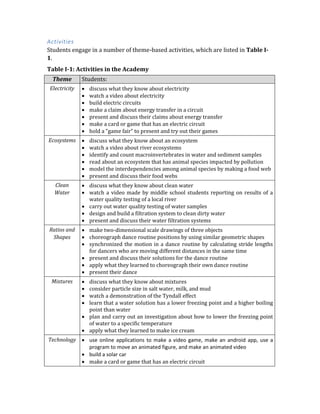
The STEMStarter Academy is a five-day summer program that aims to increase middle school students' understanding and interest in STEM fields through hands-on activities. Students will engage in theme-based activities focused on electricity, ecosystems, clean water, ratios and shapes, mixtures, and technology. Instructional strategies emphasize developing STEM practices like investigating, modeling, and problem solving. Assessments include pre- and post-surveys on students' STEM interests and self-assessments of their work using rubrics.