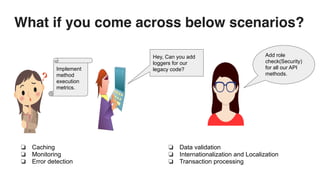
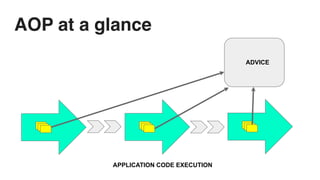
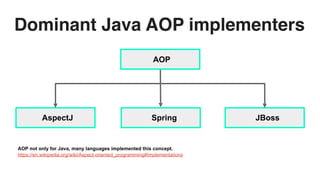
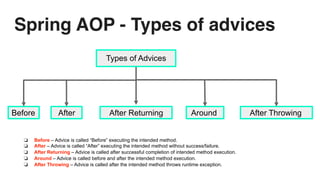
This document discusses cross-cutting concerns in programming and introduces aspect-oriented programming (AOP) as a solution to improve modularity by encapsulating these concerns into reusable aspects. It outlines the importance of addressing issues like scattered code and maintainability, as well as the key terminology and various types of advice used in AOP, particularly within Java frameworks like Spring. The document highlights the benefits of AOP such as clean code isolation, simplified maintenance, and improved code structure.