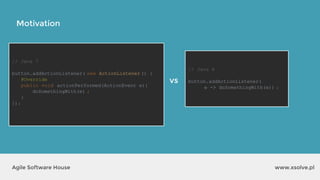
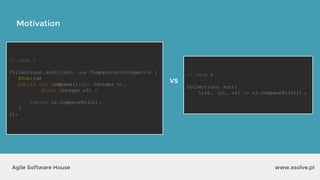
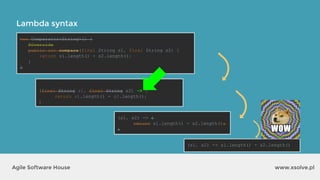
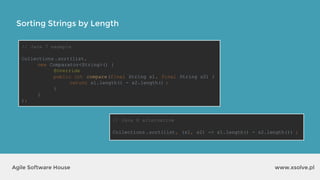
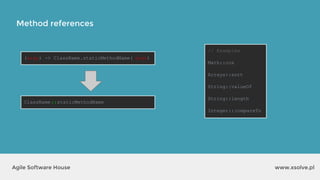
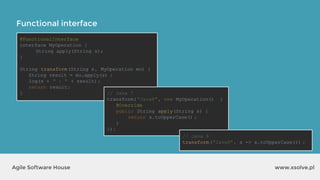
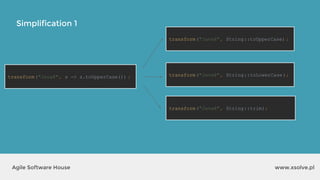
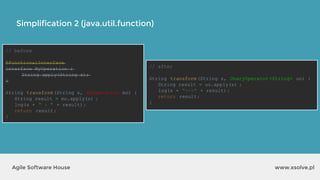
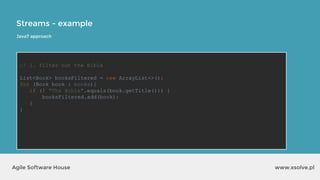
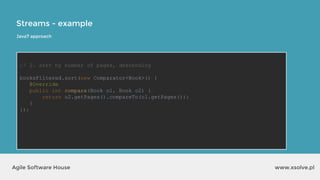
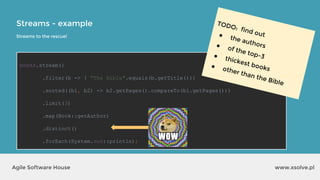
The document outlines the advantages of functional programming in Java 8, highlighting features such as lambdas, streams, and method references that simplify coding by reducing boilerplate. It contrasts Java 7 and 8 syntax for actions like sorting and filtering collections, illustrating how streams enable a more declarative programming style. Furthermore, the document explains core stream operations such as filtering, mapping, and reducing, emphasizing their efficiency and flexibility in utilizing functional programming principles.














![Streams - characteristics
www.xsolve.plAgile Software House
● Easily obtained from arrays or Collections
List aList = new ArrayList();
aList.stream();
Collection aCollection = new LinkedHashSet<>();
aCollection.stream();
Integer[] anArray = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
Stream.of(anArray); // Stream<Integer>
Stream.of("Hickory", "Dickory", "Dock");
// Stream<String>
aList.stream().filter(o -> o != null);
// Stream from another stream!
Chaining!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xsolvelaboratory1java823-160822083638/85/Xlab-1-Advantages-of-functional-programming-in-Java-8-29-320.jpg)
![Streams - characteristics
www.xsolve.plAgile Software House
● Easily obtained from arrays or Collections
● ...and transformed into arrays or Collections
List aList =
aStream.collect(Collectors.toList());
Object[] anArray = aStream.toArray();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xsolvelaboratory1java823-160822083638/85/Xlab-1-Advantages-of-functional-programming-in-Java-8-30-320.jpg)
![Streams - core methods (1/3)
www.xsolve.plAgile Software House
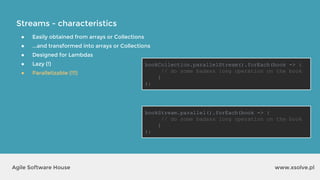
● forEach
void forEach(Consumer)
void forEachOrdered(Consumer)
Stream.of("Facebook", "Google", "xSolve")
.forEach(System.out::println);
output?
List<String> list =
Arrays.asList("Facebook",
"Google", "xSolve");
list.stream().forEach(String::toUpperCase);
System.out.println(list);
output?
Stream.of("Facebook", "Google", "xSolve")
.forEach(System.out::println).forEach
Stream.of("Facebook", "Google", "xSolve")
.forEach(System.out::println);
output:
Facebook
Google
xSolve
List<String> list =
Arrays.asList("Facebook",
"Google", "xSolve");
list.stream().forEach(String::toUpperCase);
System.out.println(list);
output: [Facebook, Google, xSolve]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xsolvelaboratory1java823-160822083638/85/Xlab-1-Advantages-of-functional-programming-in-Java-8-34-320.jpg)
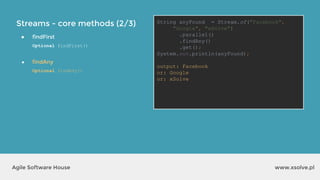
![Streams - core methods (2/3)
www.xsolve.plAgile Software House
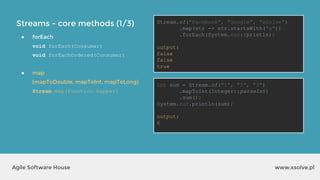
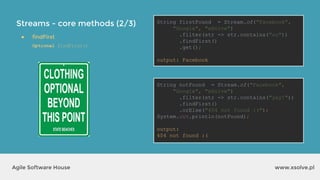
● findFirst
Optional findFirst()
● findAny
Optional findAny()
● collect
collect(Collector collector)
List<String> uppers = Stream.of("cyan",
"magenta", "yellow", "black")
.map(String::toUpperCase)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(uppers);
output?
List<String> uppers = Stream.of("cyan",
"magenta", "yellow", "black")
.map(String::toUpperCase)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(uppers);
output: [CYAN, MAGENTA, YELLOW, BLACK]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xsolvelaboratory1java823-160822083638/85/Xlab-1-Advantages-of-functional-programming-in-Java-8-39-320.jpg)
![Streams - core methods (2/3)
www.xsolve.plAgile Software House
● findFirst
Optional findFirst()
● findAny
Optional findAny()
● collect
collect(Collector collector)
● toArray
Object[] toArray()
Object[] objArray = Stream.of("cyan",
"magenta", "yellow", "black")
.map(String::toUpperCase)
.toArray();
String[] strArray = Stream.of("cyan",
"magenta", "yellow", "black")
.map(String::toUpperCase)
.toArray(String[]::new);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xsolvelaboratory1java823-160822083638/85/Xlab-1-Advantages-of-functional-programming-in-Java-8-40-320.jpg)


