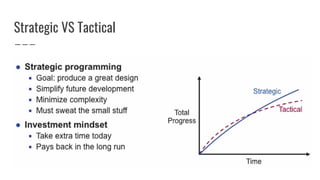
This document contains software design notes and principles from Diego Pacheco. Some key points include:
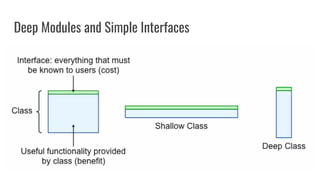
- Modules should be designed to be deep with simple interfaces. Classes should also be designed to be deep modules.
- Interfaces that resemble implementations indicate shallow design that leaks information and creates poor abstractions.
- Comments should describe how to use interfaces, not implementation details, and need to stay close to the code.
- Code should be designed to be obvious through use of precise names, patterns, and avoidance of obscurity through event-driven code or generic objects.
- Composition should be used over inheritance in object-oriented design. Patterns also risk over-application.