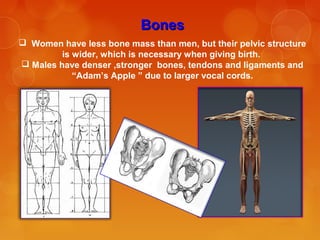
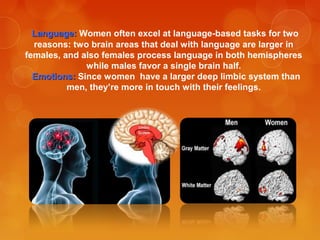
The document discusses the biological and social differences between men and women, detailing aspects such as reproductive anatomy, muscle mass, fat distribution, and brain characteristics. It highlights that while biological sex is genetically defined, gender is culturally constructed, and it delves into the physiological impacts of these differences. Additionally, it touches on stereotypes influencing performance in cognitive and behavioral tests, supported by research references.




















![Fausto -Sterling, Anne “Of Gender and Genitals” from Sexing the
body: gender politics and the construction of sexuality New York, NY:
Basic Books, 2000, [Chapter 3, pp. 44-77]
Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology, Technical Issues In
Reproductive Health, Columbia Mailman School of Public Health
Glucksman , A. (1981) Sexual Dimorphism in Human and Mammalian
Biology and Pathology (Academic Press, 1981), (pp. 66-75)
Gustafsson A & Lindenfors P (2004). "Human size evolution: no
allometric relationship between male and female stature". Journal of
Human Evolution 47 (4): (253–266)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fizjjhv1s4owtjqx4ake-140628045119-phpapp01/85/Biological-differences-between-the-sexes-27-320.jpg)