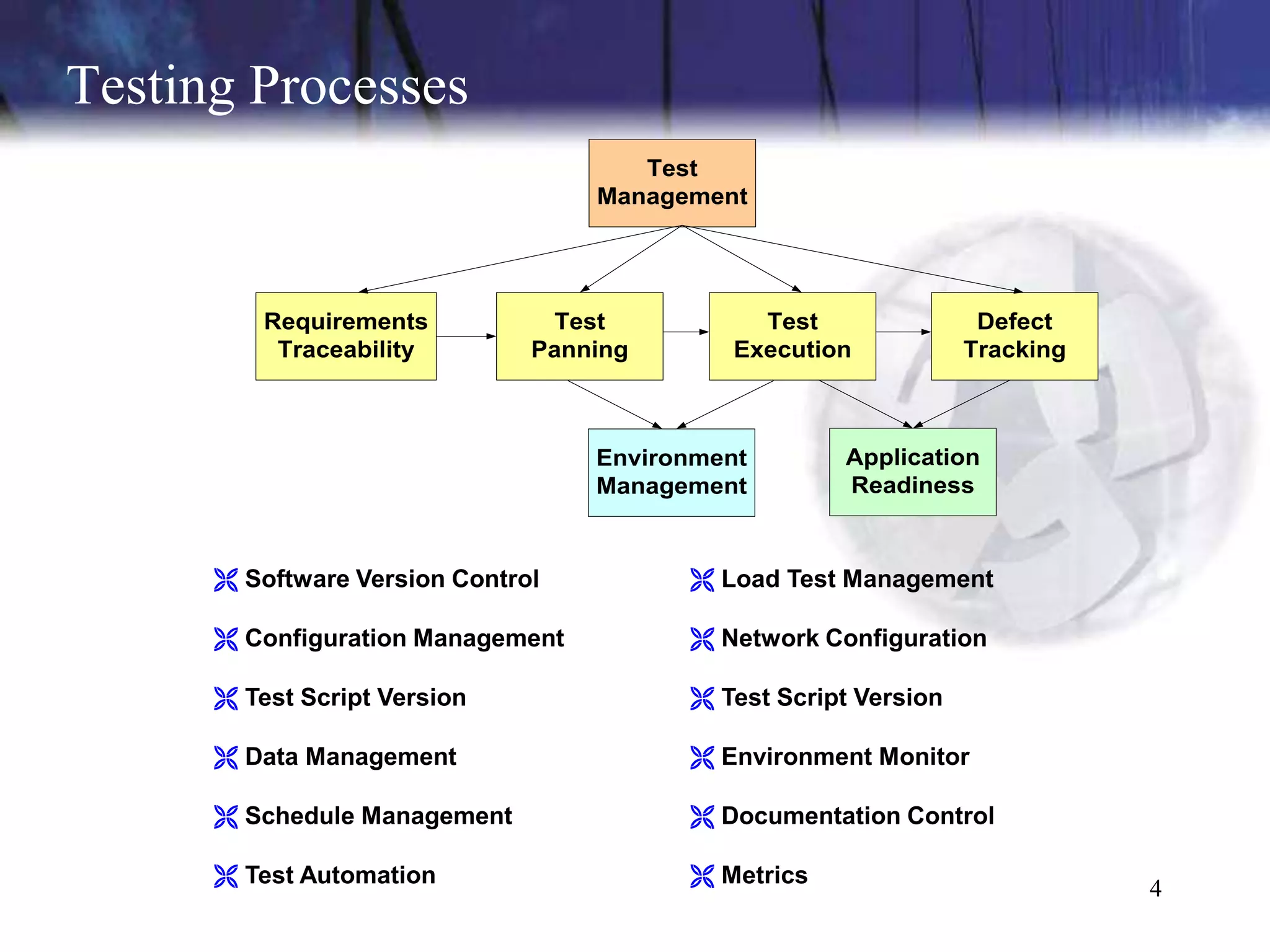
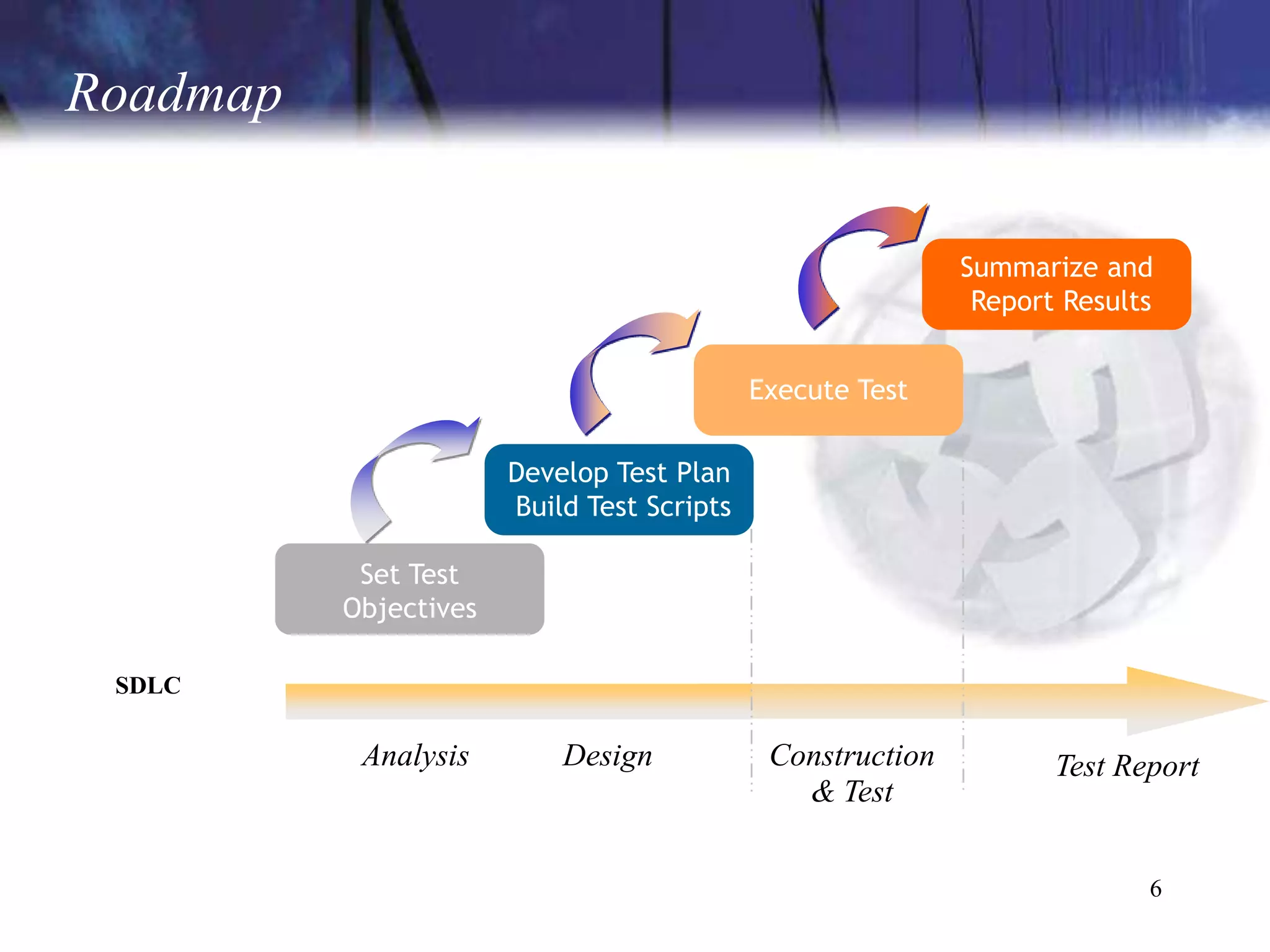
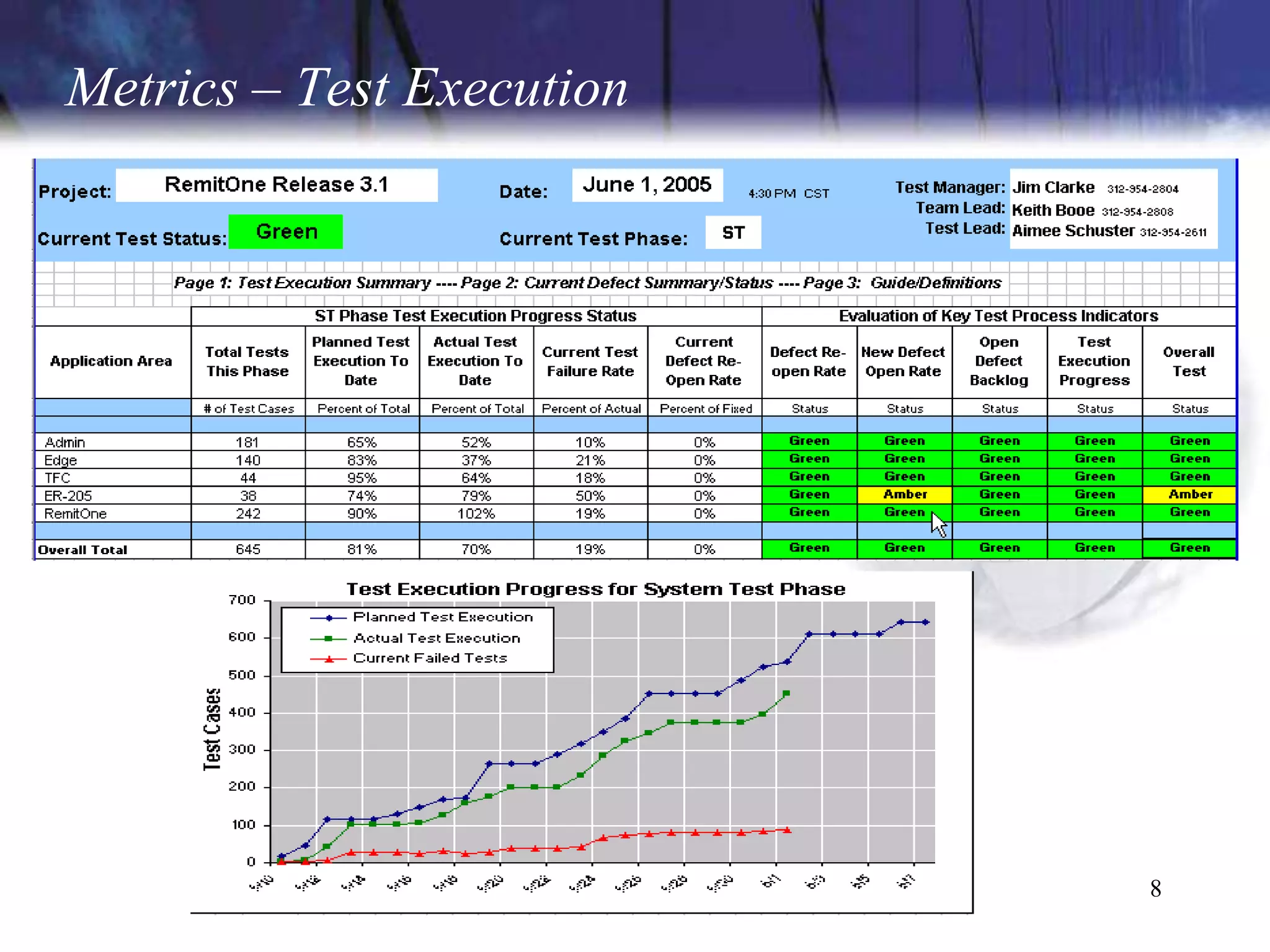
