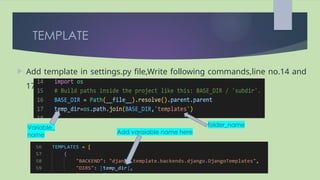
The document explains the use of templates in the Django web framework, emphasizing their role in generating dynamic HTML pages and organizing HTML files in a single directory for simplicity. It describes the Django template language which includes variables, filters, and tags, providing syntax examples for rendering and modifying template content. Key constructs like variables and tags facilitate logical conditions and loops within templates, enhancing functionality in rendering web applications.