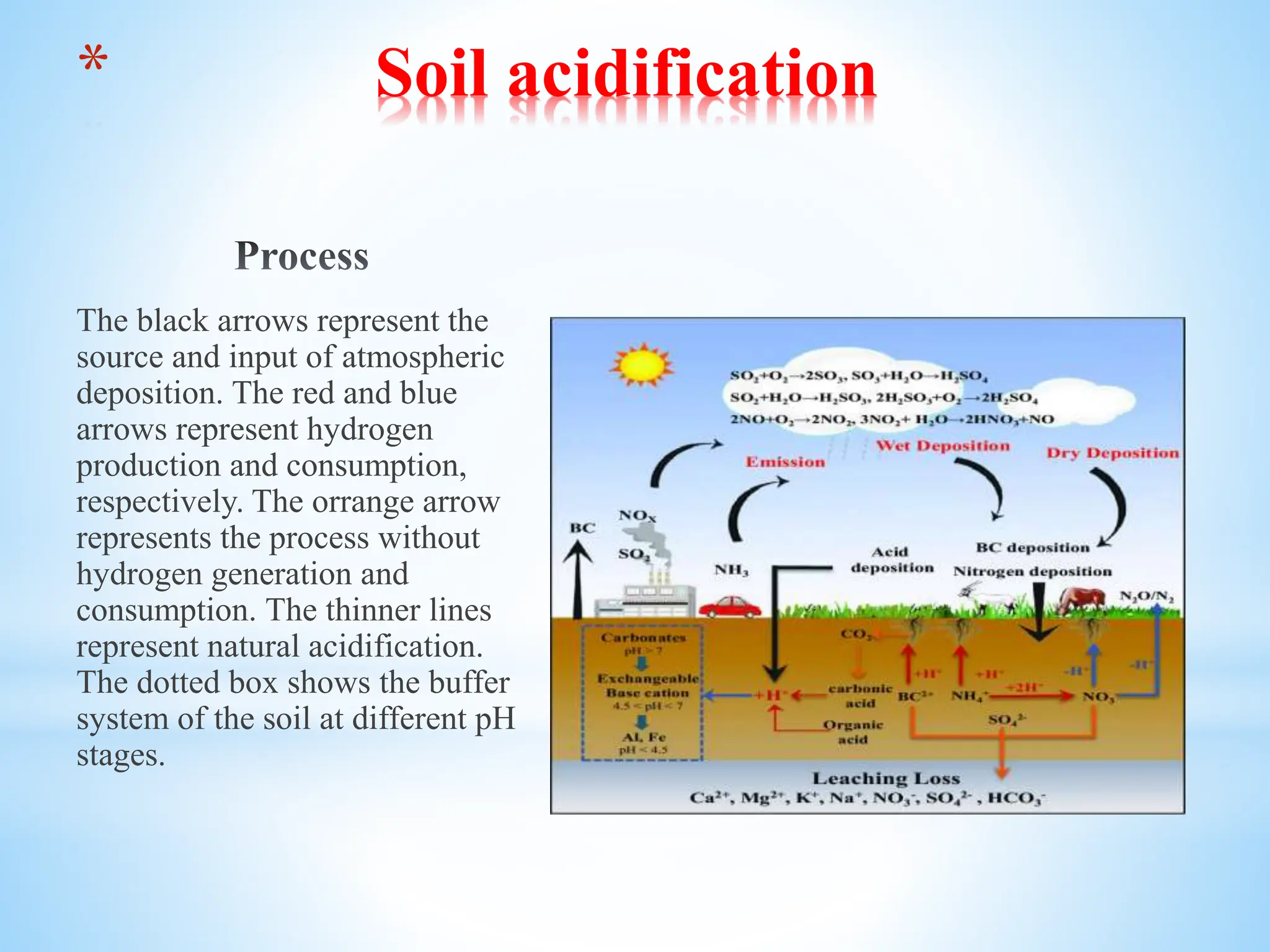
This presentation summarizes topics related to soil solidification, acidification, alkalinization, and pollution. It discusses the processes and causes of each, as well as remediation methods. Soil solidification involves adding materials like cement or lime to increase soil stability for construction. Acidification lowers soil pH through acid rain or fertilizers and harms nutrients, while alkalinization raises pH through irrigation and accumulates salts. Soil pollution contaminates soil from industry, agriculture, mining, or waste and impacts fertility, water, and crops. The presentation provides details on each topic.