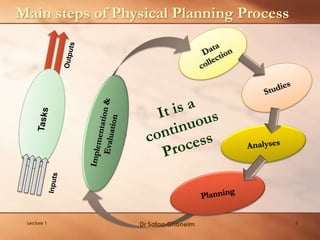
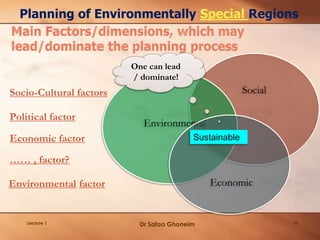
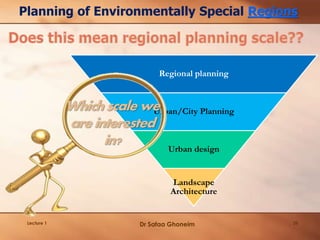
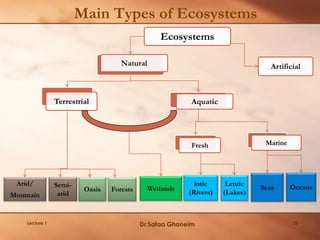
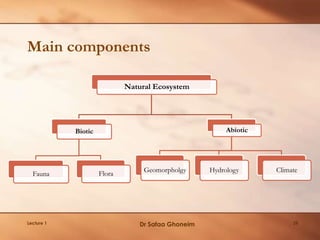
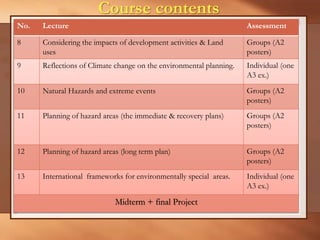
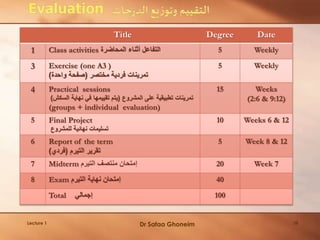
This lecture provides an overview and agenda for the course "Planning of Environmentally Special Regions". It discusses the focus of the course, outlines the planning process, and emphasizes the importance of understanding ecosystems as the first step. Key points covered include identifying the types and components of ecosystems, their interactions and dynamics, as well as the benefits they provide. The lecture also highlights various socio-cultural, political, economic and environmental factors that influence planning for special regions and stresses the need for an integrated and responsive planning approach.