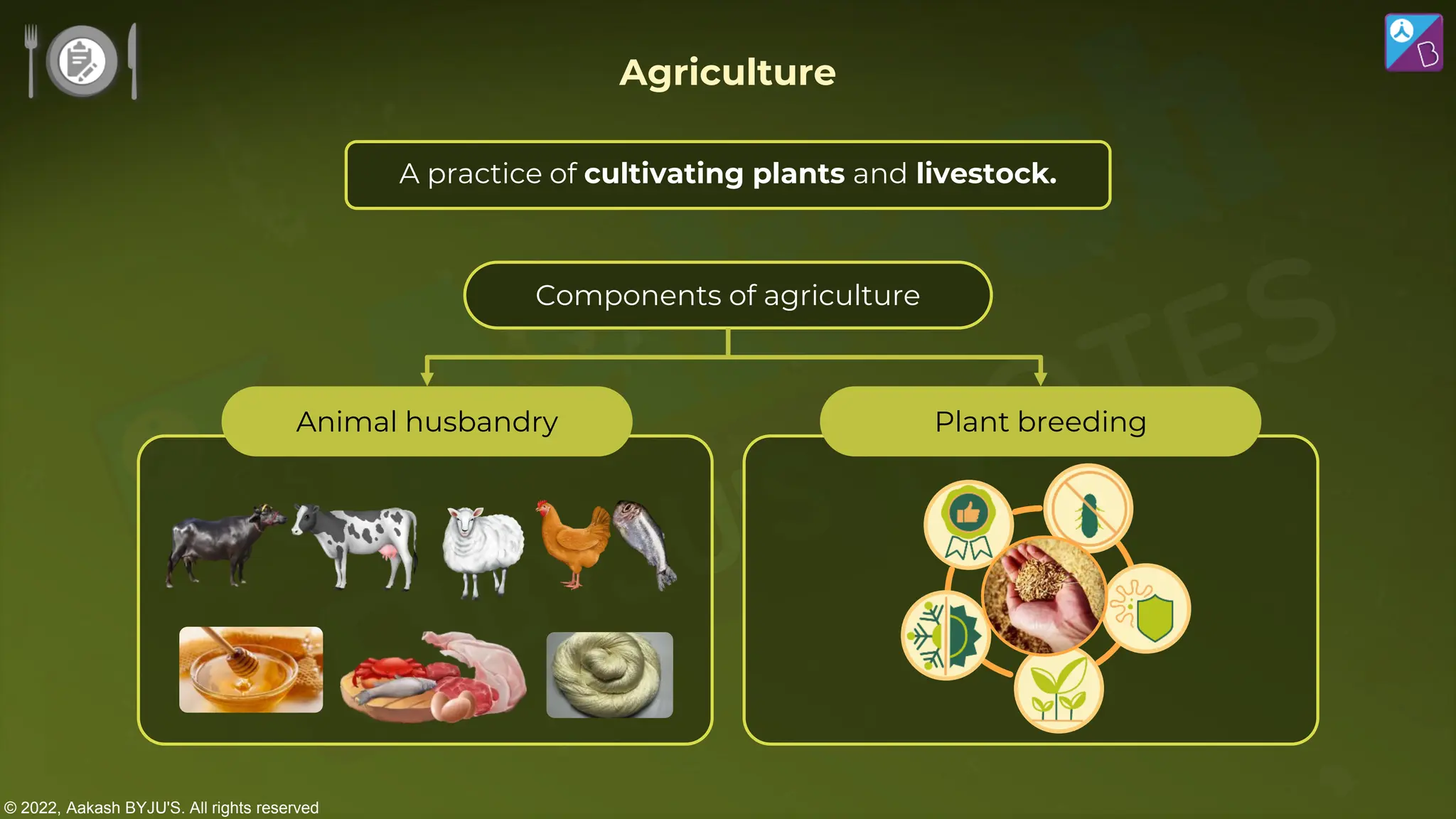
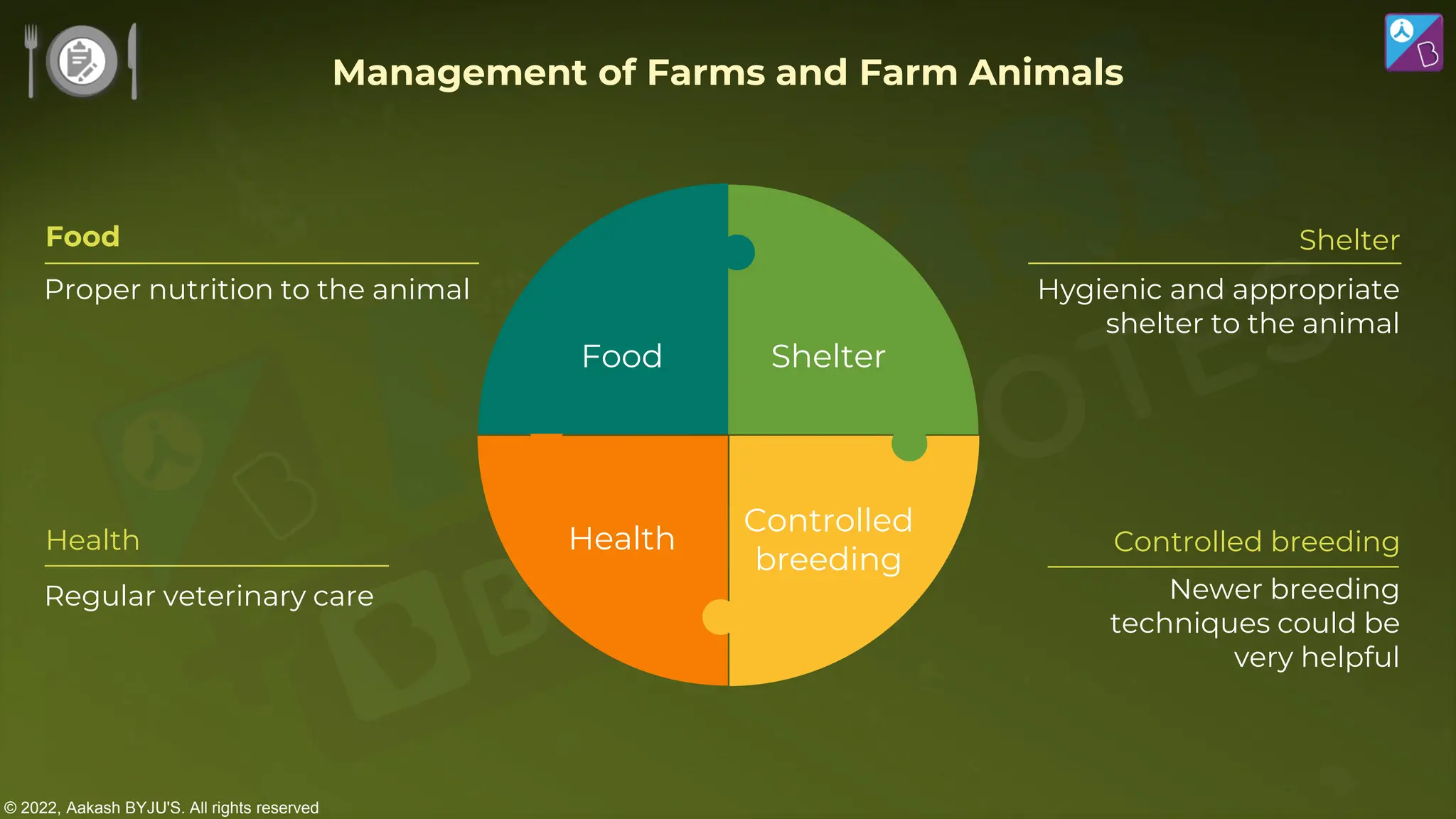
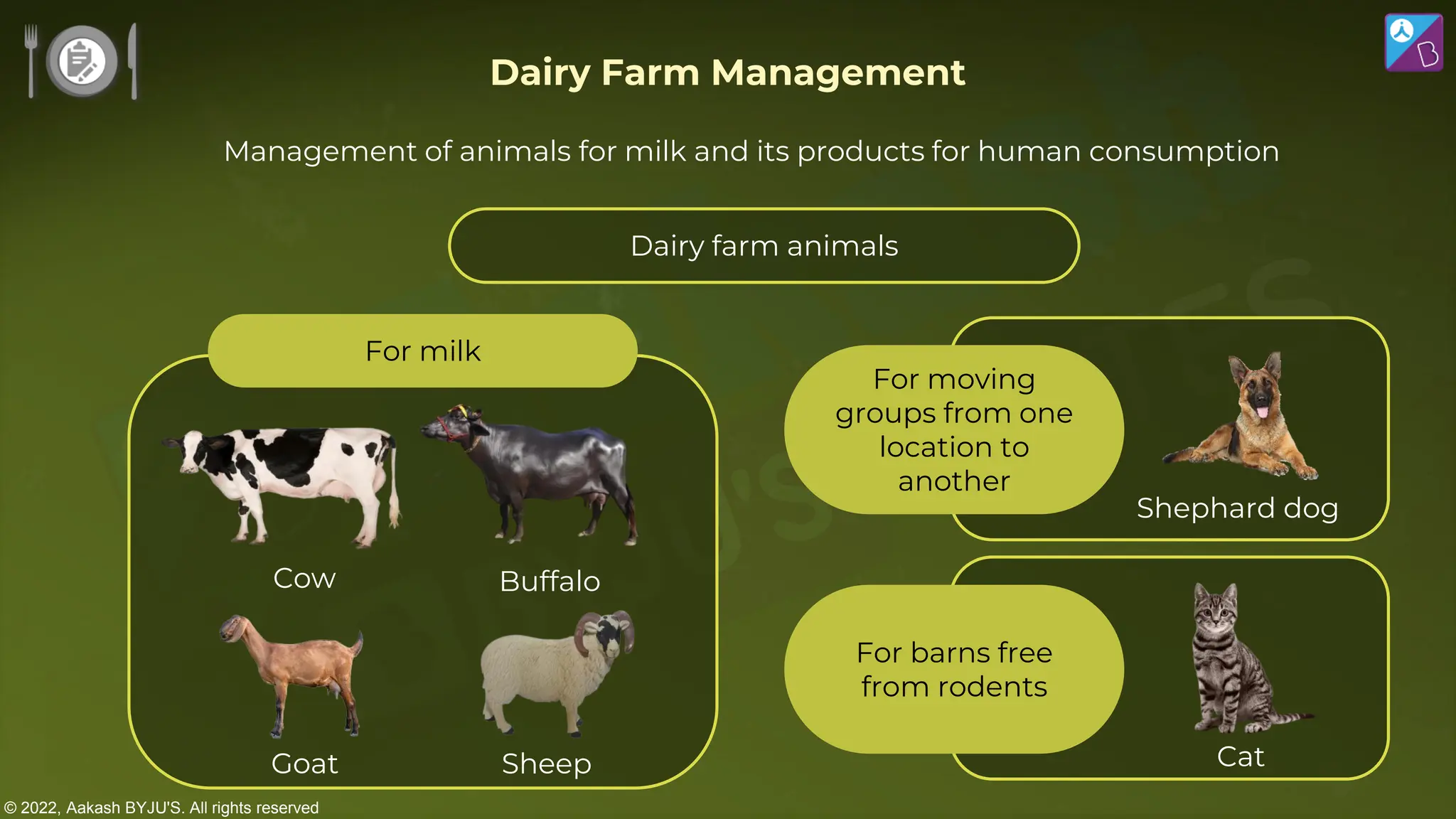
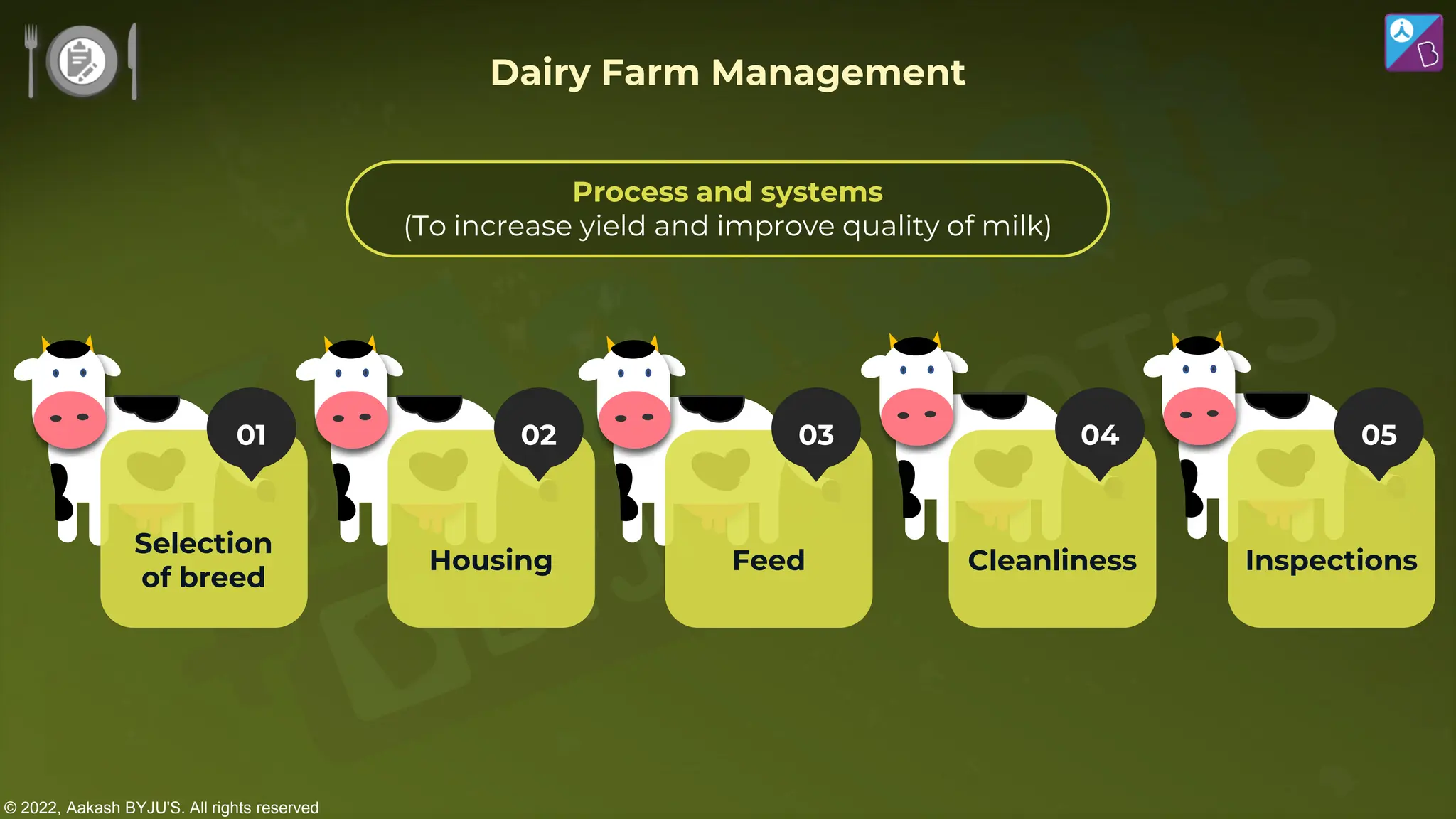
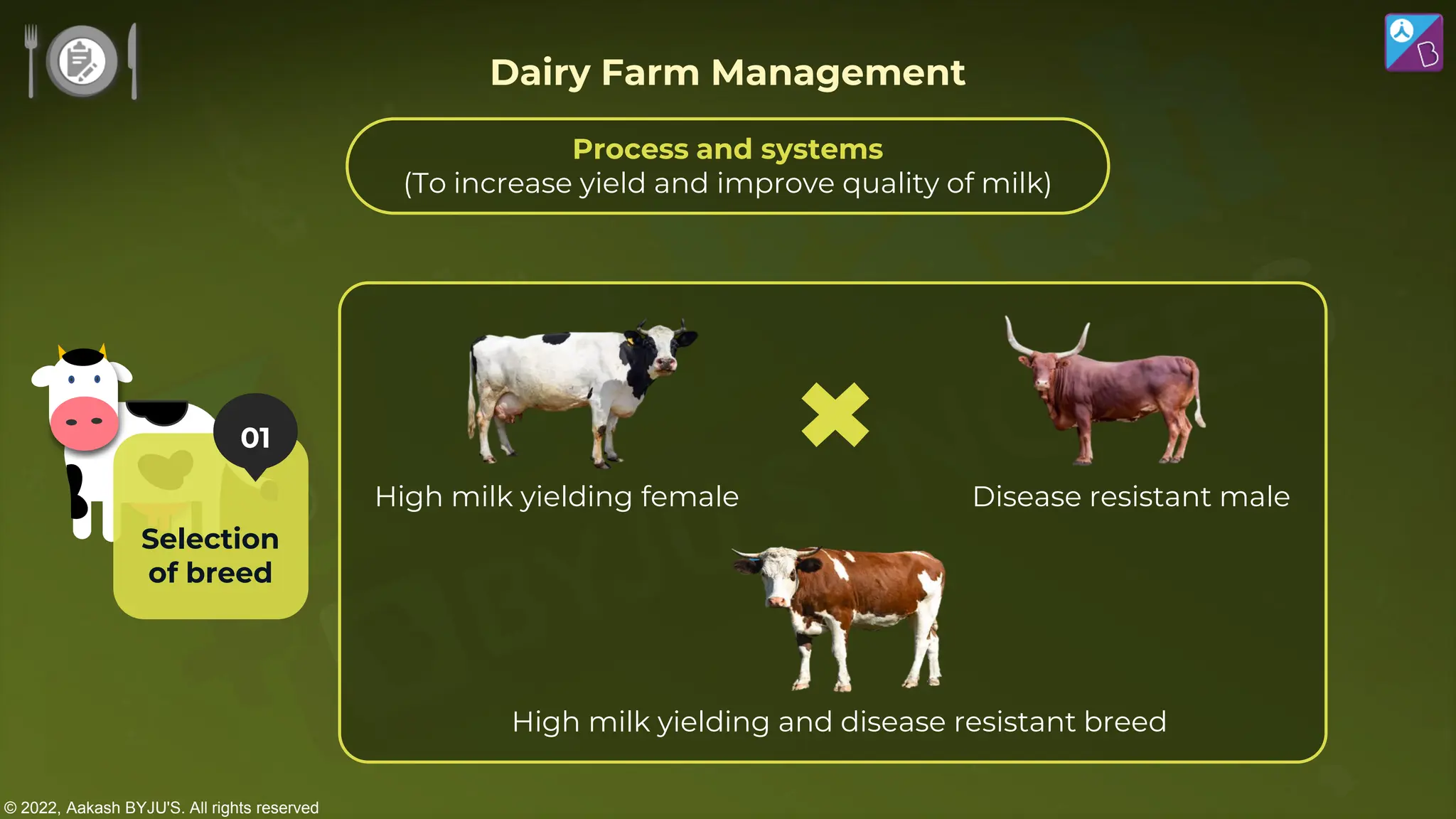
The document outlines strategies for enhancing food production through agricultural practices, including animal husbandry, dairy farming, poultry management, and