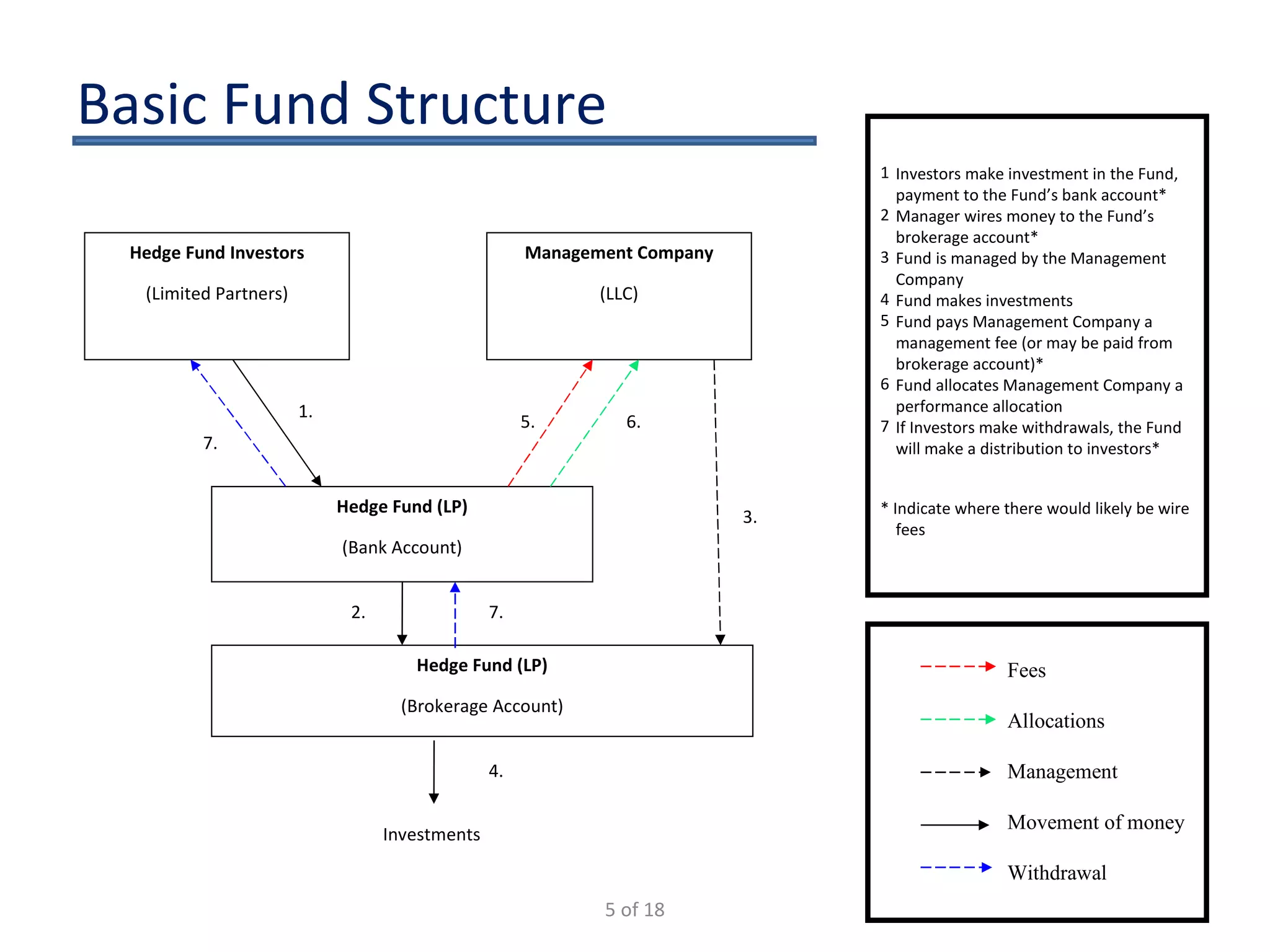
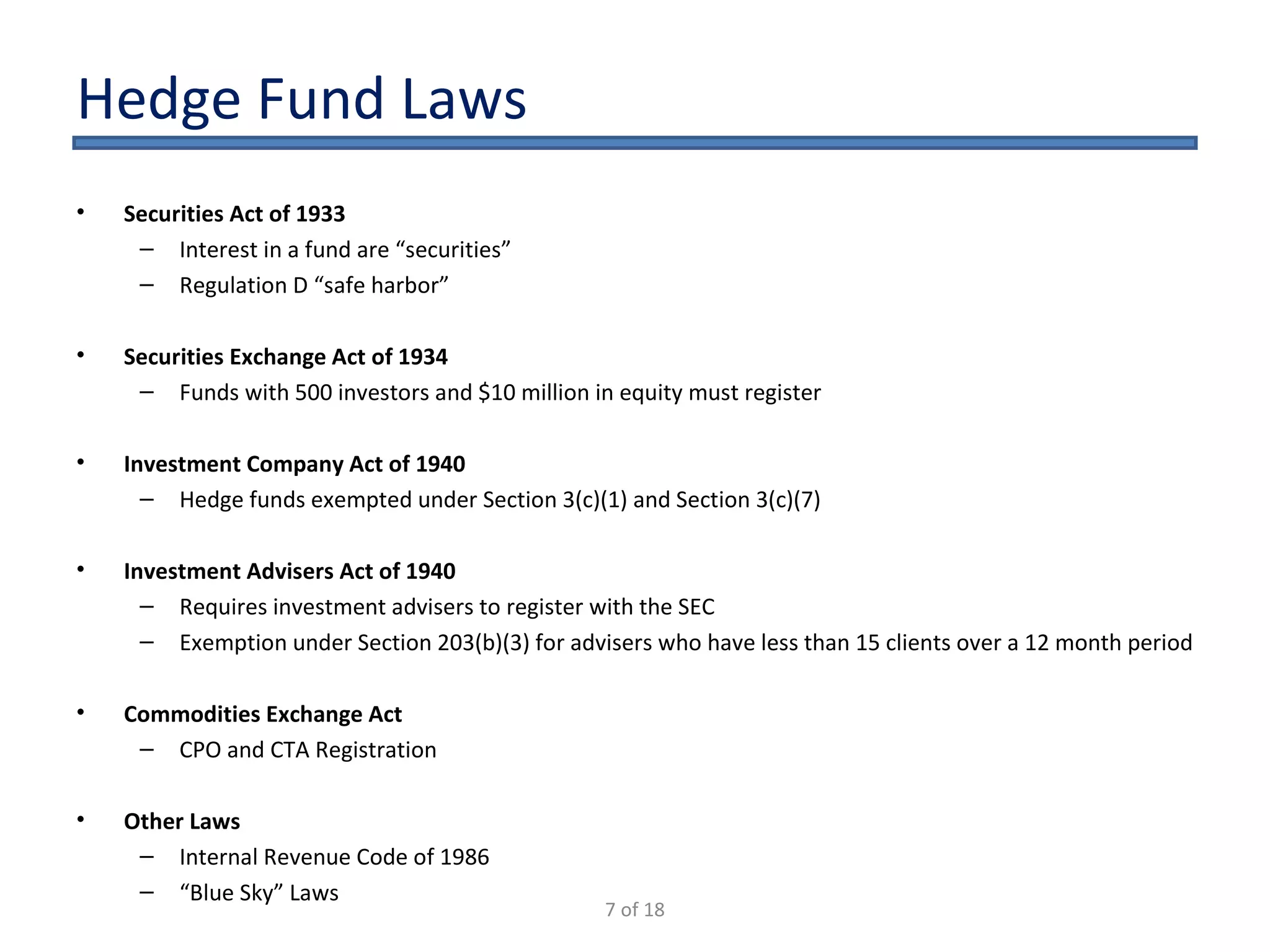
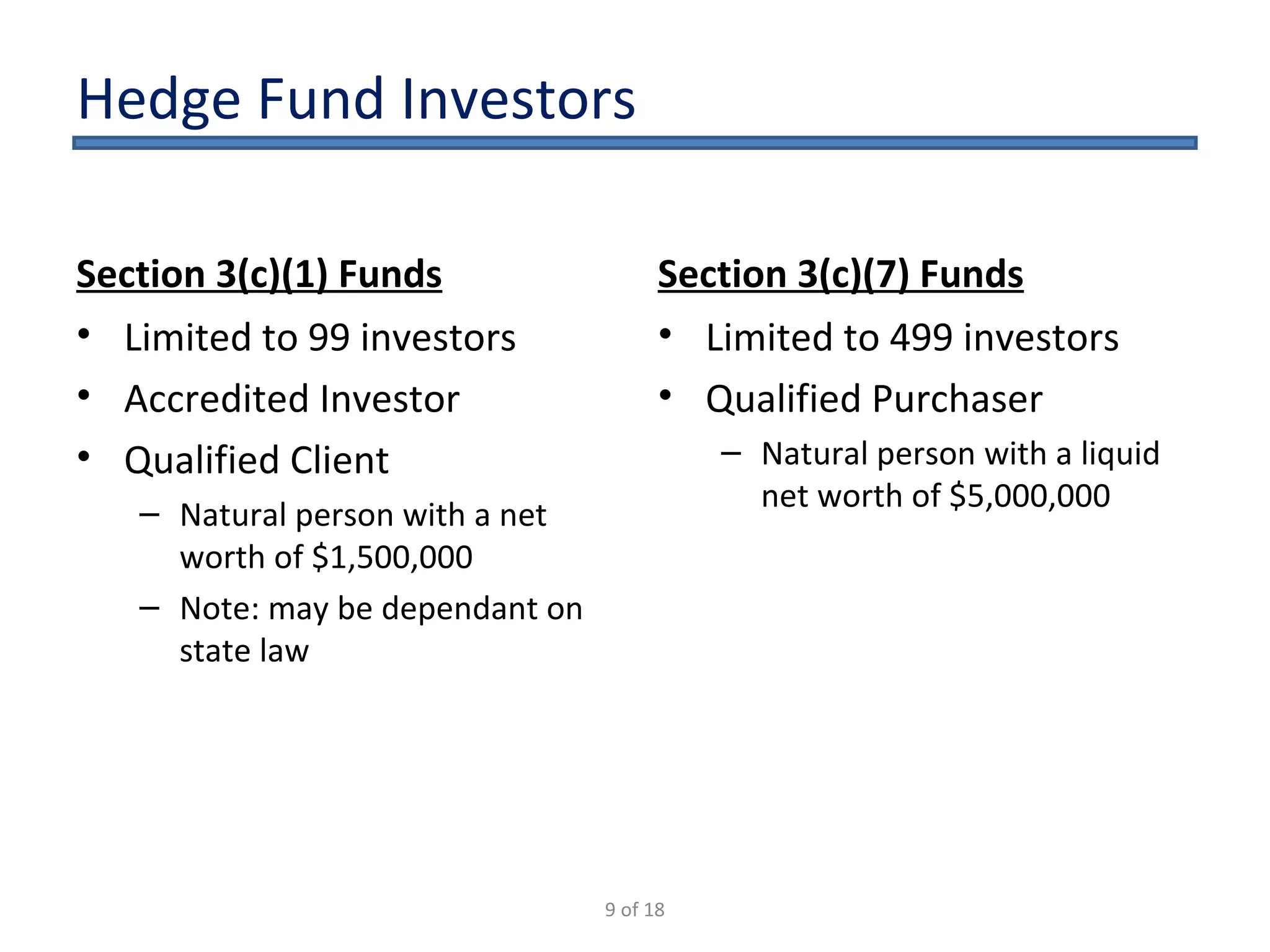
