This document provides information about Individualized Education Plans (IEPs), including:
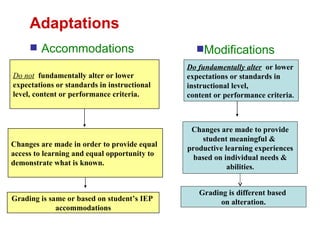
1. The difference between accommodations and modifications for students with IEPs. Accommodations change how students access or demonstrate learning but do not alter the standards, while modifications fundamentally change standards.
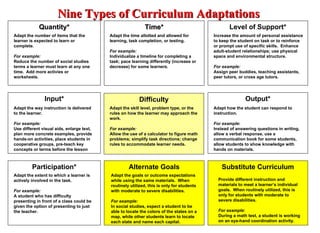
2. Nine types of curriculum adaptations that can be included in a student's IEP as accommodations or modifications, such as changes to instruction delivery, time, participation, and goals.
3. An activity where participants discuss accommodations and modifications for a sample student scenario using a provided IEP form.