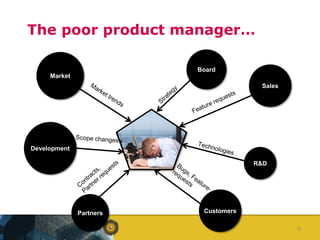
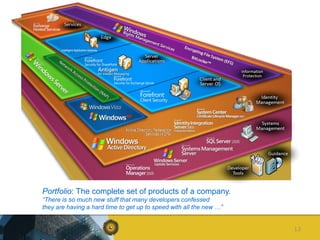
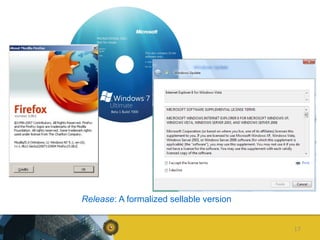
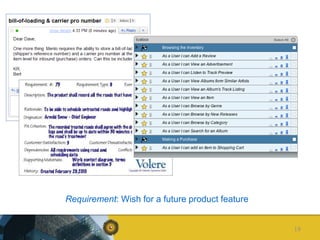
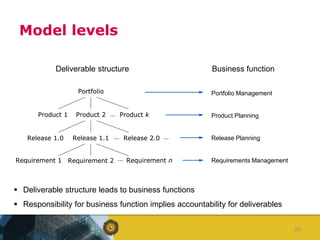
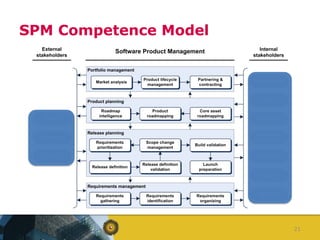
The document outlines a competence model for software product management (SPM). It describes SPM and defines a product manager. It then presents a deliverable structure for a software product company including portfolio, product, release, and requirement levels. This structure forms the basis for the SPM competence model, linking deliverables to business functions like portfolio management, product planning, release planning, and requirements management. Each function has several processes, such as market analysis, release definition, and requirements gathering. The model is intended to aid product managers, structure SPM education and research, and be found on the SPM website.