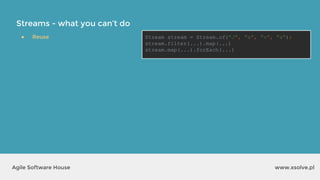
![Streams - what you can’t do
www.xsolve.plAgile Software House
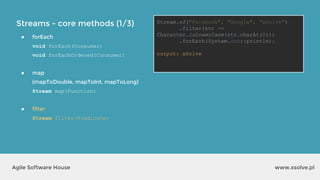
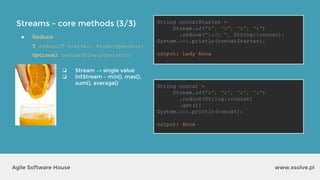
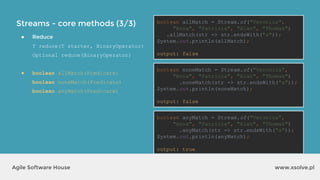
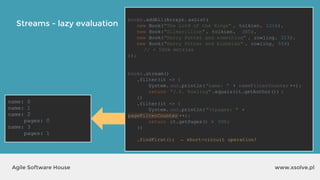
● Reuse
● Change surrounding local variables
int total = 0;
Stream.of("Mercury", "Venus", "Mars")
.forEach(str -> {
total += str.length();
});
int[] total = {0};
Stream.of("Mercury", "Venus", "Mars")
.forEach(str -> {
total[0] += str.length();
});
...but:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xsolvelaboratory1java823-160822083638/85/Xlab-1-Advantages-of-functional-programming-in-Java-8-47-320.jpg)


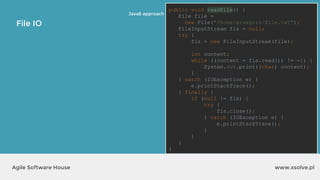
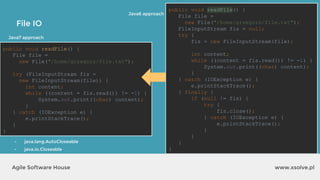

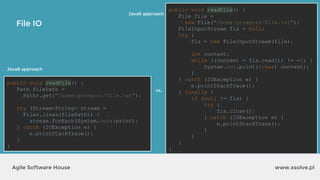

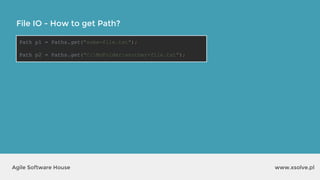

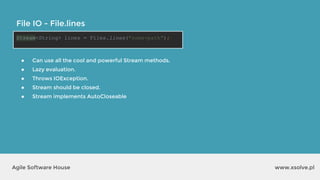
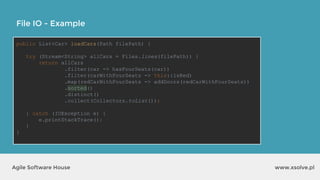
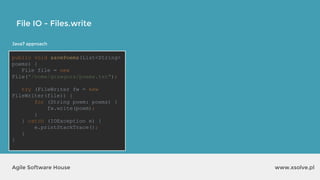
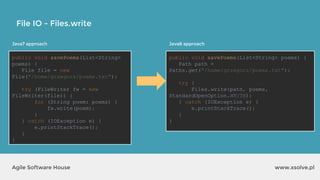
![www.xsolve.plAgile Software House
File IO - Files.write
Files.write(somePath, lines, someCharset, someOption);
Files.write(somePath, fileArray, someOption);
● somePath to file,
● lines e.g. List<String> lines, bytes[] data
● someCharset e.g. StandardCharsets.UTF_8
● someOption e.q. StandardOpenOption.APPEND](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xsolvelaboratory1java823-160822083638/85/Xlab-1-Advantages-of-functional-programming-in-Java-8-59-320.jpg)