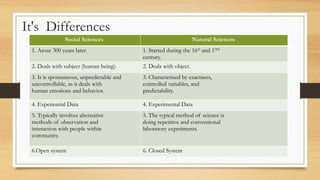
The document contrasts social sciences, which study human society and relationships, with natural sciences that focus on natural phenomena and laws. Both employ the scientific method and utilize empirical data, but differ in their subject matter, the nature of their data, methods of investigation, and predictability. Social sciences emerged later, deal with unpredictable human behavior, and use experiential data, while natural sciences have a historical foundation, deal with controlled experiments, and yield predictable outcomes.