plant breeding. It emphasizes modern techniques such as controlled breeding, artificial insemination, and genetic manipulation to improve yield and quality, while also highlighting the importance of hygiene, nutrition, and veterinary care in managing livestock. Additionally, it addresses challenges in food production and proposes innovations aimed at increasing agricultural efficiency and sustainability.


















![© 2022, Aakash BYJU'S. All rights reserved
Wheat Rice
Semi- dwarf
wheat
Kalyan Sona and Sonalika
○ Resistant to wheat rust (fungal
disease)
○ Short stature
○ Short maturity duration
Cultivated all over wheat belt of India
such as Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh,
Bihar.
IR-8, [developed at International Rice
Research Institute (IRRI), Philippines] –
a dwarf and high yielding variety
○ Later, a better yielding variety - Jaya
Taichung Native-1 (from Taiwan) –
a semi dwarf and disease-resistant
○ Later, a better yielding variety - Ratna
Jaya and
Ratna
As a result of green
revolution, wheat
production increased from
11 million tonnes to 75
million tonnes.
As a result, rice production
increased from 35 million
tonnes to 89.5 million
tonnes.
High Yielding Varieties
0
1960 2000
Years
Yield
(tonnes)
20
40
60
80
100
Wheat
Rice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strategiesforenhancementinfoodproduction-240428194723-b8752c18/75/Strategies-for-Enhancement-in-Food-Production-pdf-49-2048.jpg)