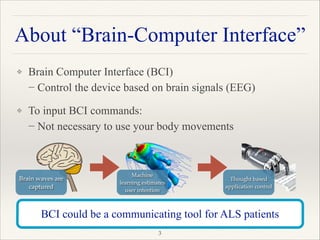
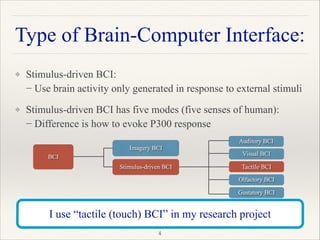
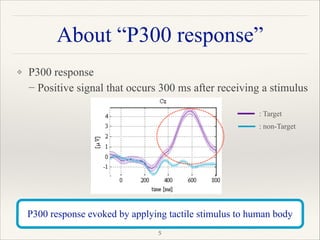
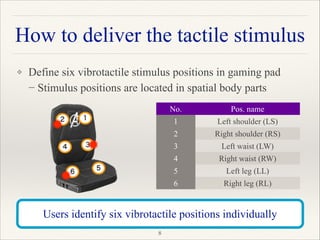
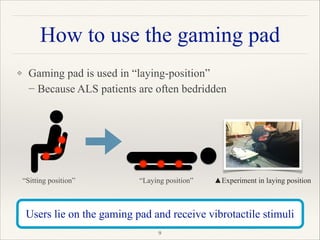
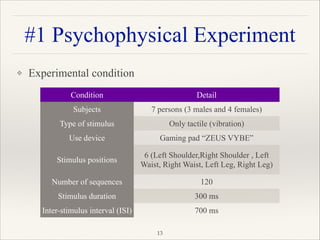
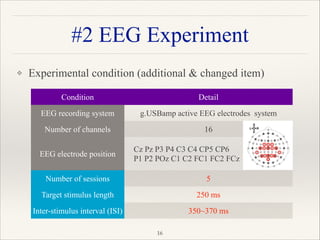
This document outlines a research project focused on developing a tactile brain-computer interface (BCI) to facilitate communication for ALS patients who cannot move their muscles. The study utilizes a gaming pad that delivers vibrotactile stimuli to various body parts and evaluates user response through psychophysical and EEG experiments to validate the effectiveness of the BCI. Results indicate that the proposed method shows high performance in command identification and clearly evokes the P300 response associated with target stimuli.






![#1 Psychophysical Experiment
One Sequence [11sec]
Vibrate!
③
Vibrate!
①
Vibrate!
⑥
Vibrate!
⑤
Vibrate!
④
Vibrate!
②
time [sec]
1. Present Target Stimulus [5sec] 2. Random Stimulus Trial [6sec]
Vibrate!
④
Vibrate
Example
[1sec]
Break Time
[2sec]
6 7 8 9 101 2 3 4 50
Vibration Each Stimulus [1sec × 6]
"12
Present Target
[2sec]
❖ The detail flow of one sequence
press!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/publother4presen-160719053127/85/Spatial-tactile-brain-computer-interface-paradigm-by-applying-vibration-stimulus-to-large-body-areas-12-320.jpg)


![❖ Boxplots of all subjects’ response
− Average and distribution of the response time for each target stimulus
"18
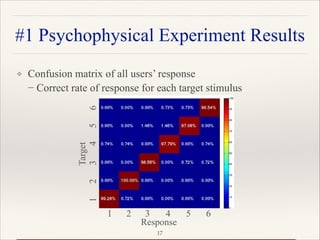
#1 Psychophysical Experiment Results
Command
Responsetime[ms]
300 ms
200300400500600700800
Median value
Minimum value
Maximum value
1/4 value
3/4 value
1 2 3 4 5 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/publother4presen-160719053127/85/Spatial-tactile-brain-computer-interface-paradigm-by-applying-vibration-stimulus-to-large-body-areas-18-320.jpg)
![❖ EEG experiment SWLDA the accuracy for each of the 7 subjects
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
#1 #2 #3 #4 #5 #6 #7Ave.
42.7%
50.0%
73.4%
16.7%
46.7%
43.3%
30.0%
38.9%
"19
#2 EEG Experiment Results
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
100%
#1 #2 #3 #4 #5 #6 #7 Ave.
76.2%
100%100%
50%
66.7%
83.3%
50%
83.3%
Accuracy[%]
Average accuracy rates Max accuracy rates
Users Users
Chance level:
16.7%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/publother4presen-160719053127/85/Spatial-tactile-brain-computer-interface-paradigm-by-applying-vibration-stimulus-to-large-body-areas-19-320.jpg)
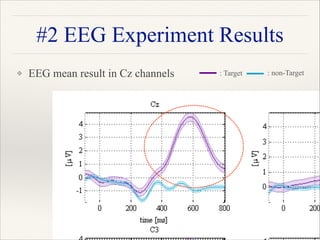
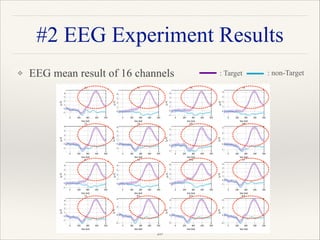

![❖ EEG experiment ITR results of 7 uses
"22
Subject Max accuracy [%] ITR [bit/min]
#1 83.3 4.30
#2 50 1.18
#3 83.3 4.30
#4 66.7 2.48
#5 50 1.18
#6 100 7.18
#7 100 7.18
#2 EEG Experiment Result](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/publother4presen-160719053127/85/Spatial-tactile-brain-computer-interface-paradigm-by-applying-vibration-stimulus-to-large-body-areas-23-320.jpg)
