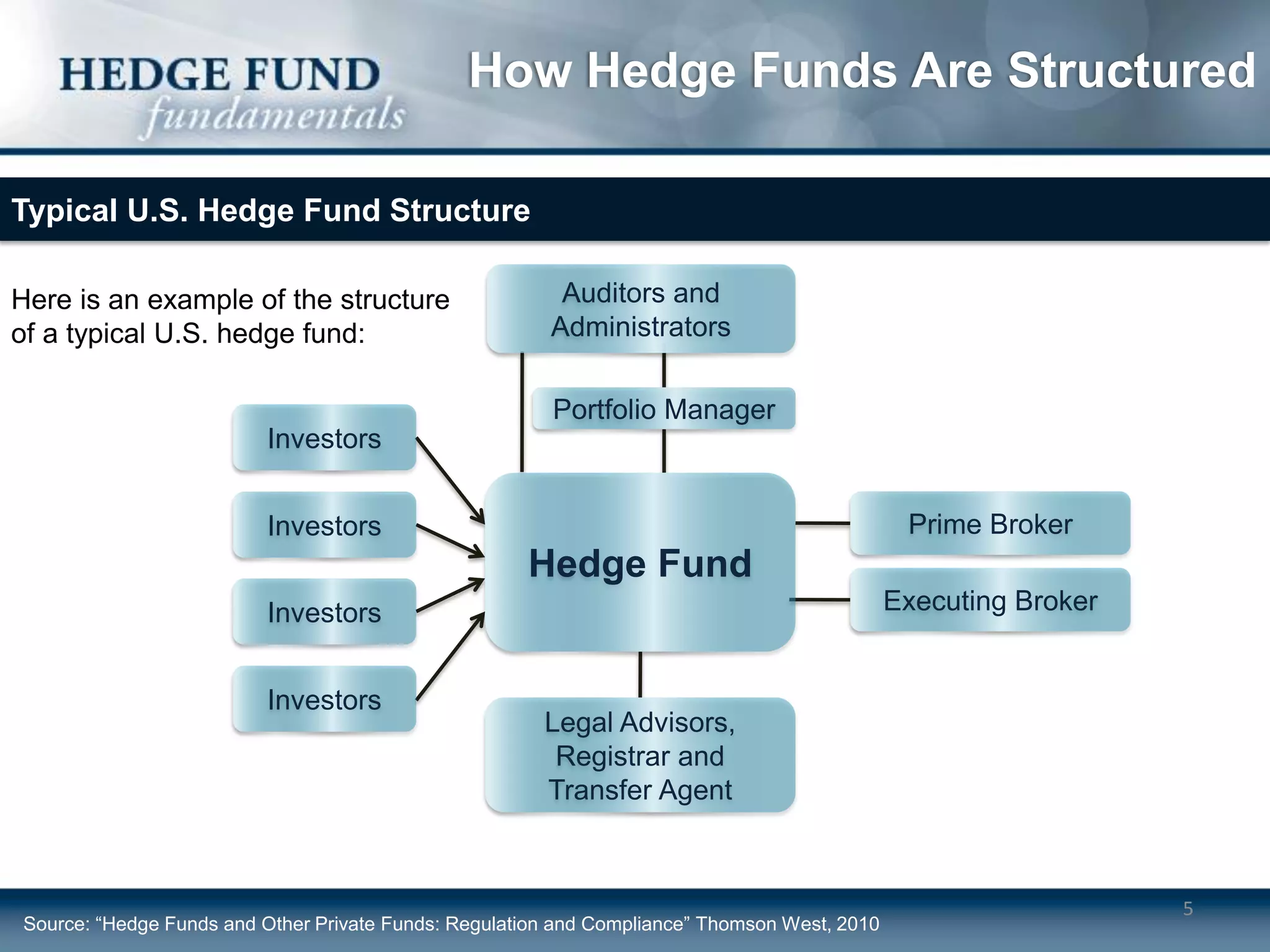
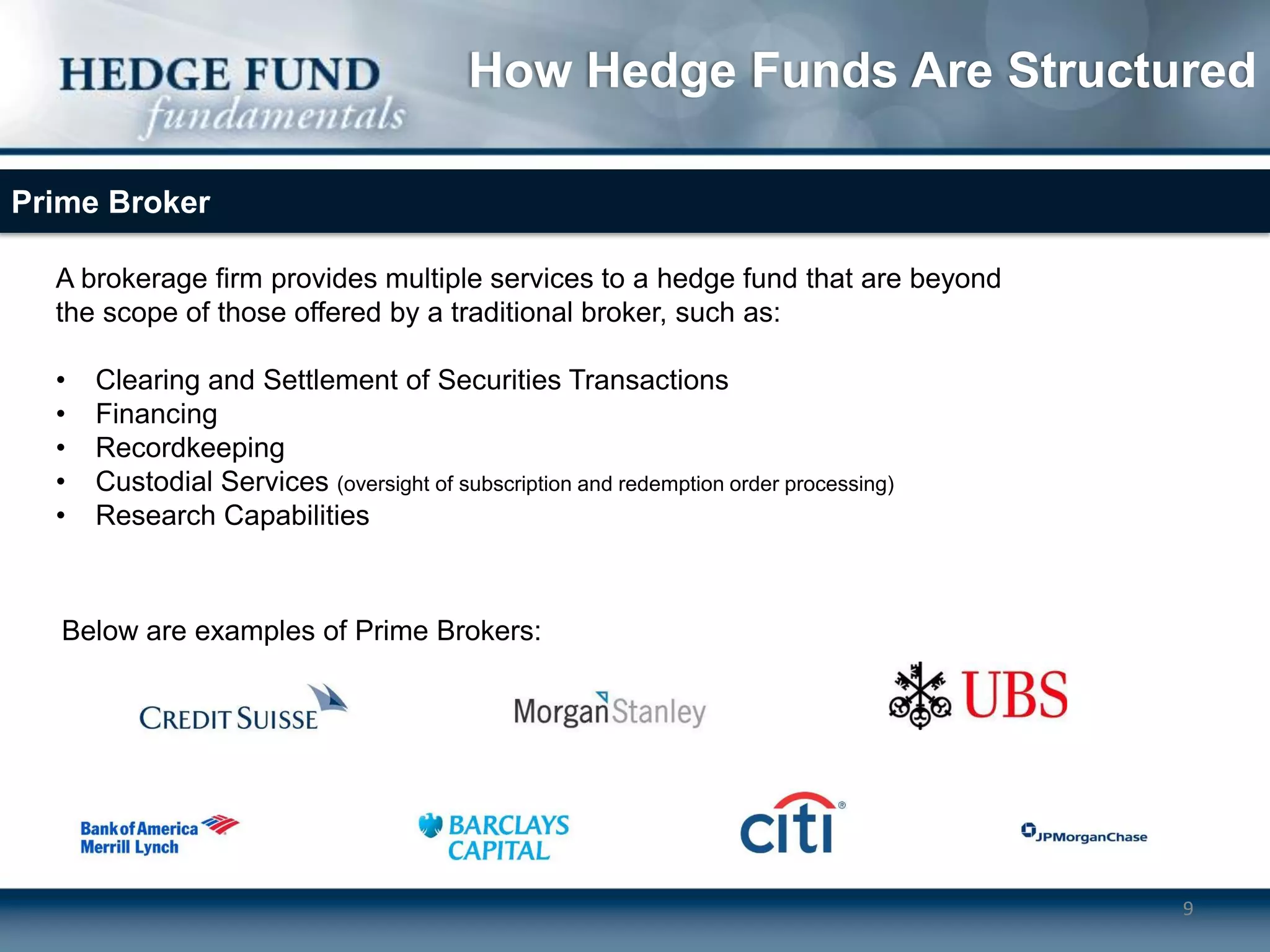
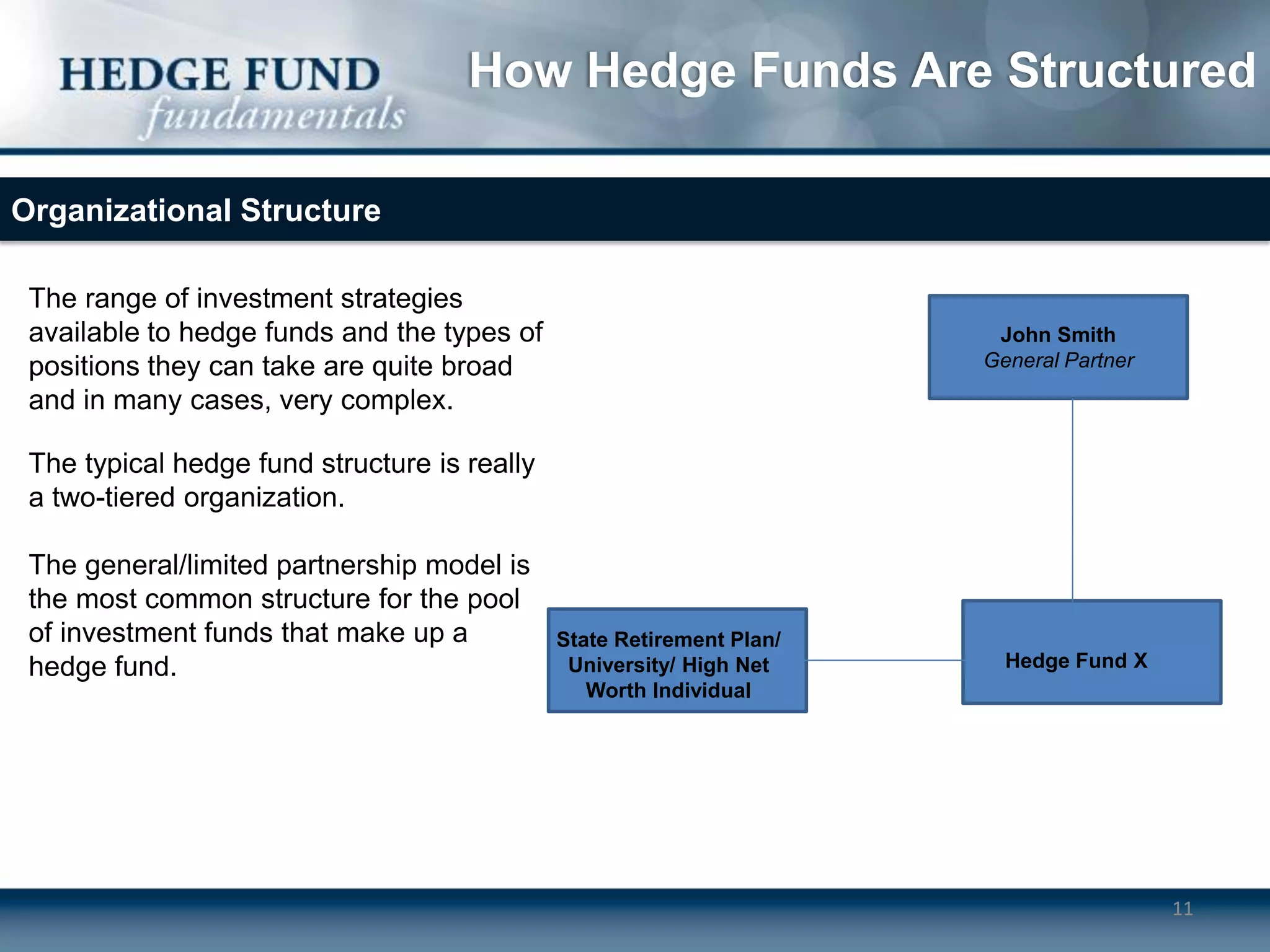
