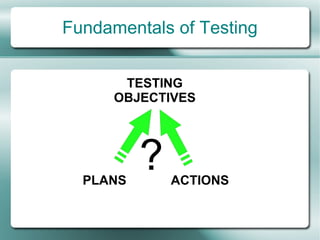
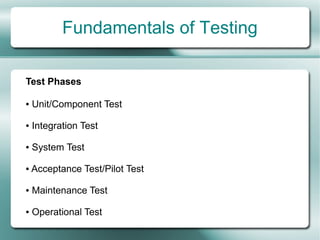
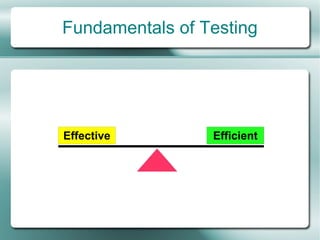
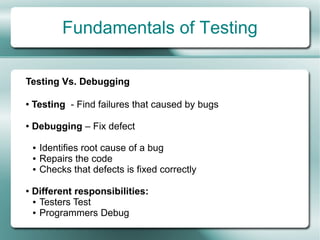
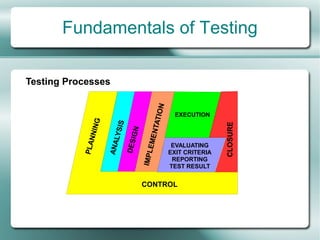
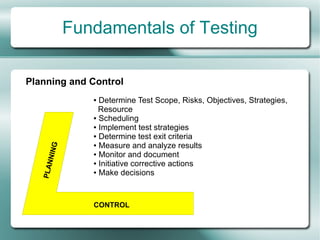
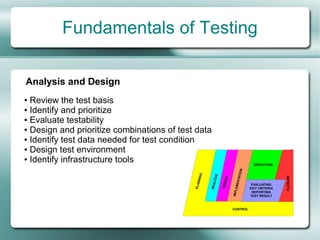
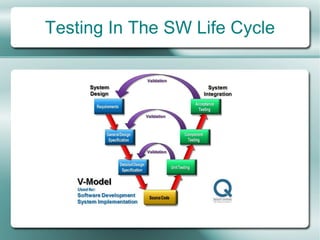
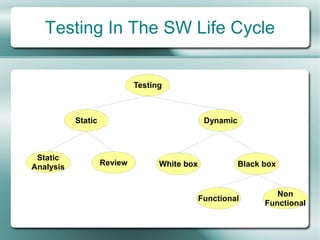
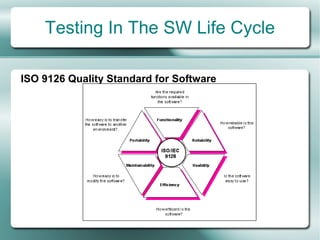
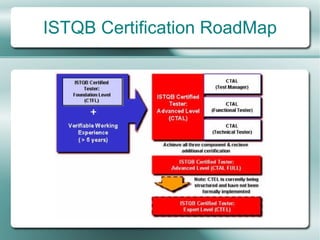
This document provides an overview of software testing fundamentals. It discusses why testing is necessary by giving examples of high-profile software failures. It then covers testing objectives, principles, processes and the psychology of testing. The document outlines different testing types like unit, integration and system testing. It also discusses testing in the software life cycle using the V-model. Finally, it provides an introduction to ISTQB certification and takes questions on software testing.