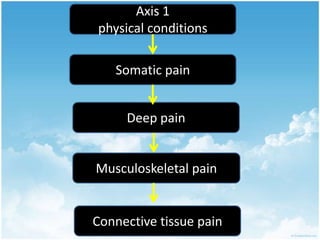
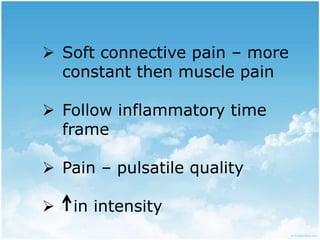
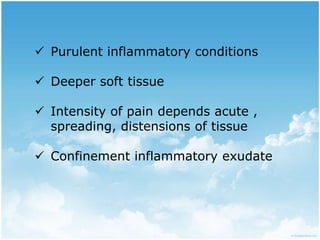
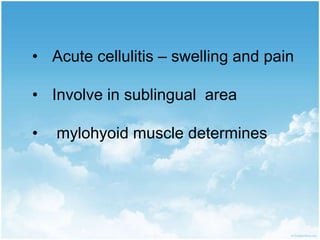
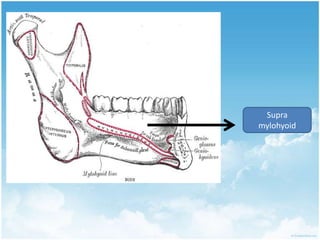
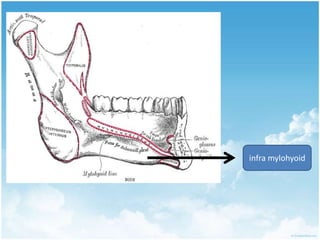
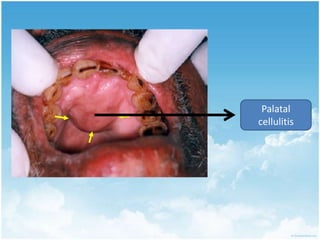
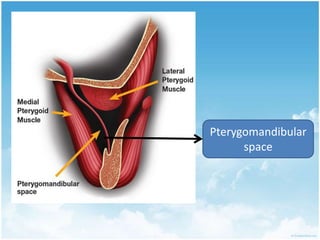
This document summarizes connective tissue pain and its causes. It discusses how connective tissue is composed of cells, fibers and intercellular substance that binds organs and tissues together. It must be strong. Connective tissue pain results from inflammation of these tissues and can be somatic, deep or musculoskeletal in nature. Cellulitis is provided as an example, which is an acute infection of loose connective tissues that causes swelling and pain. The document outlines treatments for connective tissue pain including antimicrobials, analgesics, anti-inflammatories, deep heat therapy, ice, massage and ultrasound.