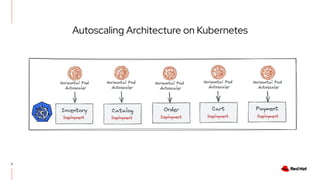
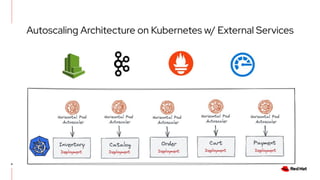
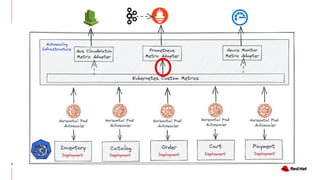
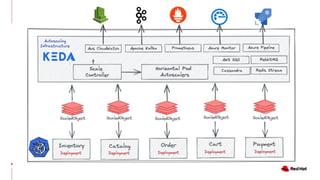
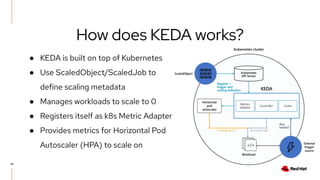
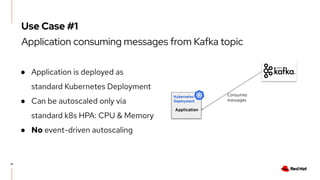
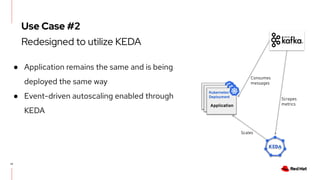
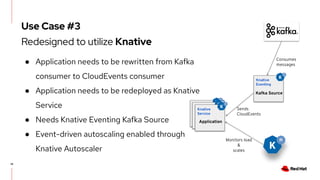
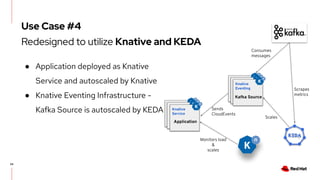
The document discusses KEDA (Kubernetes Event-driven Autoscaling) and its integration with Knative for simplifying autoscaling in Kubernetes. It outlines KEDA's capabilities, design iterations, and use cases, highlighting its event-driven approach to automatically scale deployments based on external metrics such as messages in Kafka. Additionally, it presents the distinction between KEDA's pull model and Knative's push model, showcasing how they can complement each other in handling autoscaling for serverless applications.