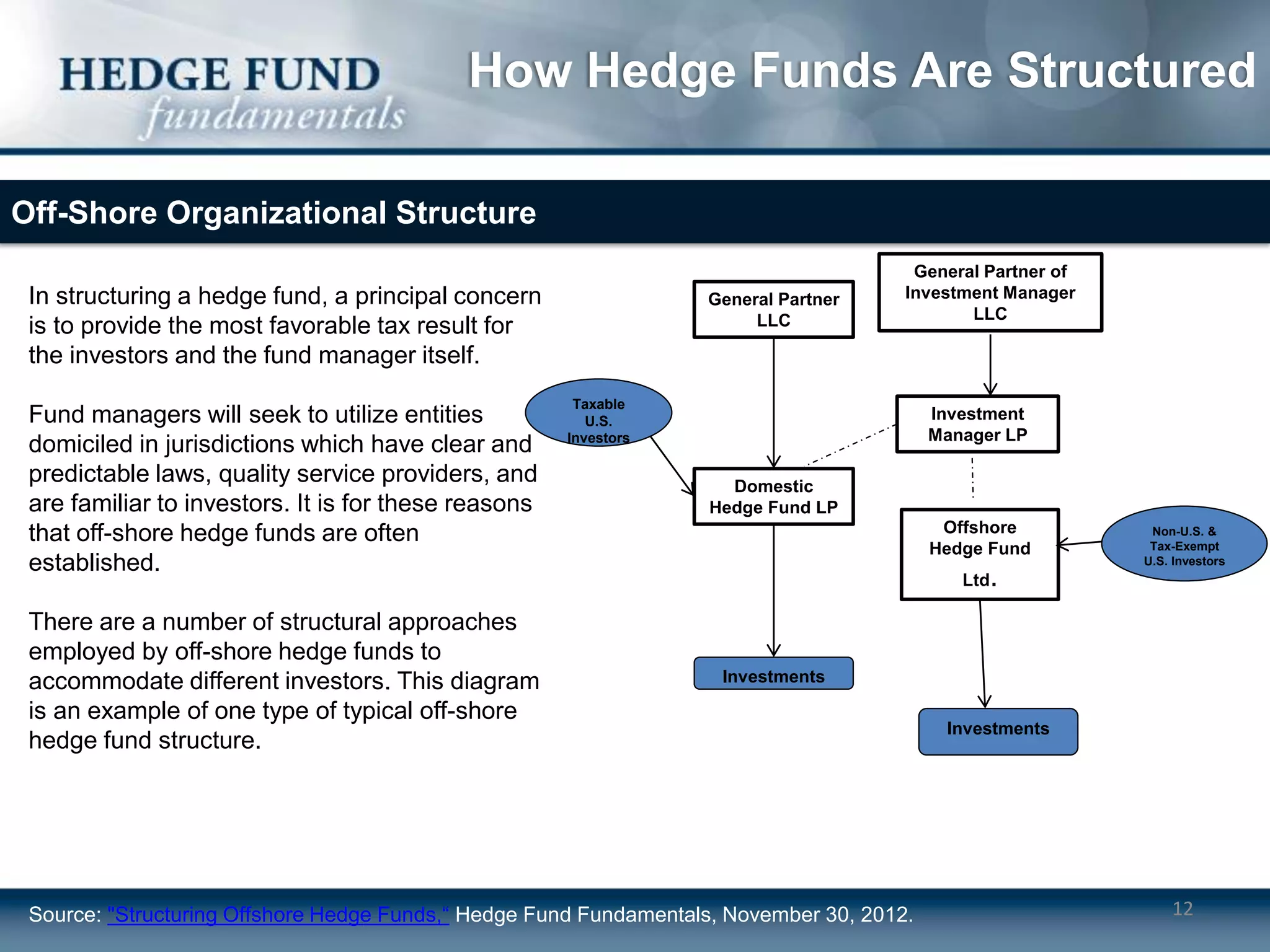
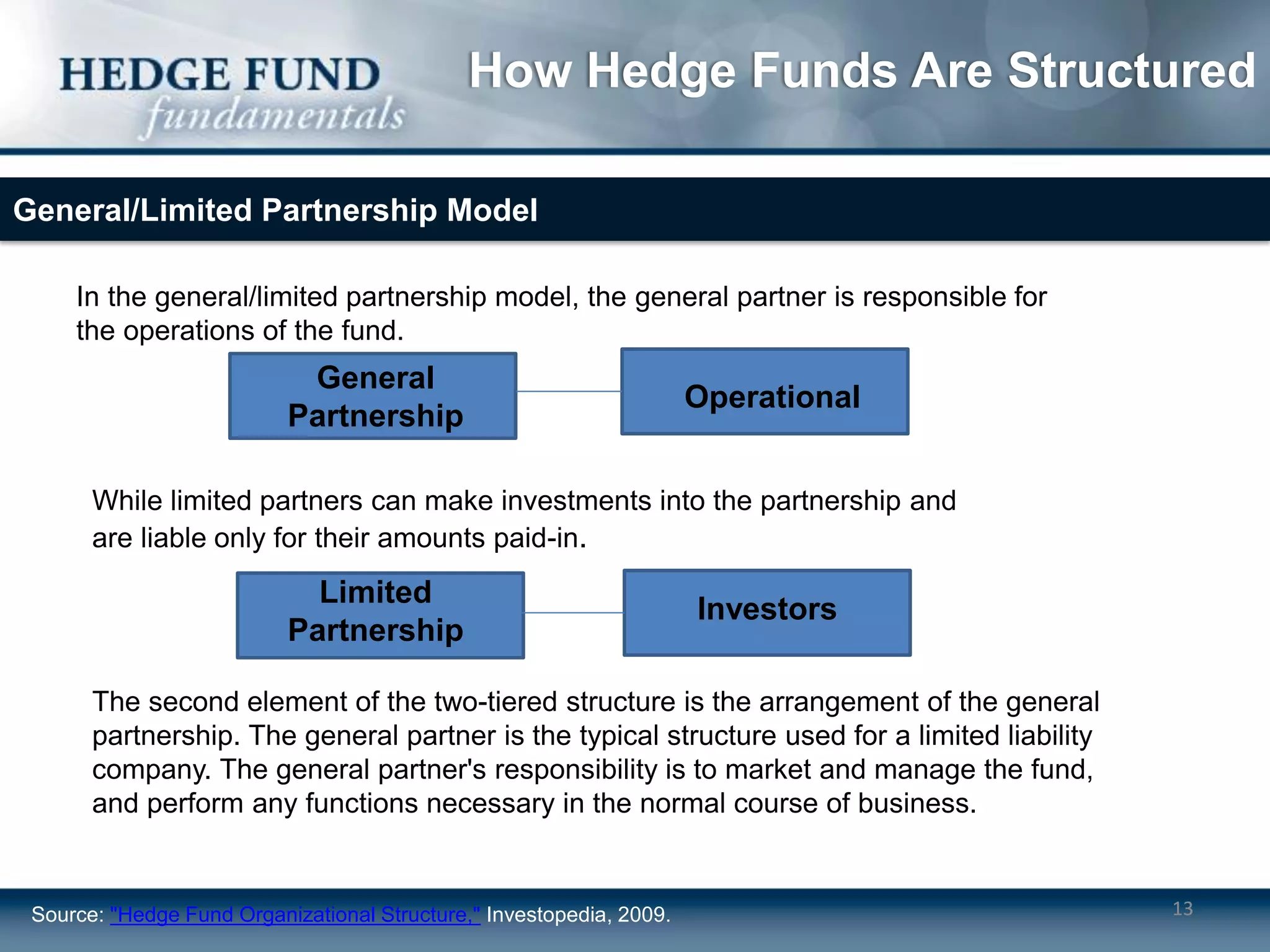
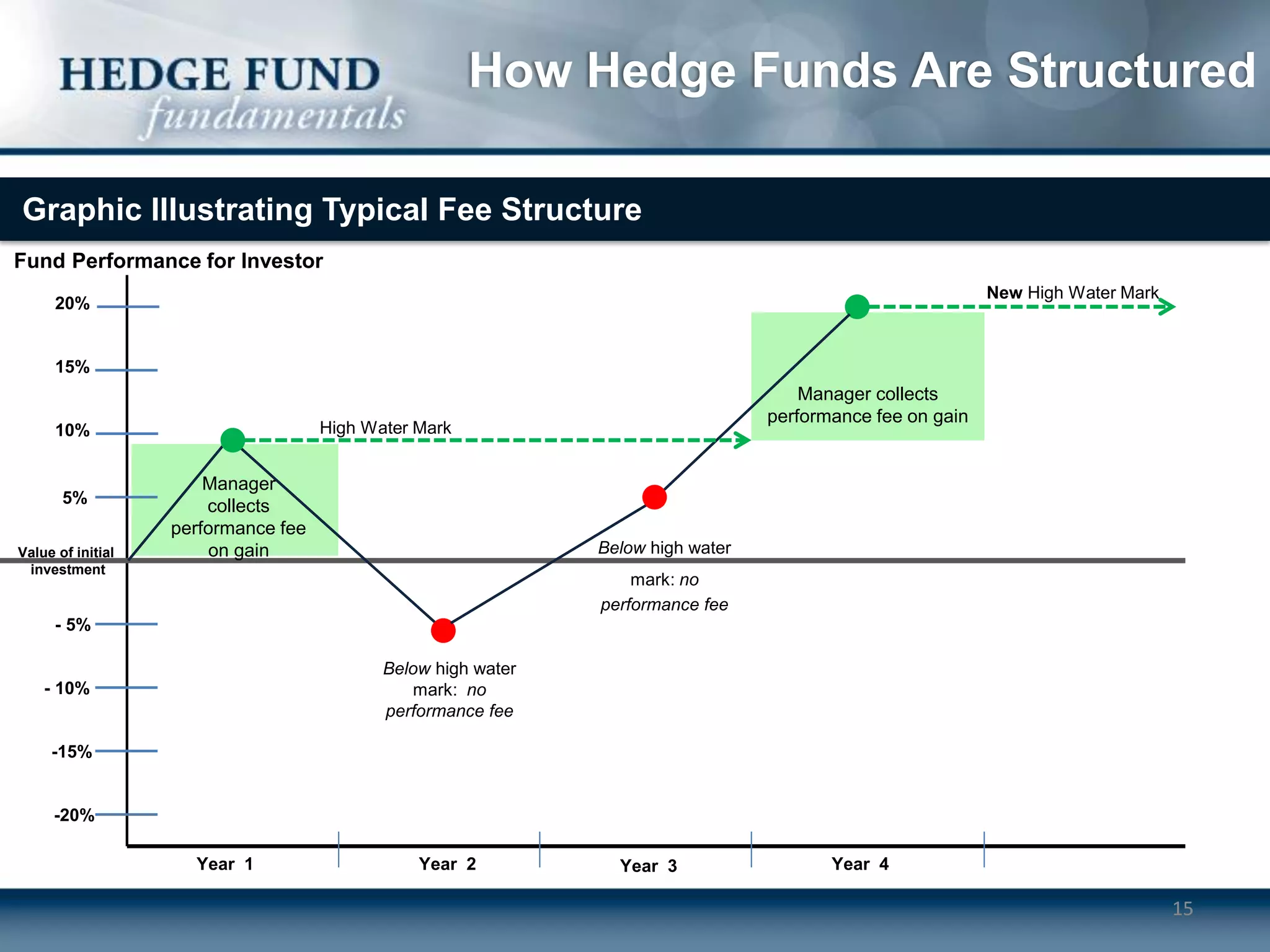
Hedge funds typically operate as limited partnerships between investors and fund managers. The fund manager determines investment strategies and makes decisions while also investing personal capital. Investors include accredited individuals and institutions. Hedge funds employ service providers like prime brokers, auditors, and lawyers. Fees include annual management fees of 1-2% of assets as well as performance fees if the fund exceeds a high-water mark.