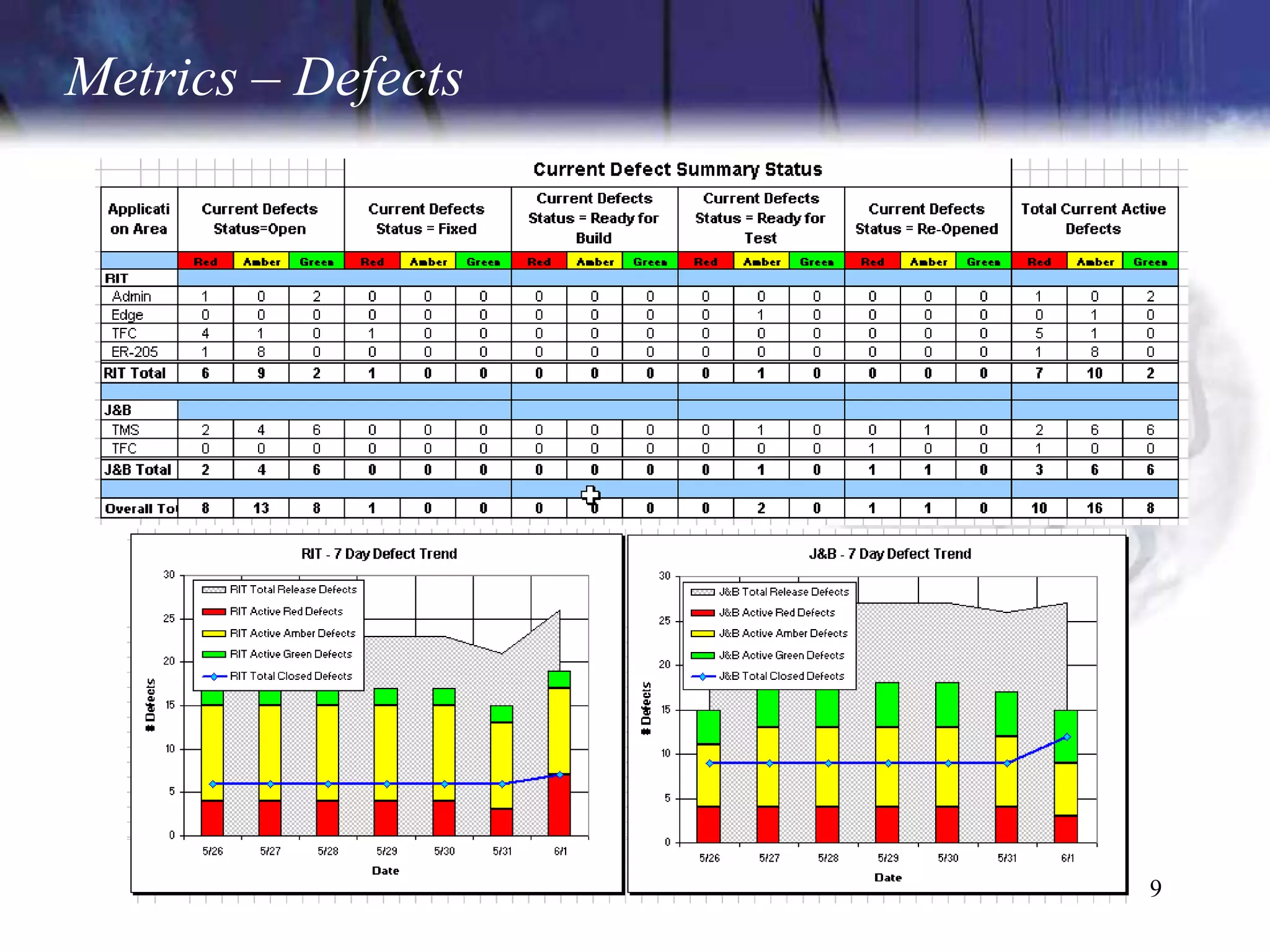
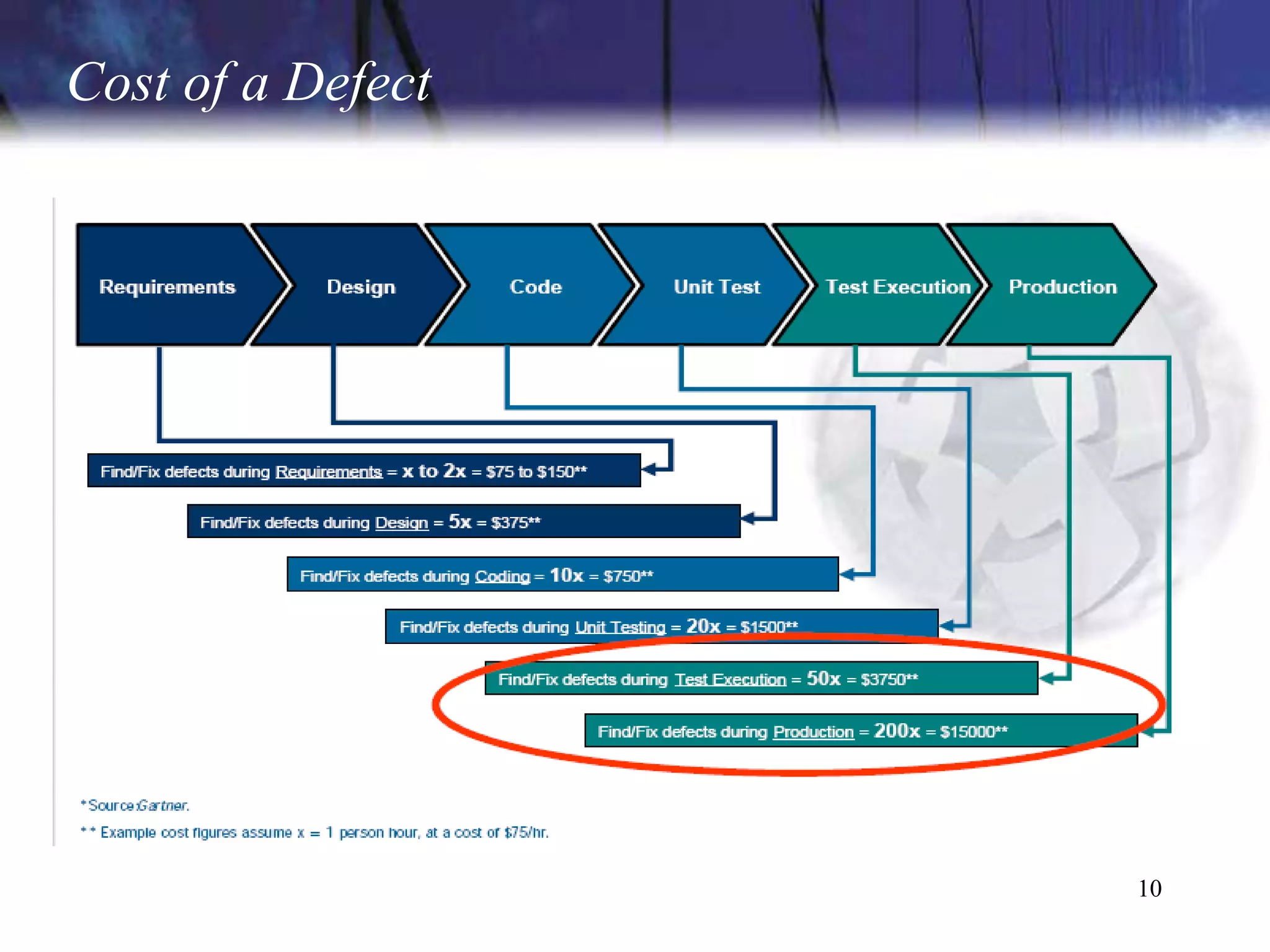
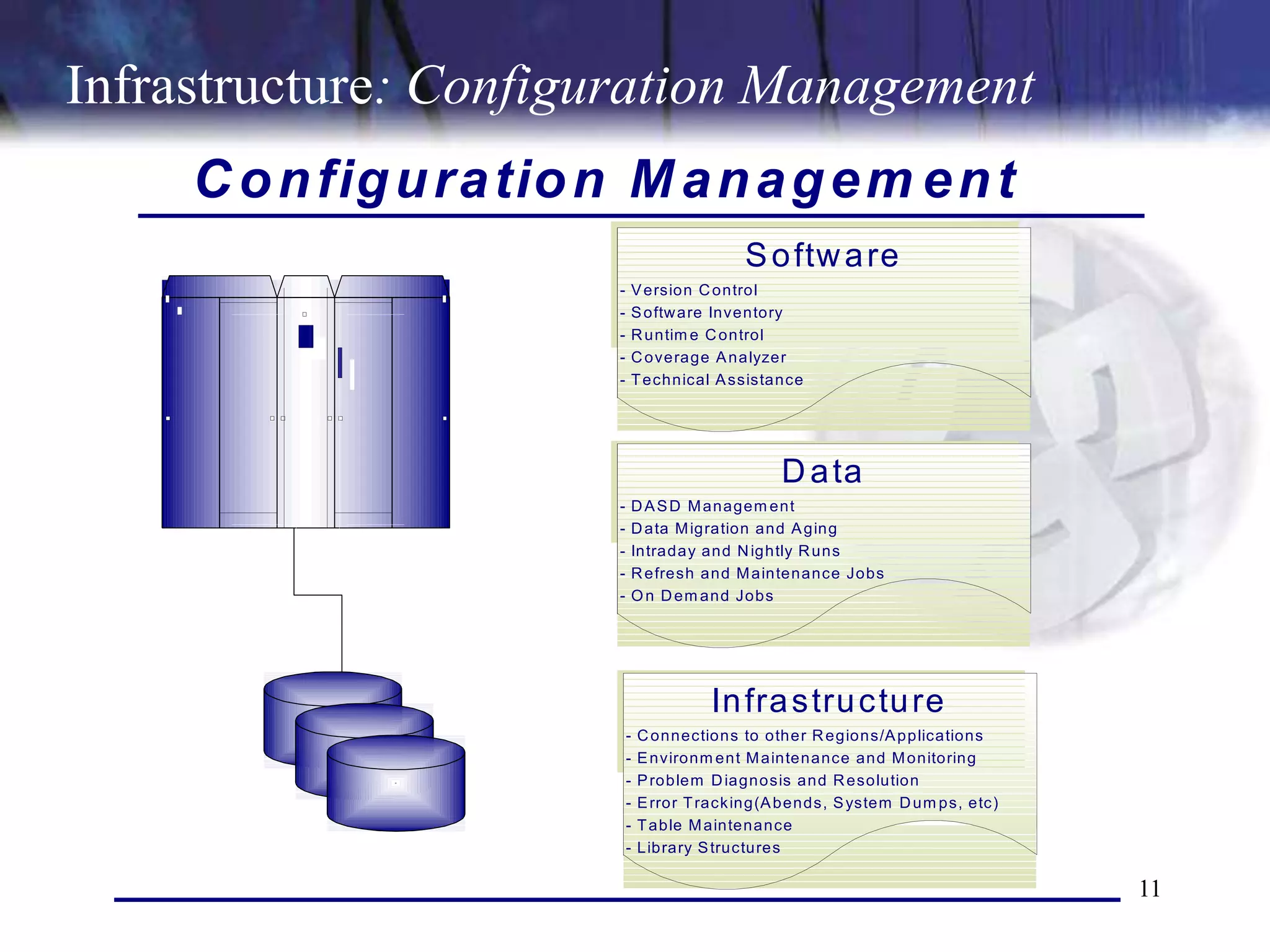