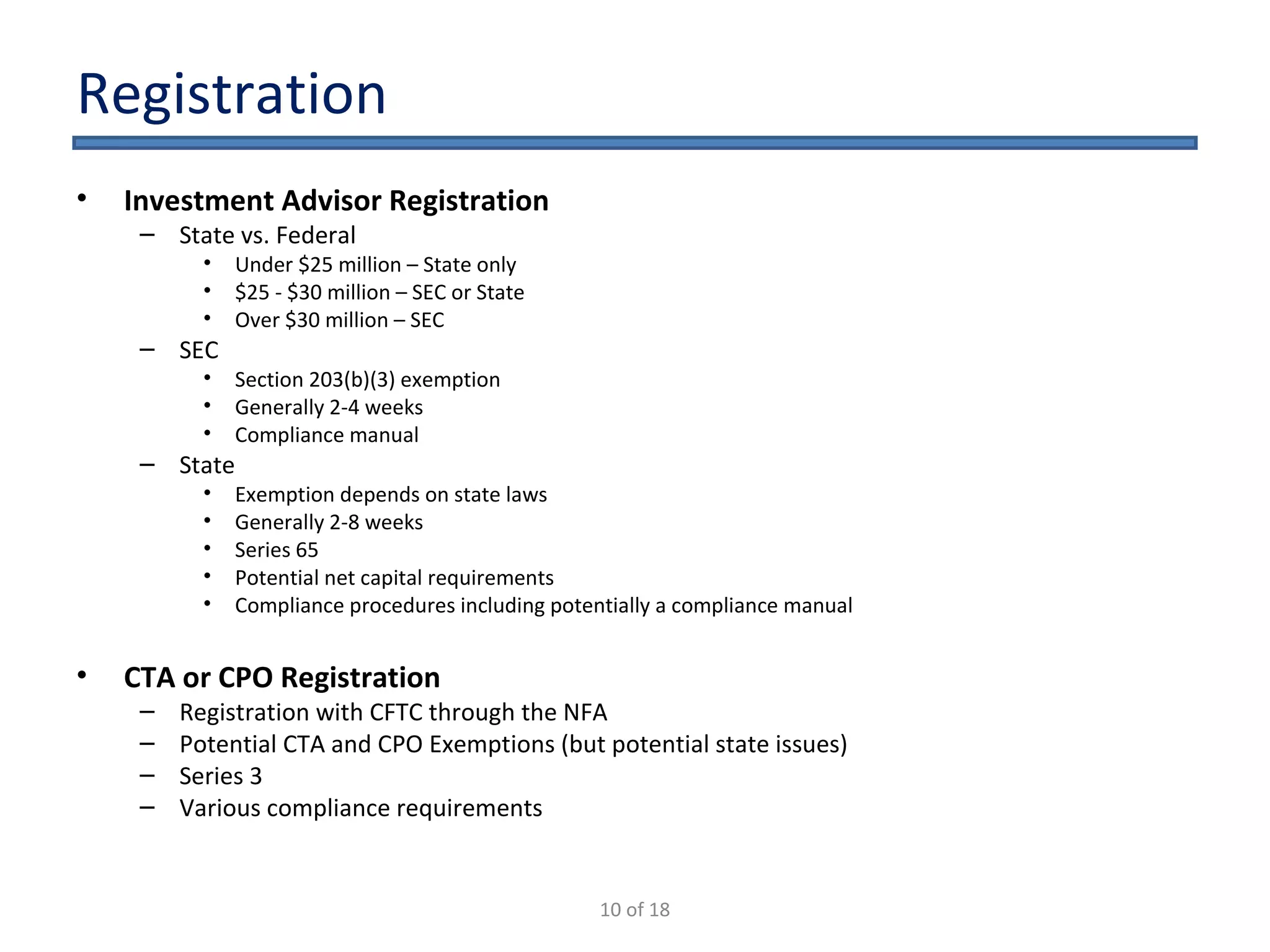
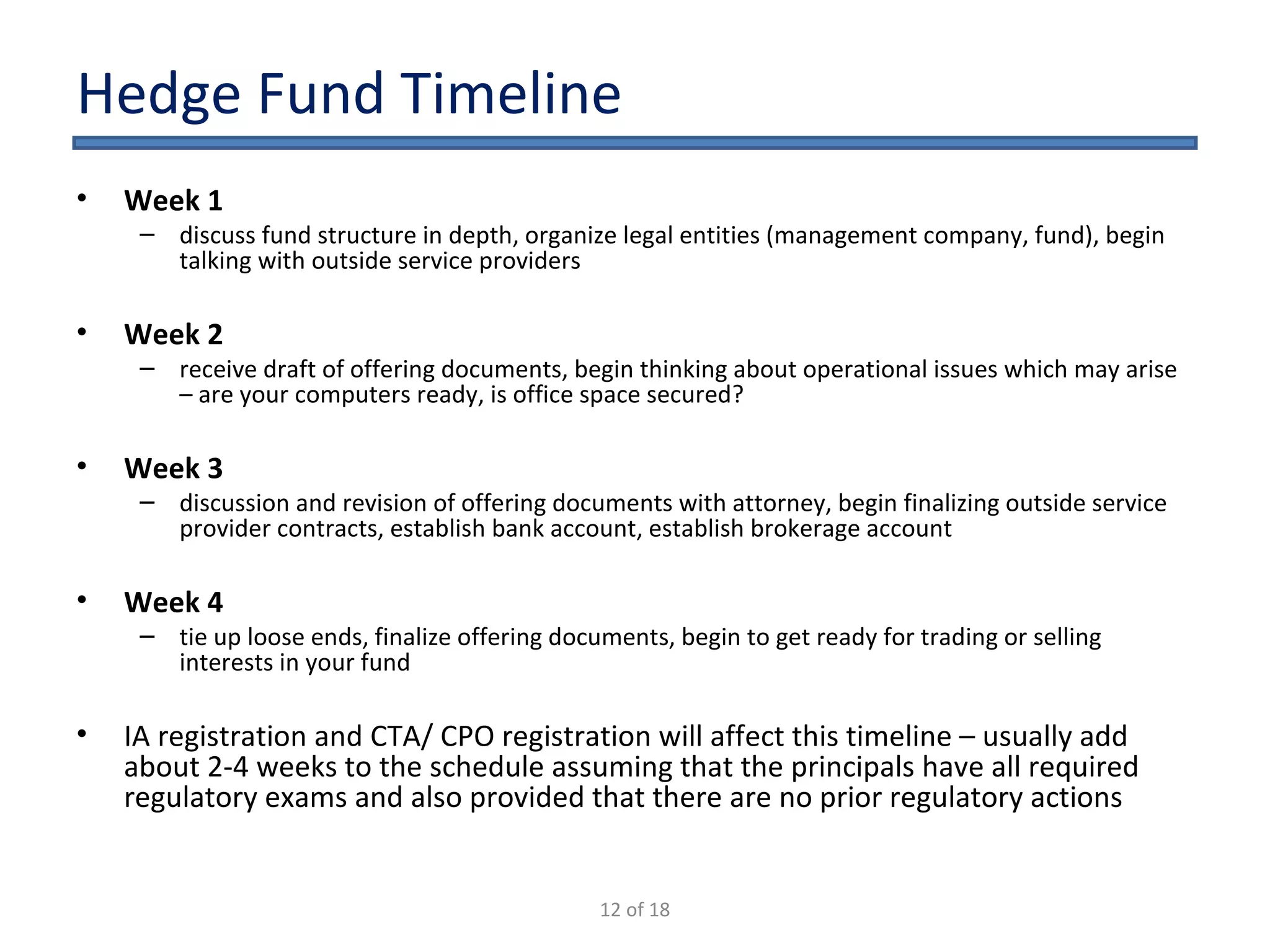
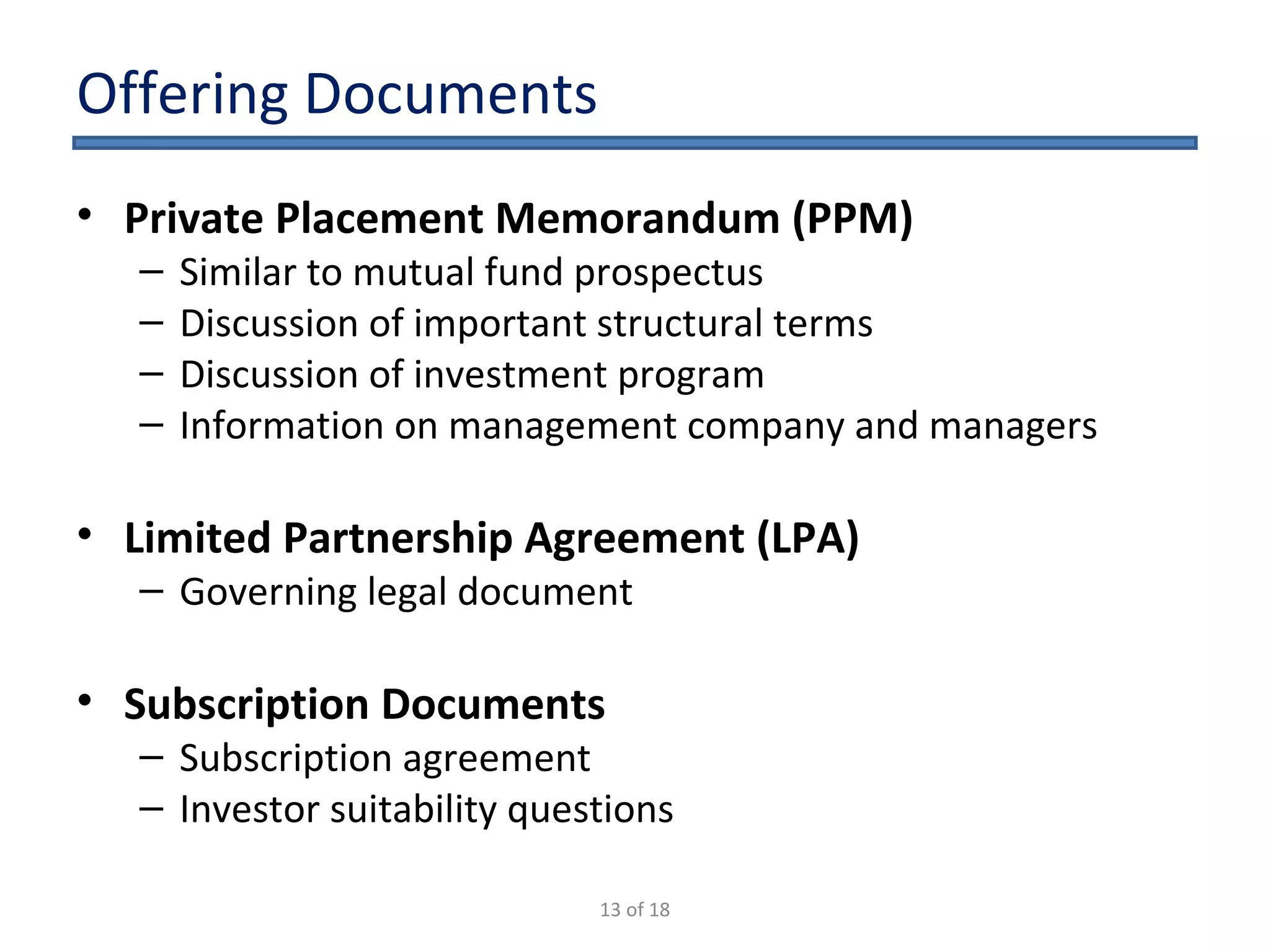
The document outlines the key considerations for starting a hedge fund in 2009, including fund characteristics, structure, and regulatory compliance issues. It details the roles of various service providers, the timeline for establishing a fund, and associated costs. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of adhering to securities regulations when raising capital and provides disclaimers regarding the legal advice offered in the presentation.