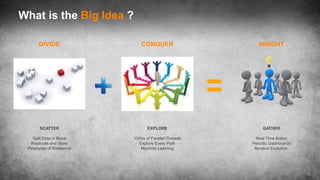
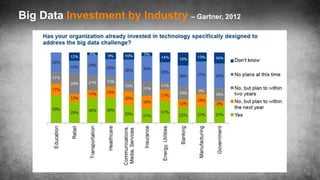
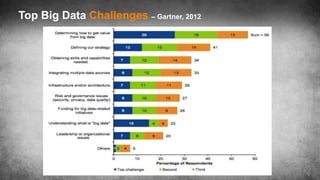
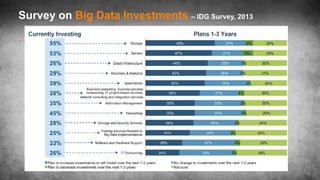
The document discusses big data science, comparing data to crude oil, and emphasizing its extraction and refinement for valuable insights. It outlines the differences between big data and traditional data analysis, illustrating how data science contributes to understanding data through various stages of processing. Lastly, it highlights the challenges and potential of big data across different sectors, underscoring the necessity of leveraging it effectively.
![BIG DATA SCIENCE
“The price of light is far less than the cost of darkness”
Chandan Rajah [ @ChandanRajah ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cdecbigdatascience20140918-141204061604-conversion-gate01/85/Steps-to-the-Big-Data-Science-Epiphany-1-320.jpg)




![Data Analytics to Data Discovery ?
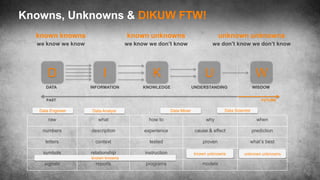
data you know
data you don’t know
questionsyou’reasking
questionsyou’renotasking
Data Analyst
Data Scientist
Data
Analytics
Data Discovery
DATA MODELLING
Y F( X, random noise, parameters)
ALGORITHMIC MODELLING
Y [ BLACK BOX ] X](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cdecbigdatascience20140918-141204061604-conversion-gate01/85/Steps-to-the-Big-Data-Science-Epiphany-7-320.jpg)