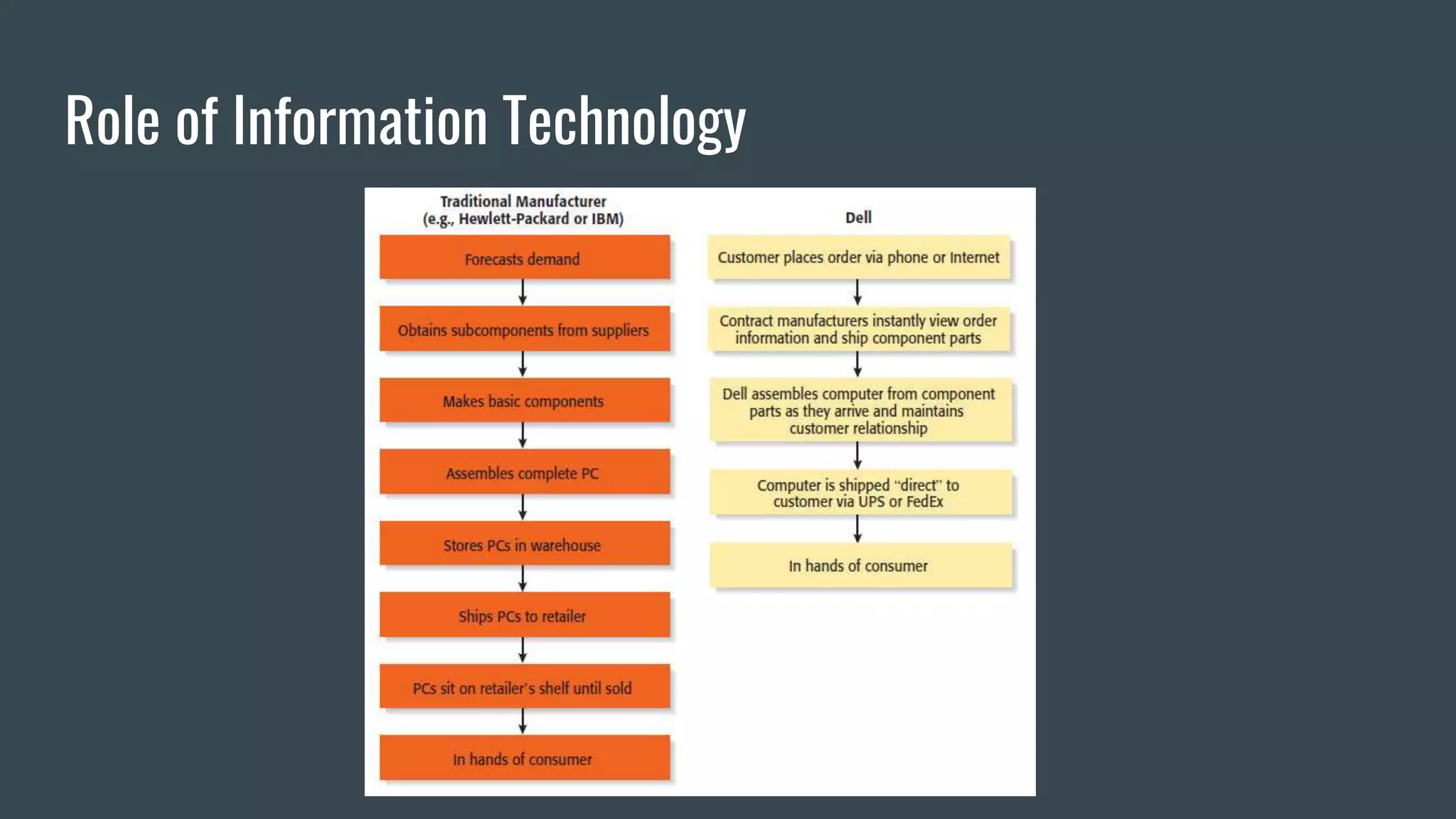
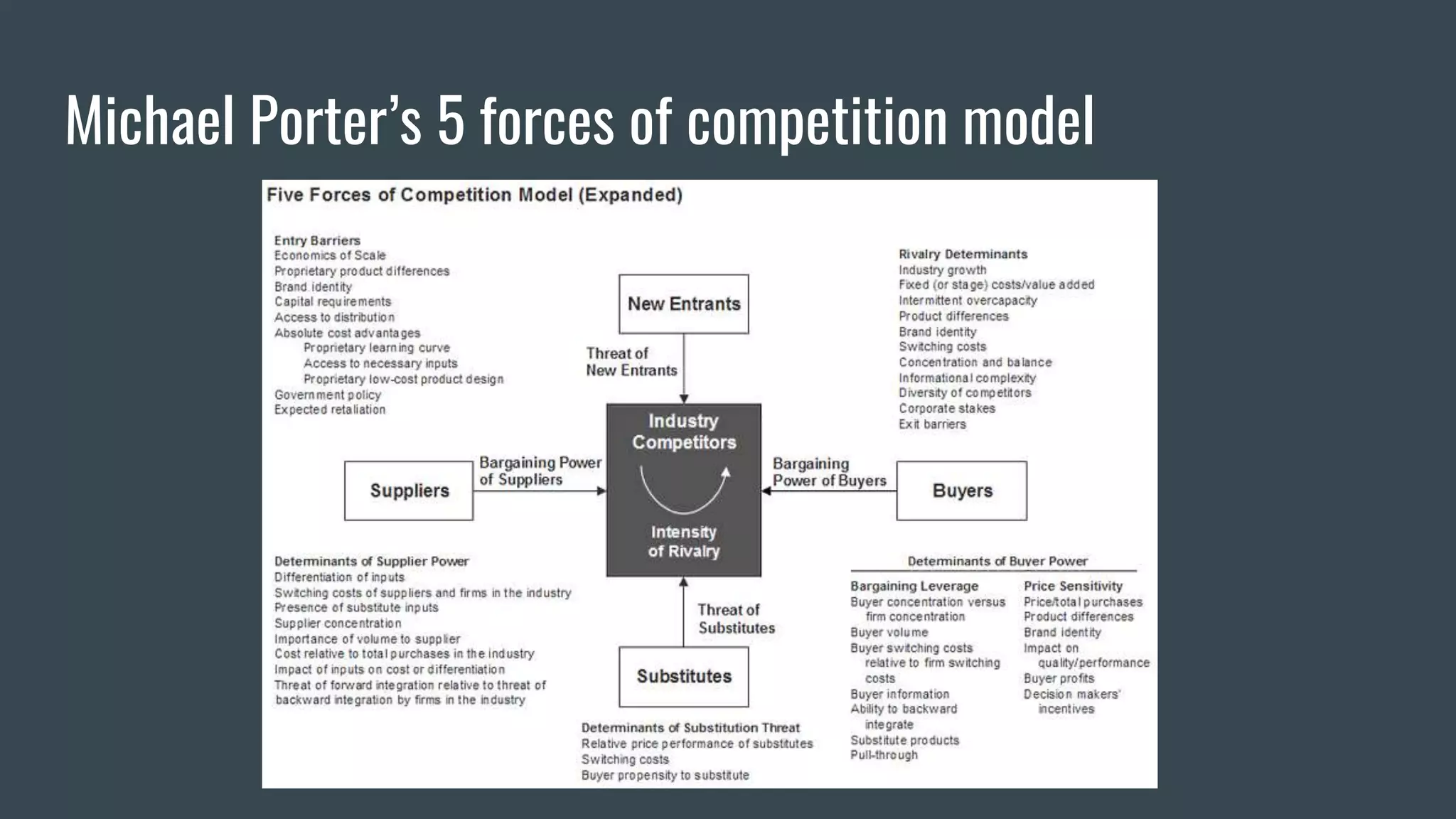
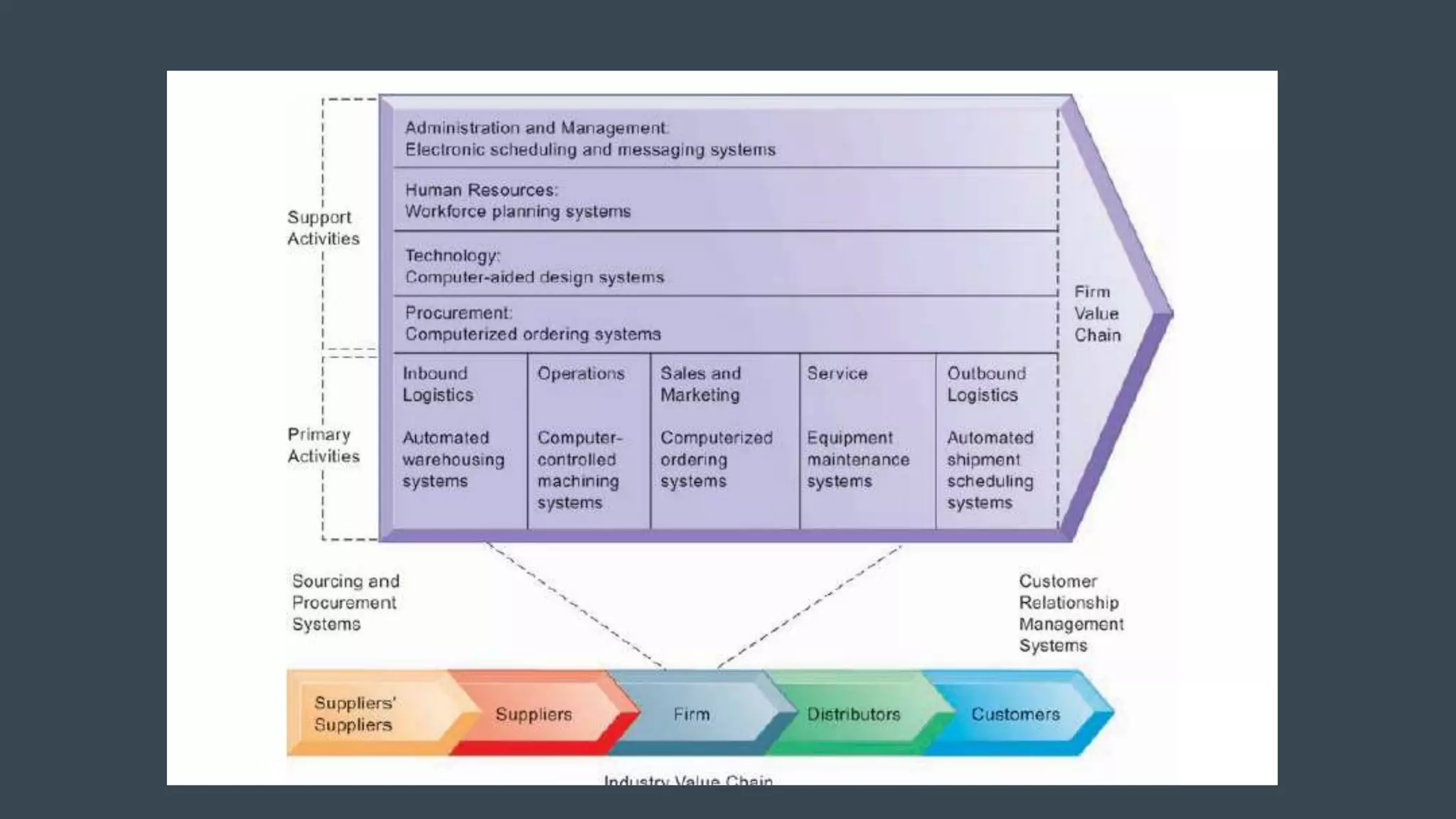
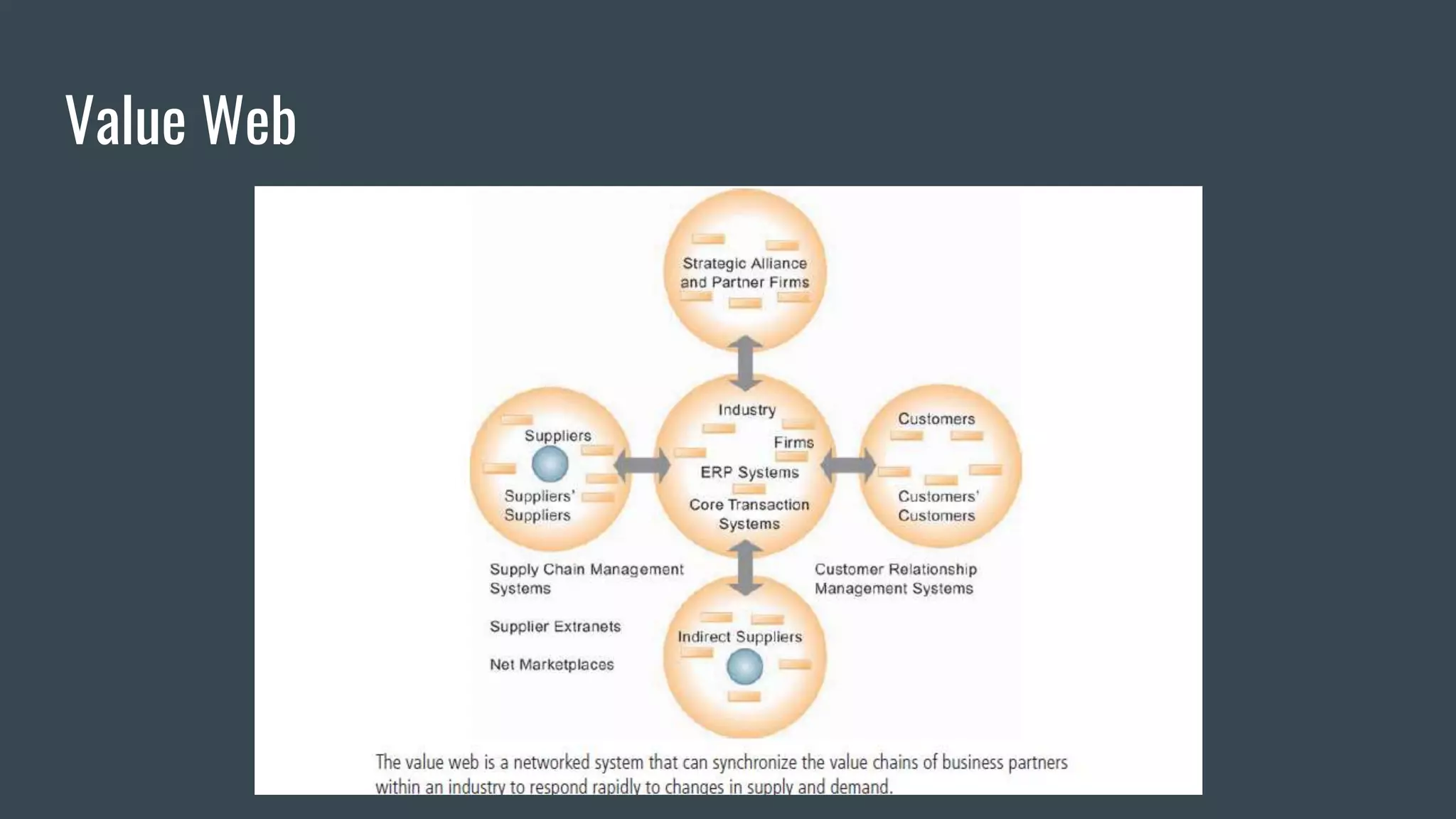
