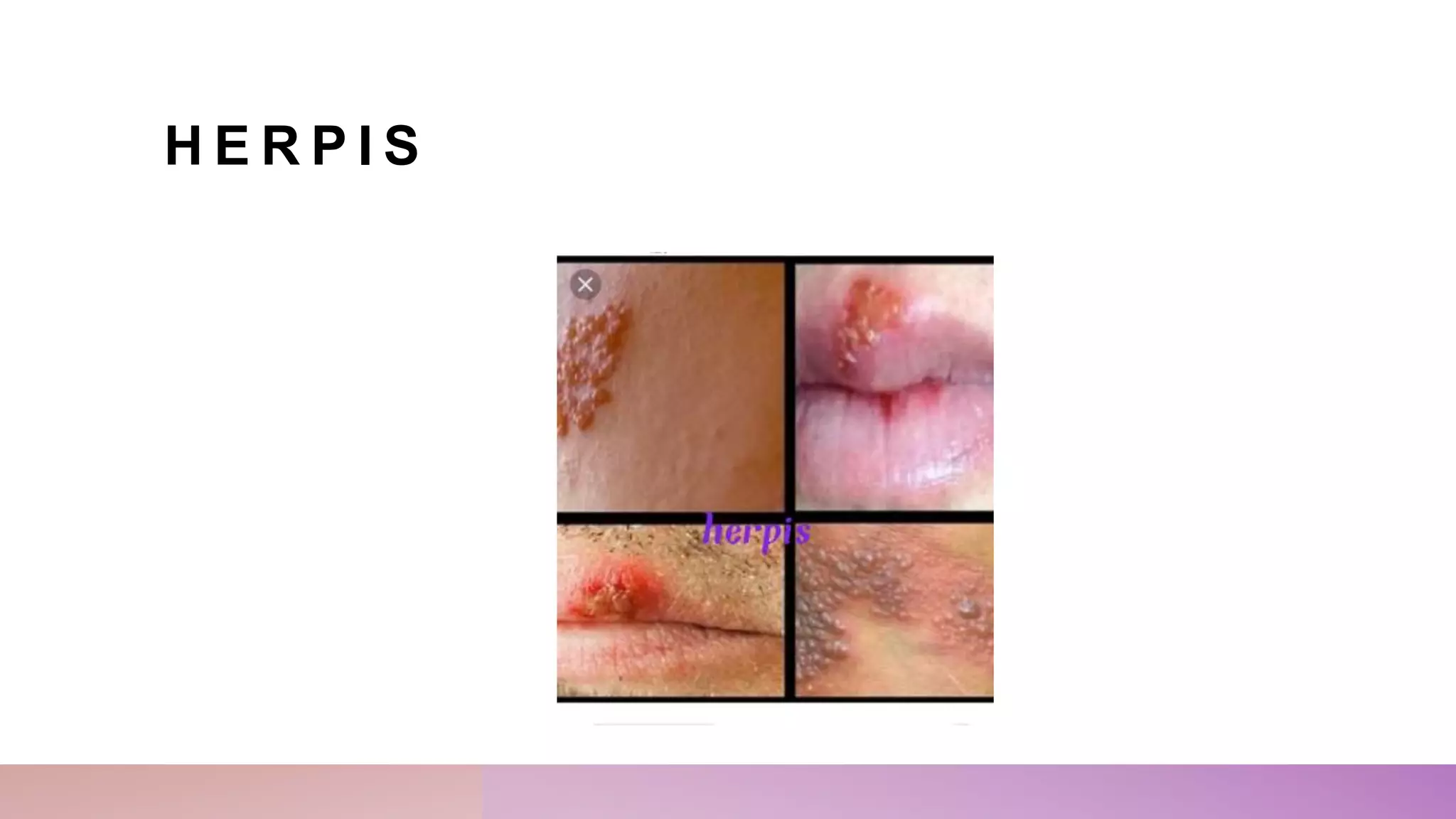
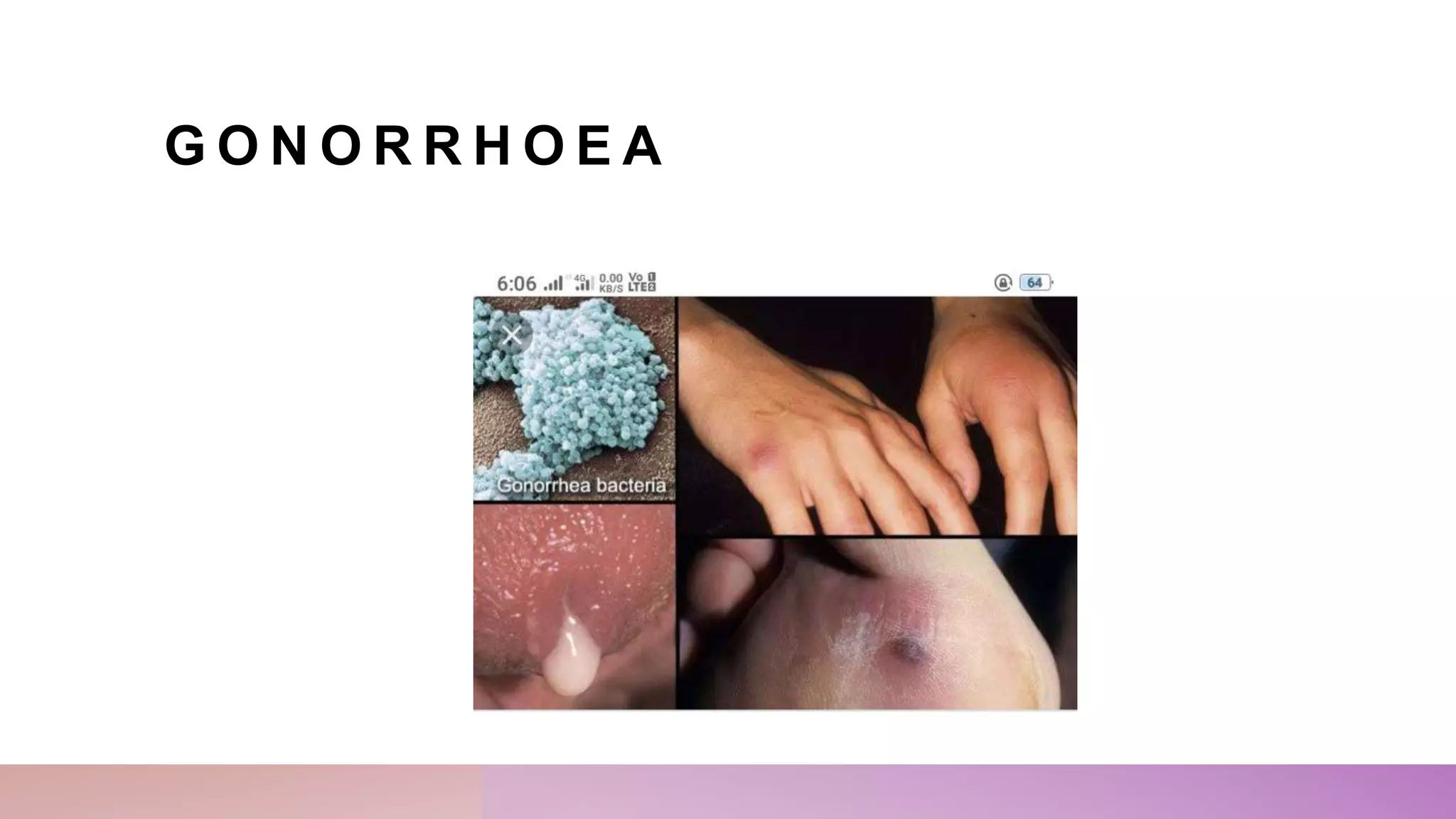
This document provides an outline for a presentation on sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). It defines STDs as infections spread through sexual contact. The outline covers causes, hosts, modes of transmission, incubation periods, signs and symptoms, risk factors, diagnostic evaluation, complications, treatments, and prevention of common STDs like chlamydia, herpes, gonorrhea, syphilis, and hepatitis. Nursing management includes promoting personal hygiene, abstaining from sex during treatment, partner treatment, universal precautions, health education, counseling, and encouraging testing of partners.