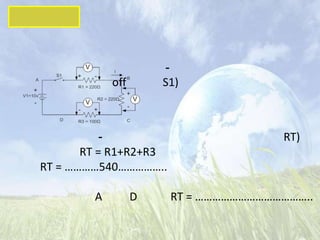
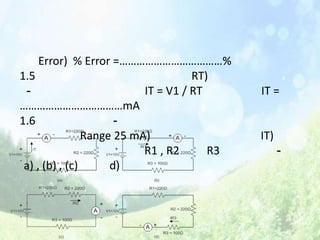
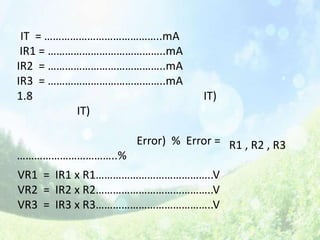
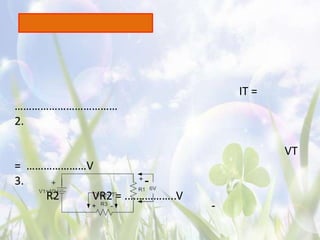
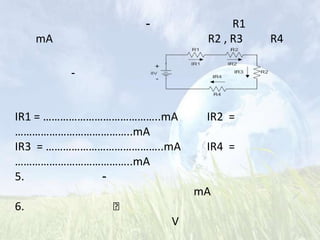
This document discusses series resistive circuits. It explains that in a series circuit, the total resistance (RT) is equal to the sum of all the individual resistances. It also states that the total voltage (V) across the circuit is equal to the current (I) multiplied by the total resistance (V=IRT). The document provides examples of calculating current, voltage drops across individual resistors, and the percentage error in several circuit calculations.