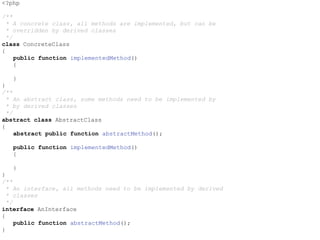
The document discusses the SOLID principles of object-oriented design:
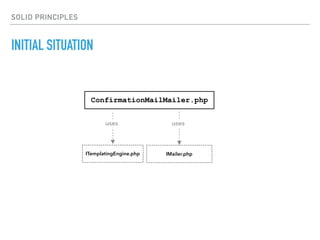
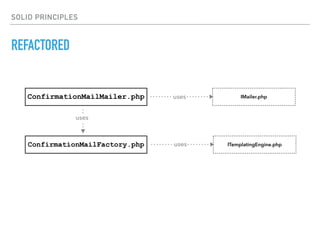
- The Single Responsibility Principle states that a class should have one, and only one, reason to change. An example class that violates this principle is refactored to separate concerns into distinct classes.
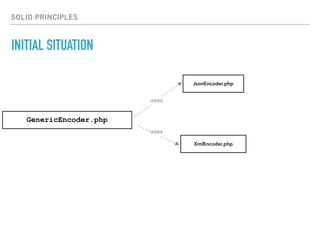
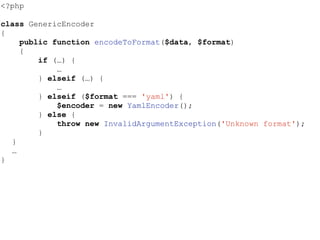
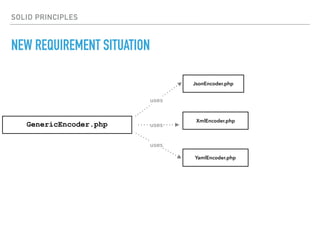
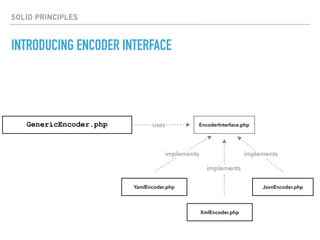
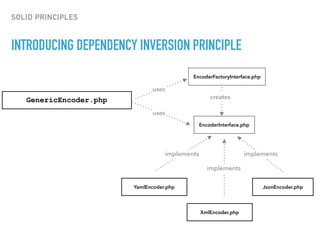
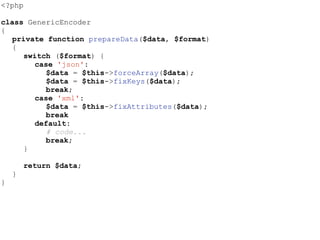
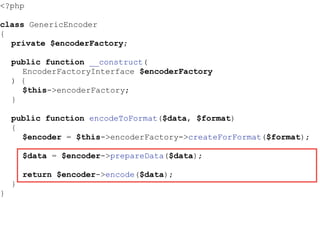
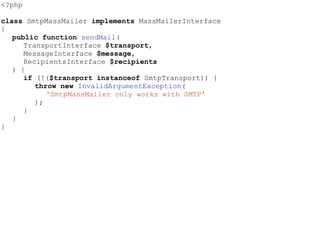
- The Open/Closed Principle states that a class should be open for extension but closed for modification. An encoder class is refactored to use polymorphism and dependency injection to follow this principle.
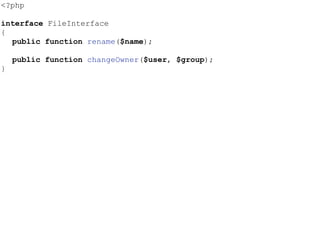
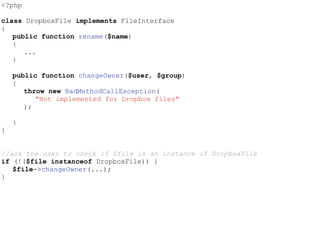
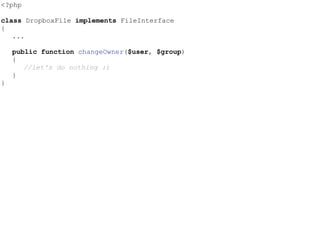
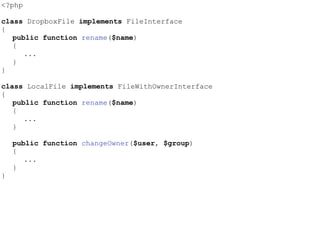
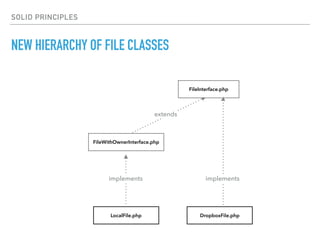
- The Liskov Substitution Principle states that subclasses must be substitutable for their base classes. Examples of violations include subclasses not implementing base class methods or having incompatible method signatures.