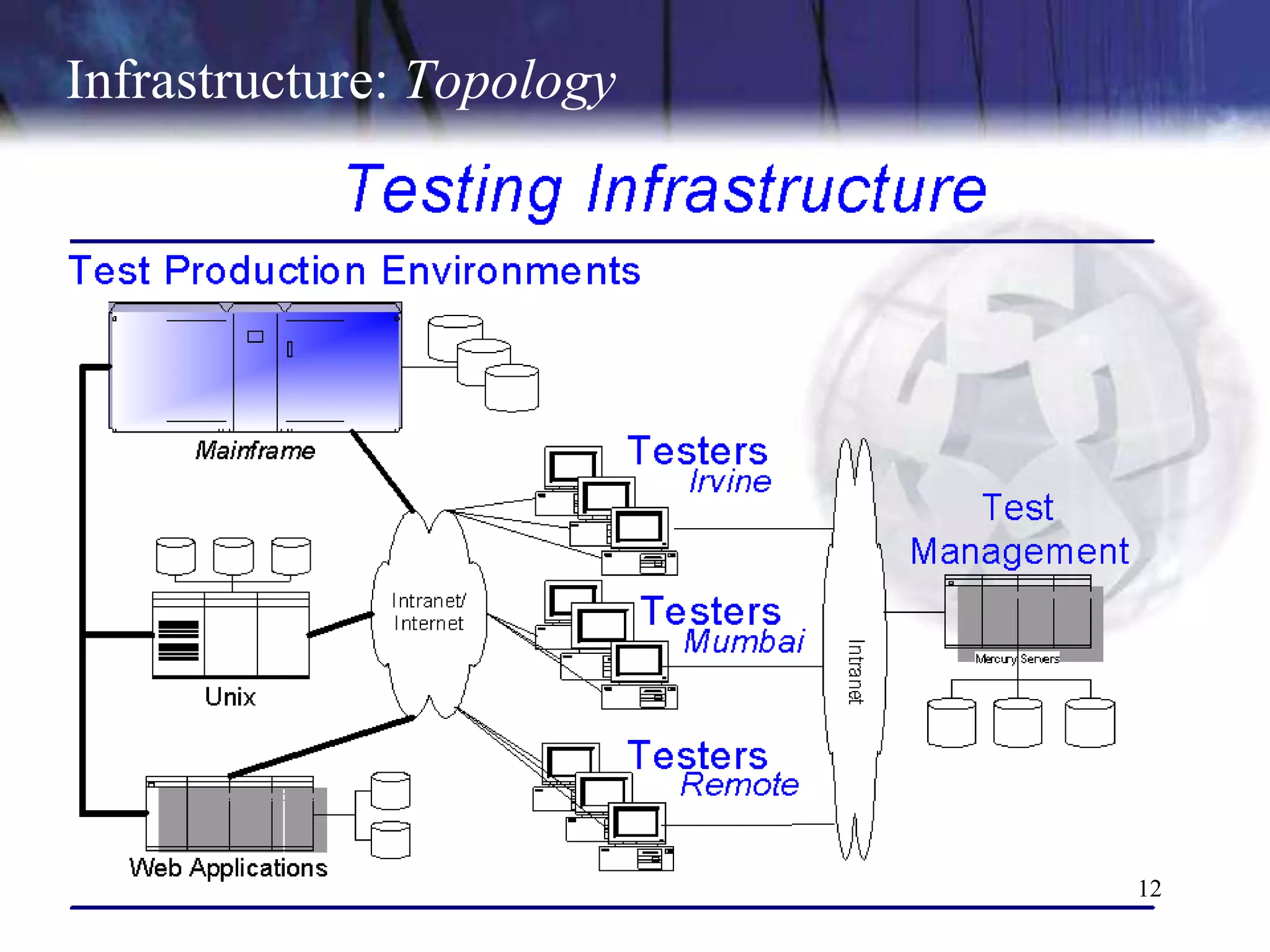
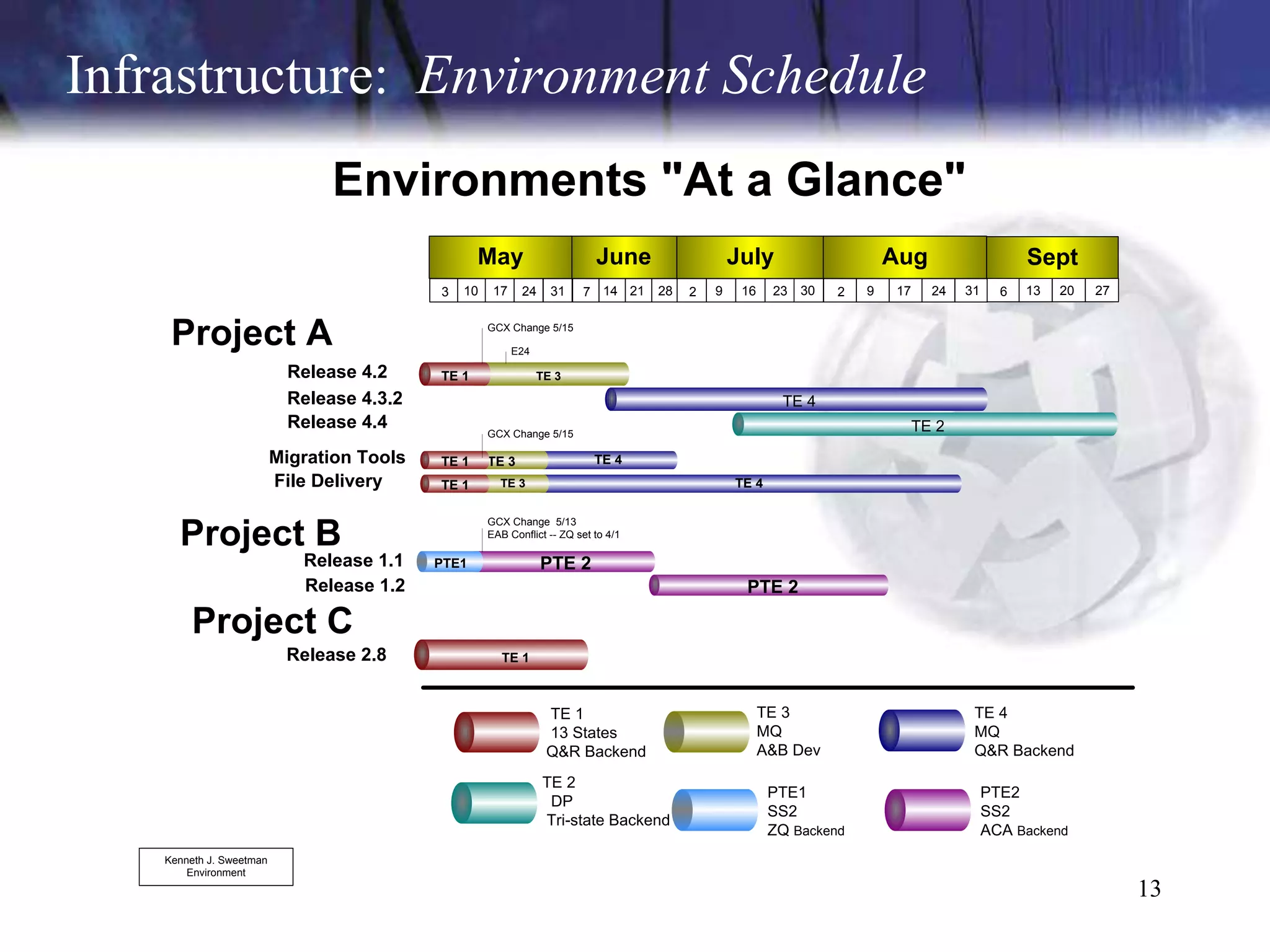
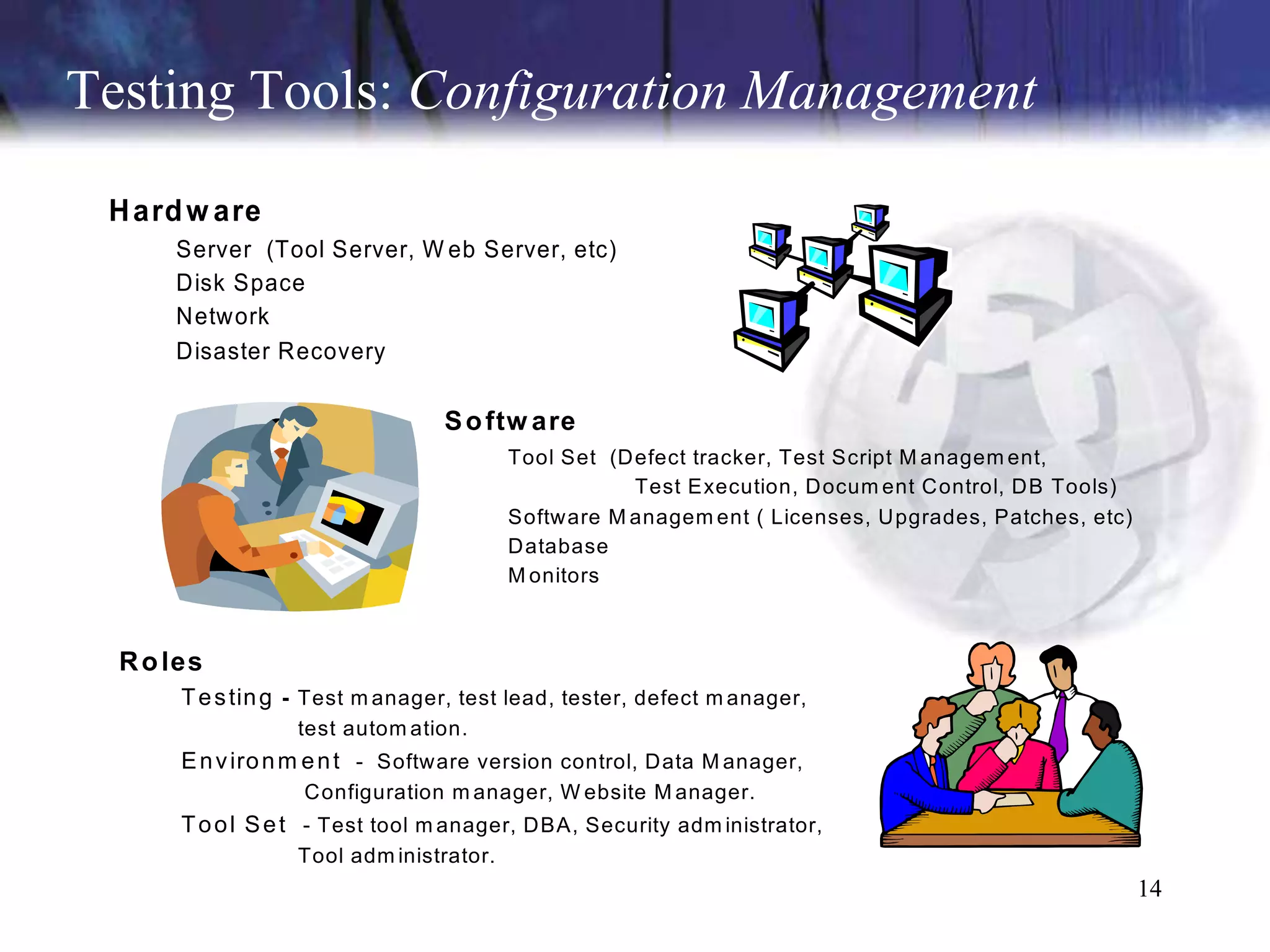
