Embed presentation
Download to read offline

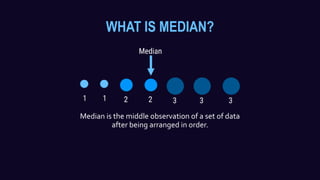
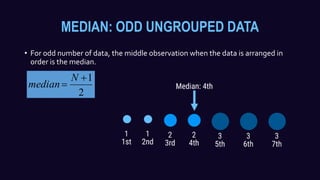


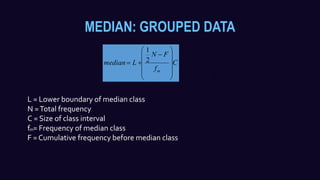

This document discusses measures of central tendency and how to calculate the median. It defines the median as the middle value in a data set arranged in order. For an odd number of values, the median is the middle value. For an even number, the median is the average of the two middle values. It provides examples of calculating the median for both ungrouped and grouped data sets.