![<?php
class ConfirmationMailMailer
{
private $templating;
private $mailer;
public function __construct(
ITemplatingEngine $templating,
IMailer $mailer
) {
$this->templating = $templating;
$this->mailer = $mailer;
}
public function sendTo(User $user)
{
$message = $this->createMessageFor($user);
$this->sendMessage($message);
}
private function createMessageFor(User $user)
{
$subject = 'Confirm your email address';
$body = $this->templating
->render(
'confirmationMail.html.tpl', [
'confirmationCode' => $user->getConfirmationCode()
]
);
$message = new Message($subject, $body);
$message->setTo($user->getEmailAdress());
return $message;
}
private function sendMessage(IMessage $message)
{
$this->mailer->send($message);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-talk-170201014528/85/SOLID-PRINCIPLES-10-320.jpg)




![<?php
class ConfirmationMailFactory
{
private $templating;
public function __construct(ITemplatingEngine $templating)
{
$this->templating = $templating;
}
public function createMessageFor(User $user)
{
$subject = 'Confirm your email address';
$body = $this->templating
->render(
'confirmationMail.html.tpl', [
'confirmationCode' => $user->getConfirmationCode()
]
);
$message = new Message($subject, $body);
$message->setTo($user->getEmailAdress());
return $message;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-talk-170201014528/85/SOLID-PRINCIPLES-16-320.jpg)













![<?php
class EncoderFactory implements EncoderFactoryInterface
{
private $factories = [];
/**
* Register a callable that returns an instance of
* EncoderInterface for the given format.
*
* @param string $format
* @param callable $factory
*/
public function addEncoderFactory($format, callable $factory)
{
$this->factories[$format] = $factory;
}
public function createForFormat($format)
{
$factory = $this->factories[$format];
$encoder = $factory;
return $encoder;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-talk-170201014528/85/SOLID-PRINCIPLES-36-320.jpg)





















![<?php
interface RouterInterface
{
public function getRoutes() : RouterCollection;
}
class SimpleRouter implements RouterInterface
{
public function getRoutes()
{
$routes = [];
//add Route objects to $routes
$routes[] = ...;
return $routes
}
}
class AdvancedRouter implements RouterInterface
{
public function getRoutes()
{
$routeCollection = new RouteCollection();
...
return $routeCollection;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-talk-170201014528/85/SOLID-PRINCIPLES-66-320.jpg)
![<?php
interface RouterInterface
{
public function getRoutes() : RouterCollection;
}
class SimpleRouter implements RouterInterface
{
public function getRoutes() : RouteCollection
{
$routes = [];
//add Route objects to $routes2
$routes[] = ...;
return $routes
}
}
class AdvancedRouter implements RouterInterface
{
public function getRoutes() : RouteCollection
{
$routeCollection = new RouteCollection();
...
return $routeCollection;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-talk-170201014528/85/SOLID-PRINCIPLES-67-320.jpg)









![<?php
class FizzBuzz
{
public static function generateList($limit)
{
$list = [];
for ($number = 1; $number <= $limit; $number++) {
$list[] = self::generateElement($number);
}
return $list;
}
private static function generateElement($number)
{
if ($number % 3 === 0 && $number % 5 === 0) {
return 'FizzBuzz';
}
if ($number % 3 === 0) {
return 'Fizz';
}
if ($number % 5 === 0) {
return 'Buzz';
}
return $number;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-talk-170201014528/85/SOLID-PRINCIPLES-79-320.jpg)



![<?php
class FizzBuzz
{
private $rules = [];
public function addRule(RuleInterface $rule) {
$this->rules[] = $rule;
}
public static function generateList($limit)
{
...
}
private static function generateElement($number)
{
foreach ($this->rules as $rule) {
if ($rule->matches($number)) {
return $rule->getReplacement();
}
}
return $number;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-talk-170201014528/85/SOLID-PRINCIPLES-84-320.jpg)



![<?php
use DoctrineDBALConnection;
class Authentication
{
private $connection;
public function __construct(Connection $connection)
{
$this->connection = $connection;
}
public function checkCredentials($username, $password)
{
$user = $this->connection->fetchAssoc(
'SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = ?',
[$username]
);
if ($user === null) {
throw new InvalidCredentialsException(
"User not found."
);
}
//validate password
...
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-talk-170201014528/85/SOLID-PRINCIPLES-90-320.jpg)

![<?php
class UserRepository
{
private $connection;
public function __construct(Connection $connection)
{
$this->connection = $connection;
}
public function ofUsername($username)
{
return $this->connection->fetchAssoc(
'SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = ?',
[$username]
);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-talk-170201014528/85/SOLID-PRINCIPLES-93-320.jpg)