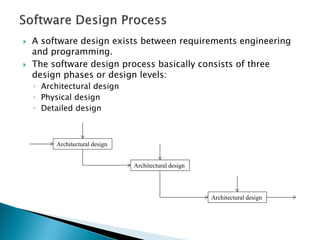
The document discusses the software design process, highlighting its importance within the software development life cycle (SDLC) and its phases: architectural, physical, and detailed design. It covers key concepts such as abstraction, information hiding, modularity, and the principles of coupling and cohesion, which aid in creating maintainable and scalable software. Additionally, it outlines various design methodologies, specifically function-oriented and object-oriented design, to structure software effectively.