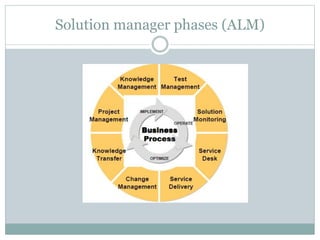
This document provides an overview of SAP Solution Manager (SolMan). SolMan is a centralized system management suite that can manage a large SAP system landscape. It takes a consistent, phase-oriented approach to application lifecycle management, and provides functionality for implementation, operation, and optimization of SAP solutions. Key offerings of SolMan include project management, service desk, test management, change request management, business process monitoring, and e-learning capabilities.