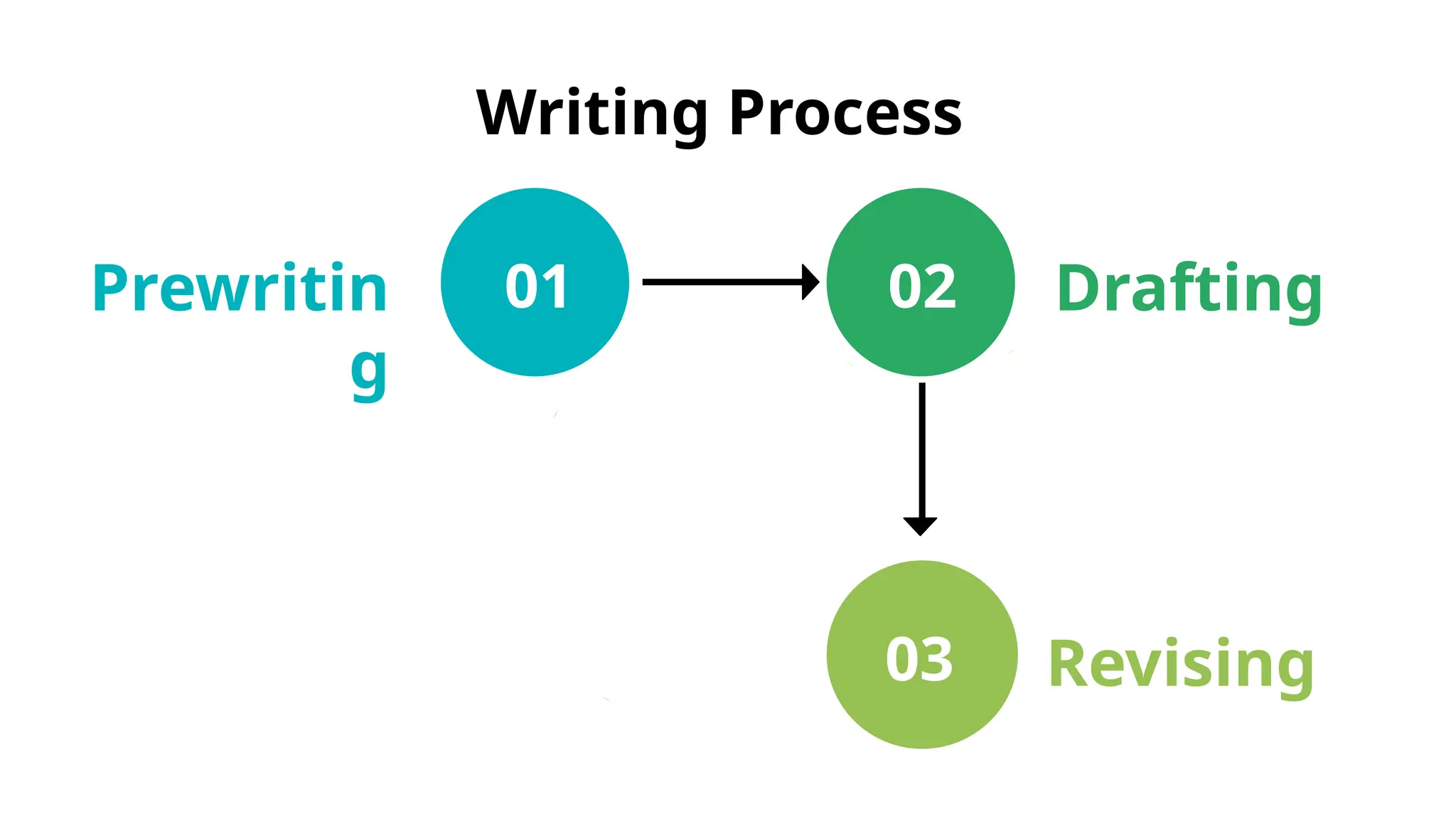
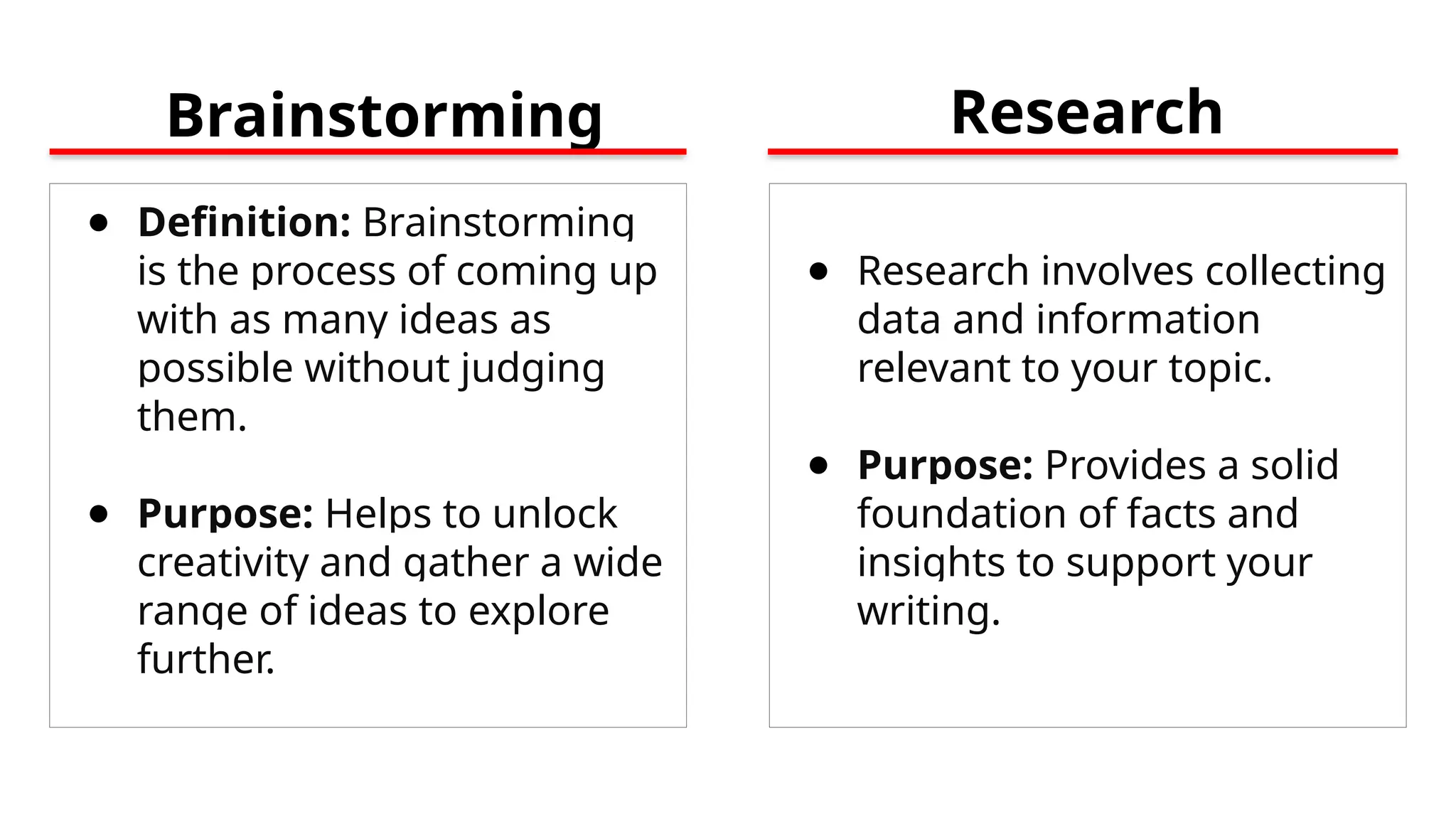
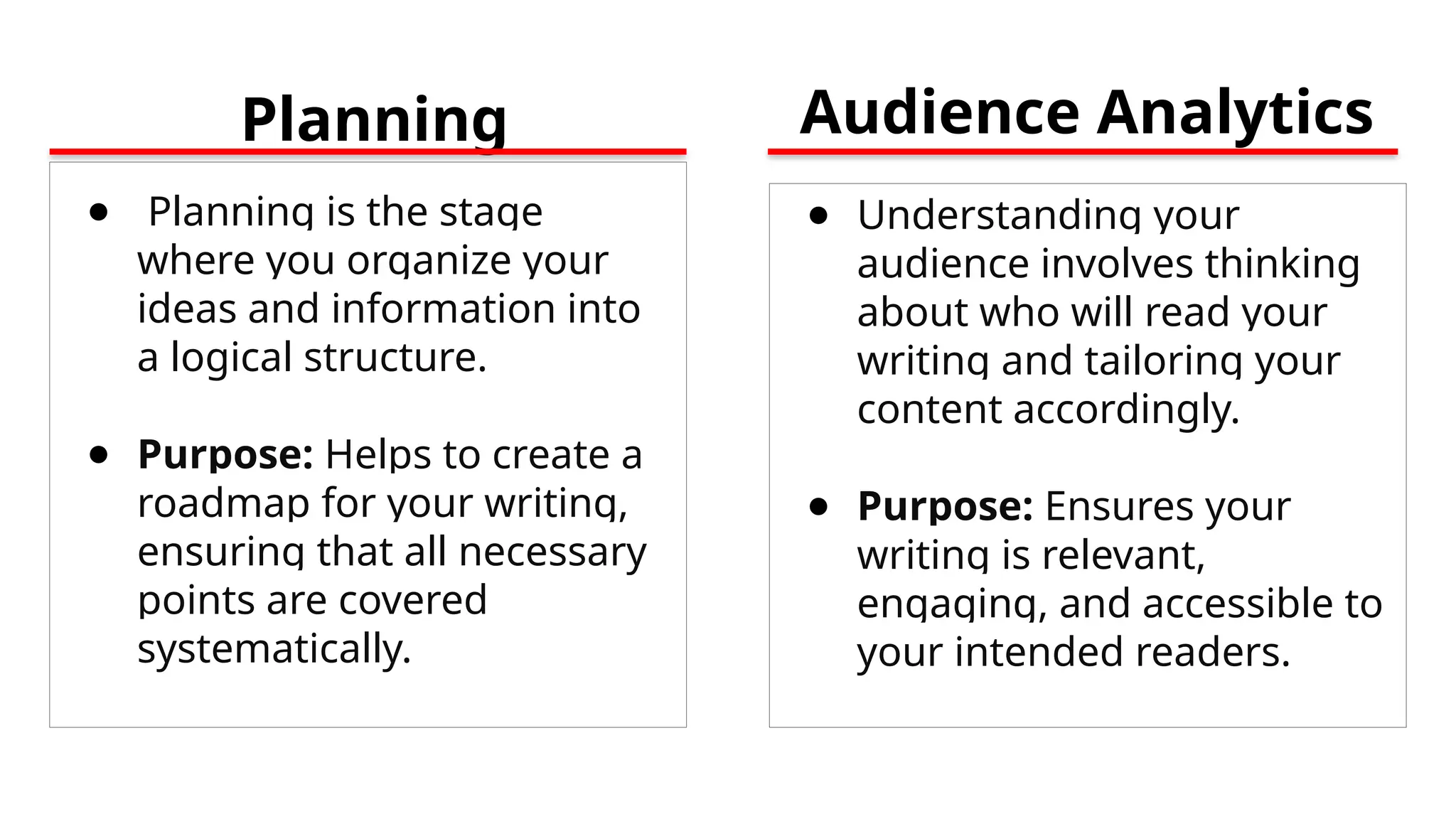
The document outlines the writing process, which includes prewriting, drafting, revising, and post-writing stages to help writers effectively communicate their ideas. Prewriting involves brainstorming, research, planning, and understanding the audience, while drafting focuses on content creation without perfection. The final stages include revising for clarity and coherence, and post-writing tasks like editing and formatting the document for submission.