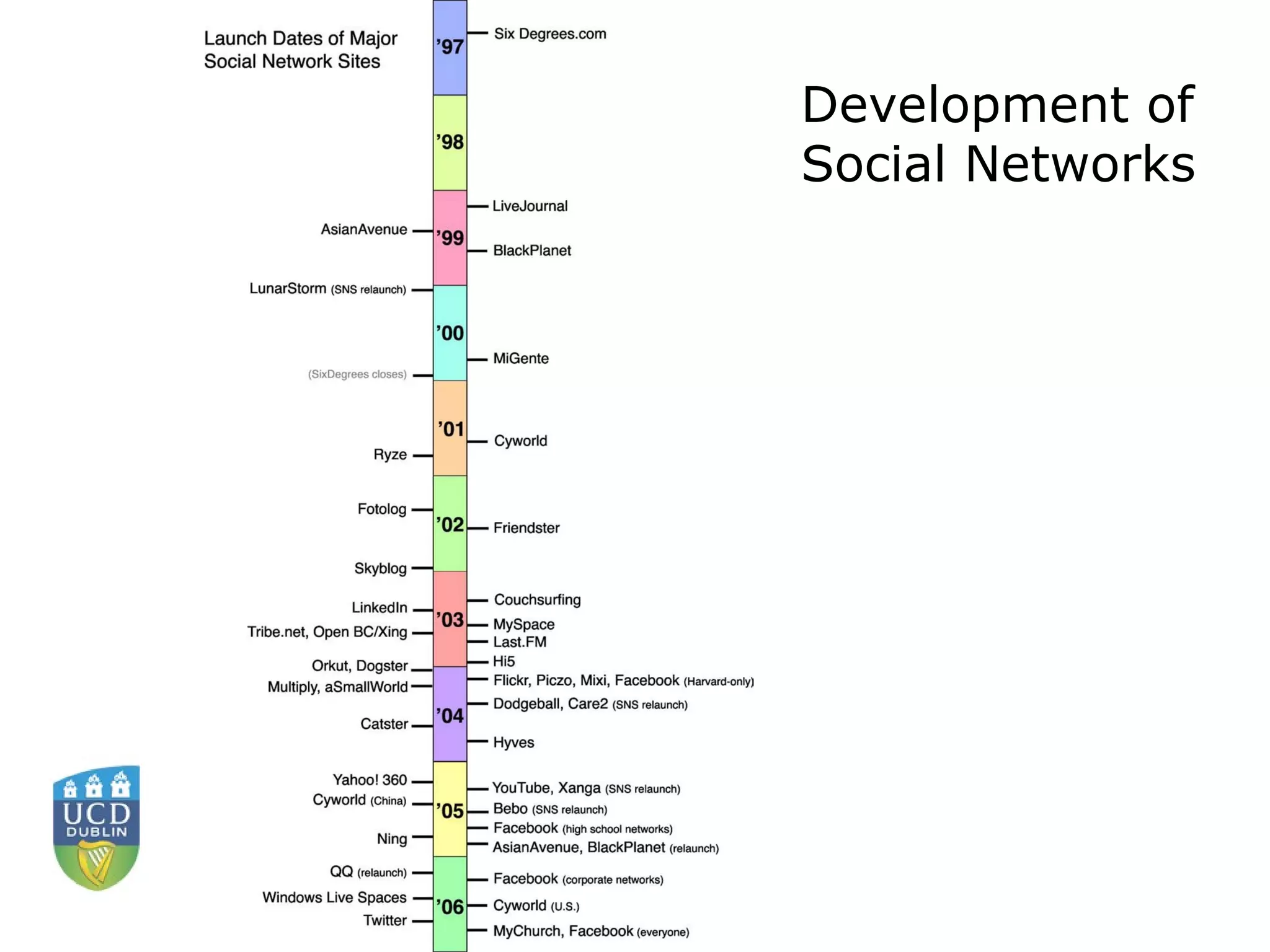
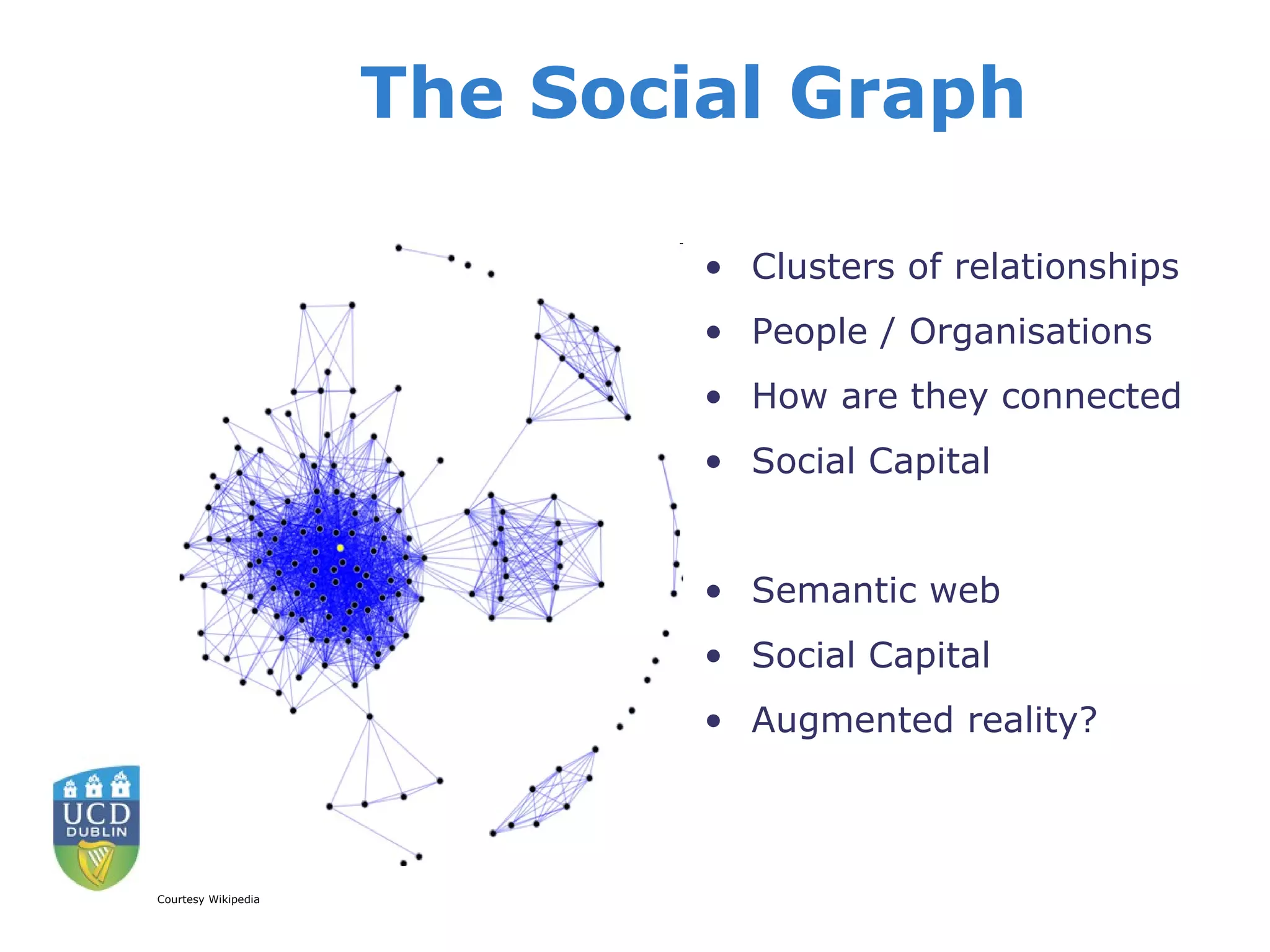
Social networks allow individuals to construct online profiles, connect with other users, and share content. While early social networks focused only on connecting users, now most provide ways to interact through messaging, share multimedia content, and use applications. Some key concerns about social networks include privacy issues, identity theft through phishing, stalking, bullying, and how personal information shared could affect job opportunities. The future of social networks may see greater integration of mobile access and location-based features, as people increasingly belong to multiple networks. Ensuring privacy and portability of user data and identities across platforms will also be important issues going forward.