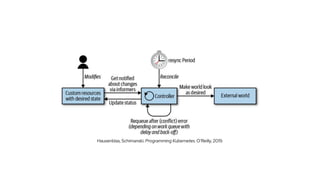
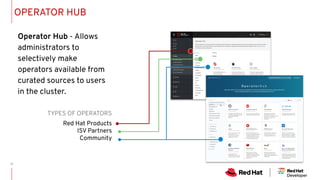
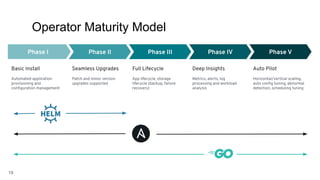
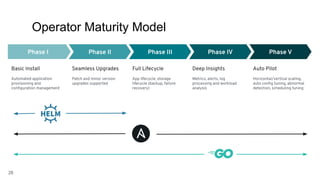
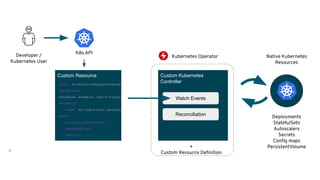
The document discusses the importance and functionality of operators in Kubernetes, emphasizing their role in automating the management of applications throughout their lifecycle, including installation, upgrades, and monitoring. It describes the operator maturity model, which outlines various phases of capabilities from basic installation to advanced autopilot features that minimize manual interventions. Key benefits of using operators include reduced upgrade risks, improved operational insights, and enhanced service delivery experiences for users.











![13
Custom Resource (CR)
kind: ProductionReadyDatabase
apiVersion: database.example.com/v1alpha1
metadata:
name: my-production-ready-database
spec:
clusterSize: 3
readReplicas: 2
version: v4.0.1
[...]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sreprincipleandoperatorpractice-devnation2020-07-16-200716172259/85/SRE-principles-and-Kubernetes-Operator-practice-DevNation-Tech-Talk-13-320.jpg)