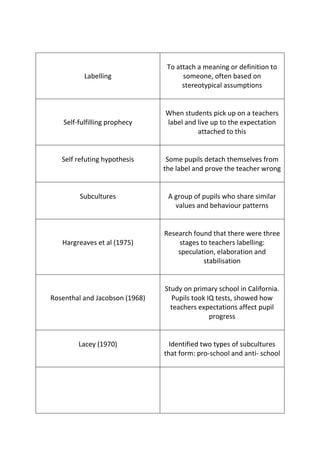
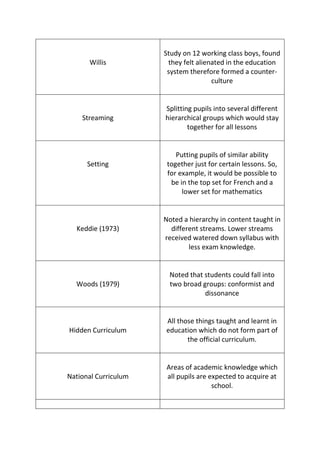
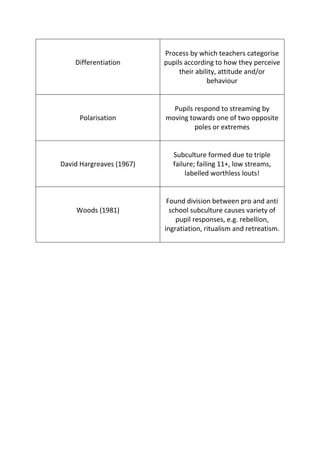
This document discusses key concepts related to how teachers' expectations and labeling of students can influence student outcomes and behavior. It covers how teachers may label students based on assumptions, which can then become self-fulfilling prophecies if students live up to the labels. However, some students may prove teacher expectations wrong. It also discusses how students may form different subcultures in response to labeling and streaming in schools. Several studies are cited that explore these concepts and their impacts.