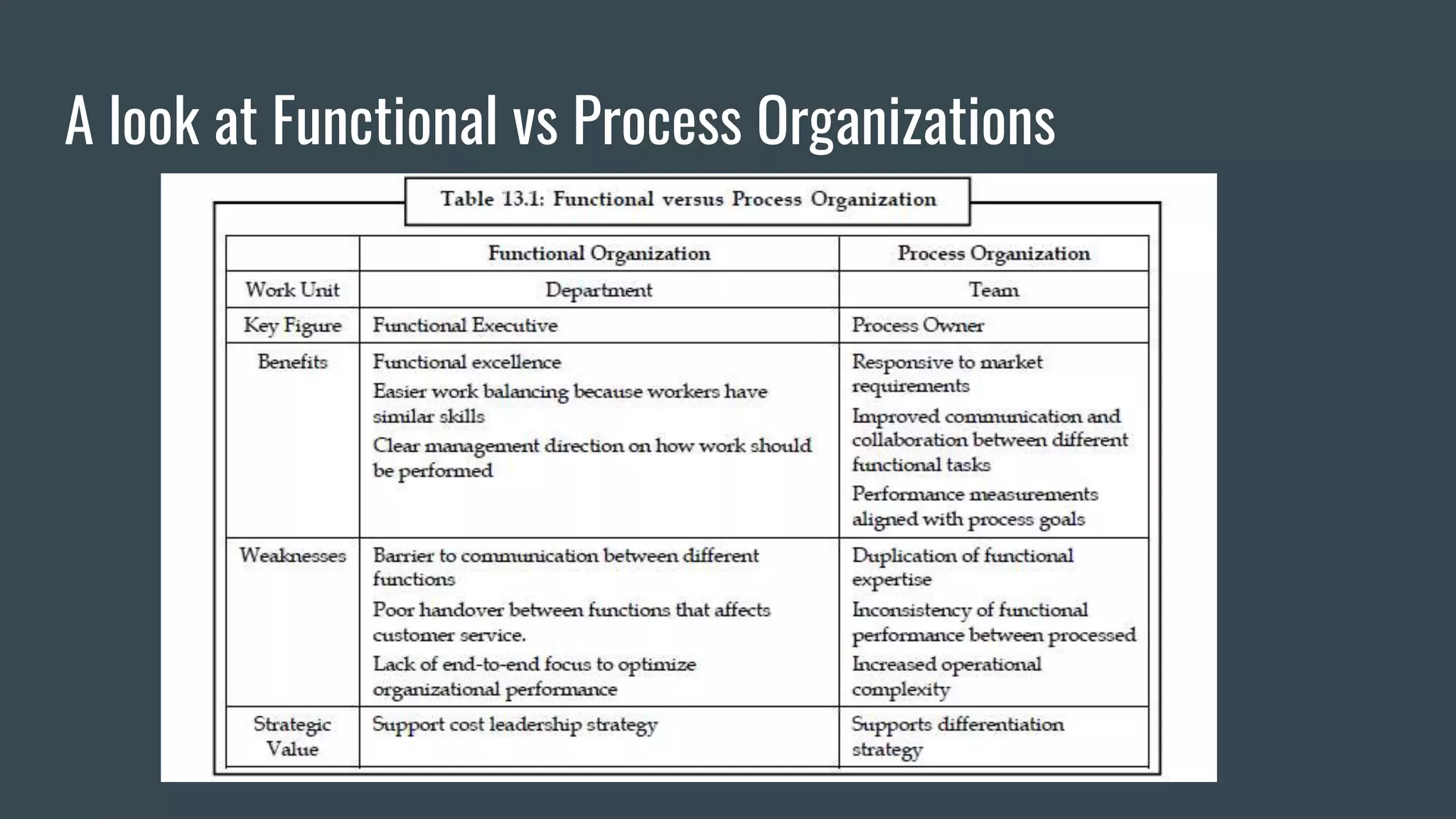
Strategic information systems are designed to help organizations gain competitive advantages. They do this through decision support, enterprise resource planning, data mining capabilities, and real-time information. Key features include helping develop strategic approaches, integrating business processes, optimizing resources, and maintaining rapid responses. Examples of strategic information systems helping companies reduce costs, create barriers to entry, increase switching costs, differentiate products, and enhance markets. Dell's strategic information systems help with product configuration, e-procurement, cost calculation, inventory management, and credit/payment processing.