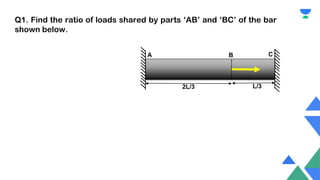
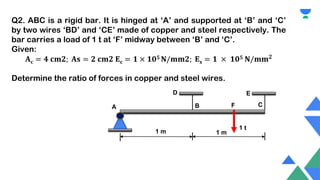
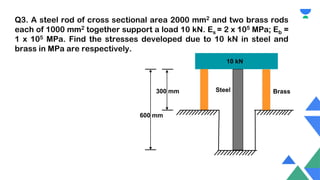
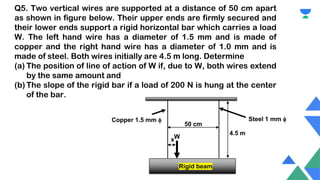
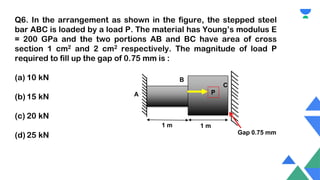
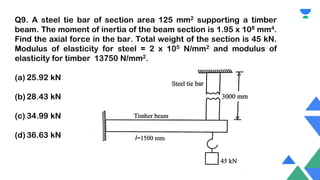
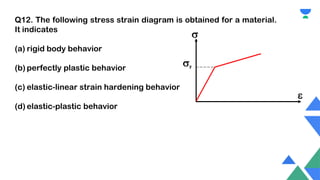
This document contains a practice session on strength of materials with 12 multiple choice questions. An expert named Lamiya Naseem who has over 3 years of teaching experience and has mentored over 50,000 students is providing online classes, study material, test preparation and personalized guidance through an education platform. Information about subscription plans and contact details are also provided.