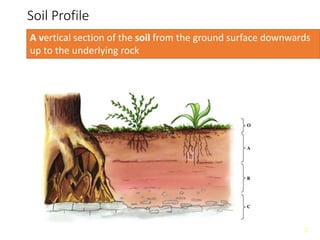
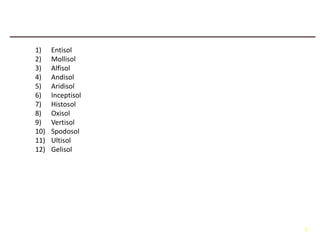
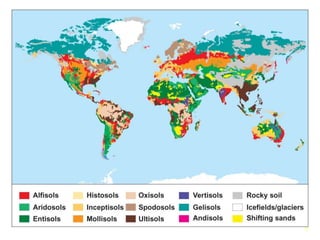
The document describes soil as a complex mixture of materials, highlighting the soil profile that illustrates its structure through various horizons, including organic layers and mineral content. It classifies soil into twelve orders, with specific characteristics of ultisol, aridisols, and spodosols based on climate and fertility. Additionally, processes like salinization and podsolization are mentioned, explaining the impact of climate on soil properties.