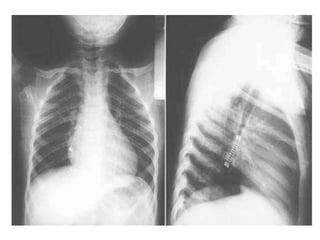
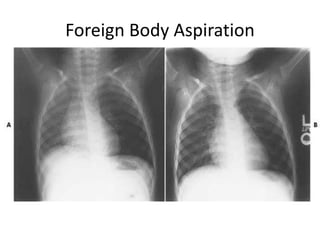
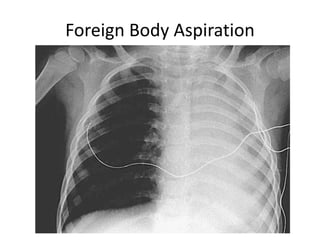
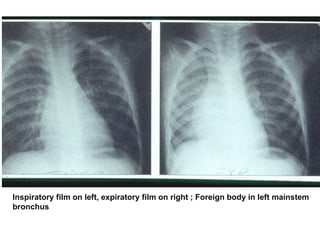
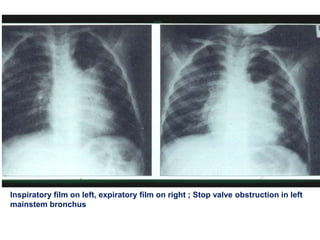
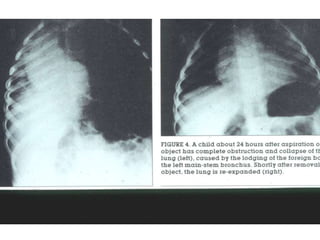
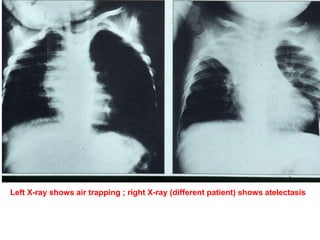
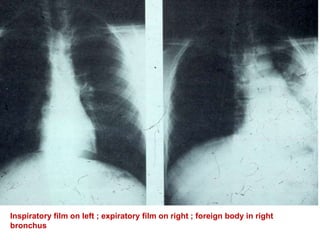
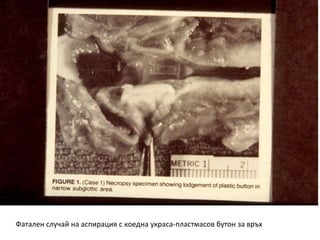
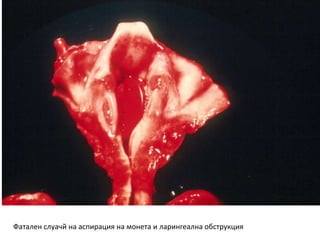
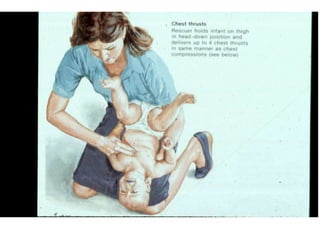
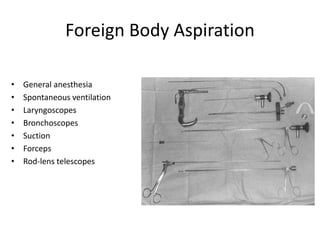
This document discusses foreign body aspiration into the tracheobronchial tree. It notes that around 1500-3000 cases occur annually in the United States, most commonly in children, where the most frequent objects aspirated are hot dogs, peanuts, and coins. It describes the potential effects such as complete or partial airway obstruction and the resulting symptoms. Common findings on imaging studies like chest x-rays are also summarized. Bronchoscopy is highlighted as the main management approach with a high success rate of removing aspirated objects.









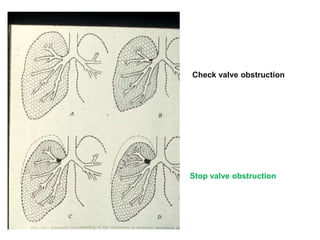
![TYPES OF OBSTRUCTION.
• 1. check valve: air can be inhaled but not
exhaled.[emphysema].
2. ball valve: air can be exhaled but not
inhaled.[broncho pul segment collapse].
• 3. bypass valve: FB partially obstructs
both in insp. and exp.
4. stop valve: total obstruction, airway
collapse and consolidation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-140607044426-phpapp01/85/slide-11-320.jpg)