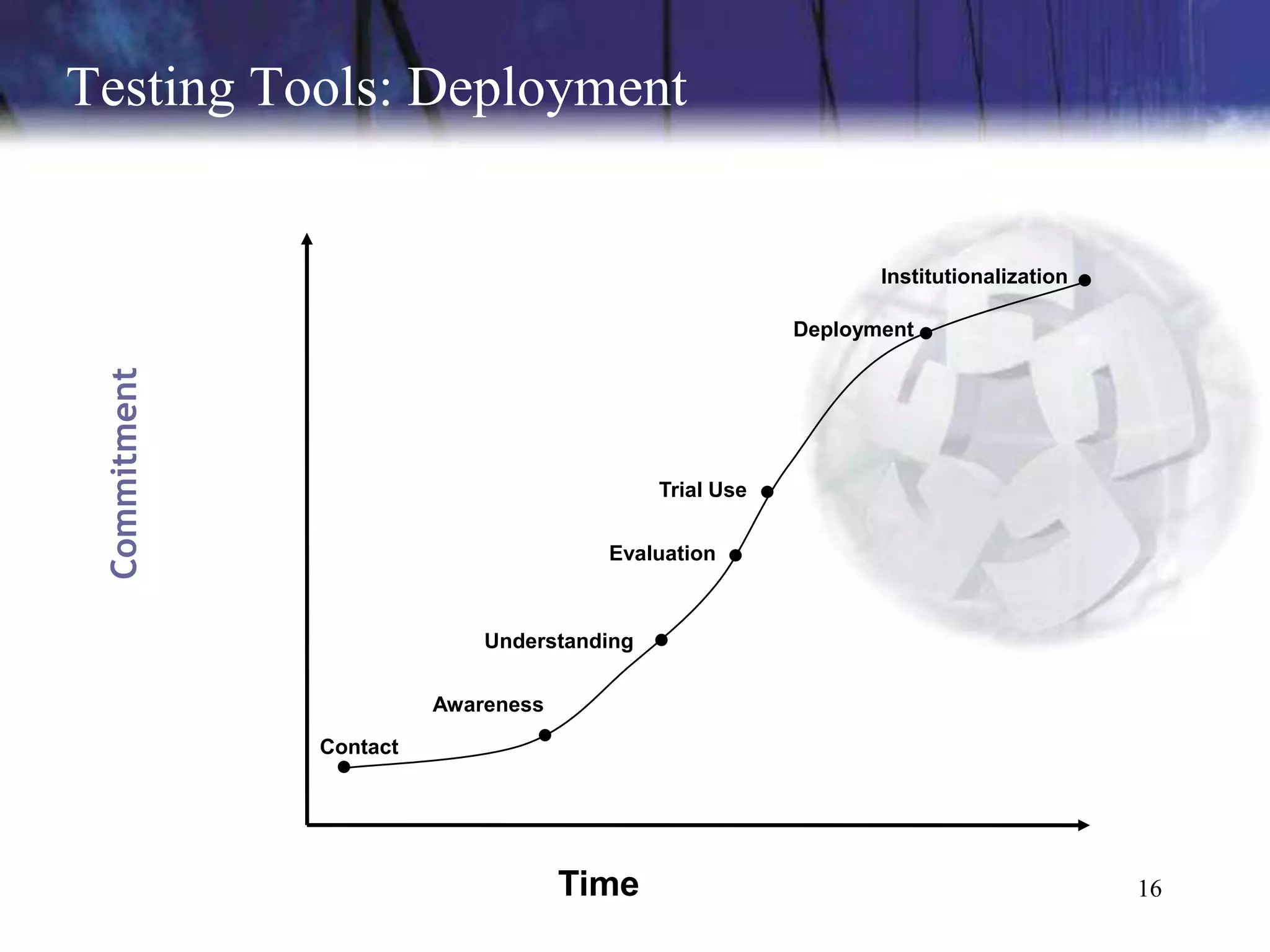
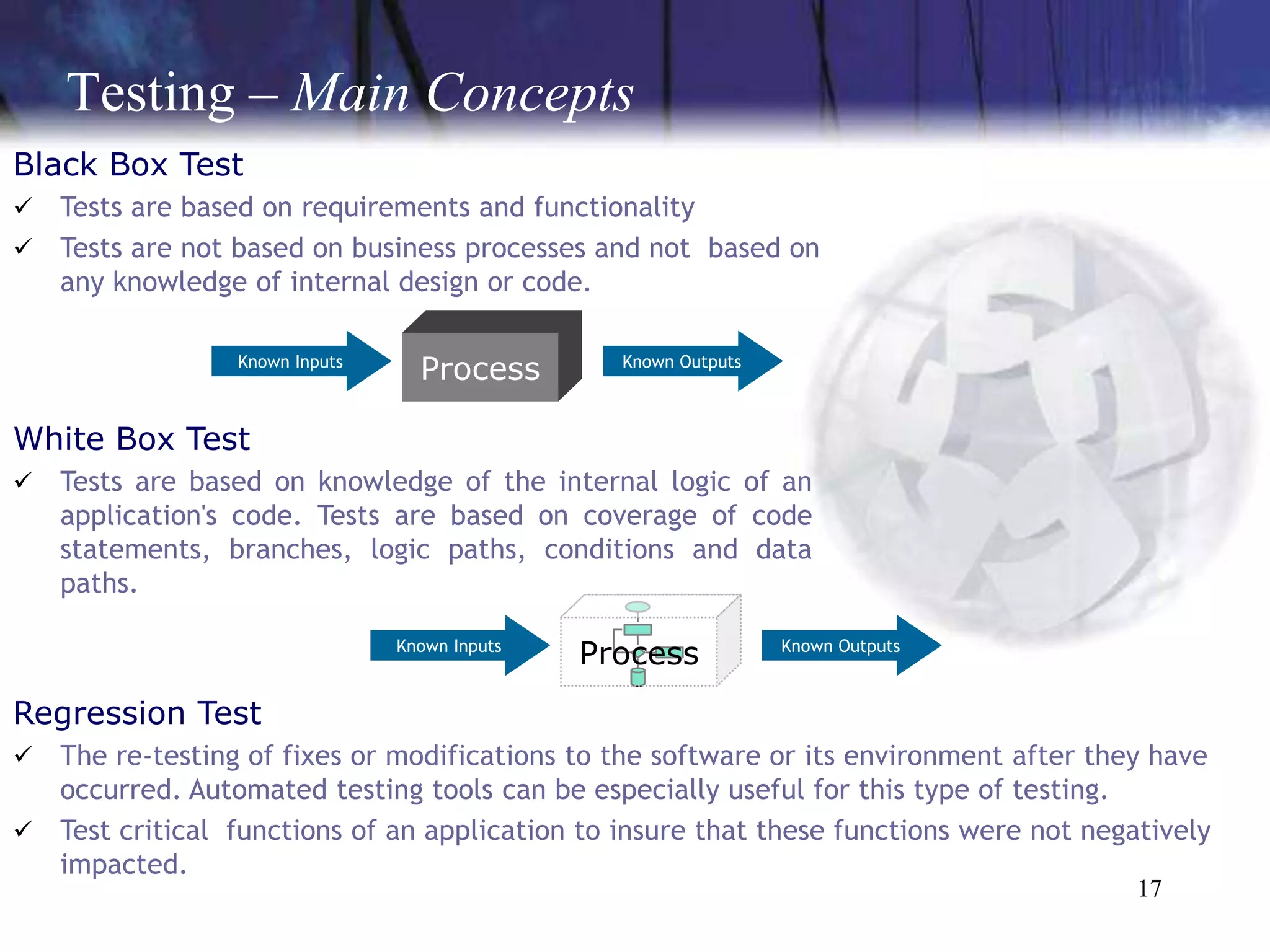
The document discusses the key components and concepts of software testing. It covers people, processes, infrastructure, testing methodologies, test planning and execution, defect tracking, metrics, and more. The core elements of testing include testing strategies, requirements tracing, test case development, test environment setup, test execution, and results reporting. Different types of testing are also outlined such as unit testing, integration testing, functionality testing, and volume testing.